I have found that I can decrypt SSL traffic in Wireshark with the server's private key.
Why isn't the client's private key enough to decrypt SSL traffic?
I have found that I can decrypt SSL traffic in Wireshark with the server's private key.
Why isn't the client's private key enough to decrypt SSL traffic?
This is because in an SSL/TLS connection the asymmetric key exchange uses the server's public key to exchange the pre-master secret. A client certificate is only used for client authentication if the server requests it. The pre-master secret is what's used to generate the session keys. This is why you need the server's private key, not the client's.
Notice how in the above exchange only the server sends its certificate. The client key exchange message is the pre-master secret encrypted with the server's public key.
SSL/TLS Key Exchange w/ Client Authentication
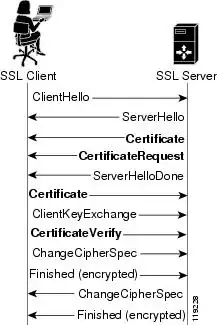
In the above exchange we see that after the server sends its certificate it also provides a CertificateRequest message. This message asks the client for its public certificate. It responds with the ClientKeyExchange message as it does in a typical handshake, and then sends a ClientVerify message which signs the hashed key exchange data. The server then uses this signature to verify the client.
The client or server never uses the client's public key to encrypt any information in the handshake. Therefore it is not necessary for session decryption.
Because client uses server public key for encrypting communication during phase 4 of negotiation (wikipedia) :
4 - Using all data generated in the handshake thus far, the client (with the cooperation of the server, depending on the cipher in use) creates the pre-master secret for the session, encrypts it with the server's public key (obtained from the server's certificate, sent in step 2), and then sends the encrypted pre-master secret to the server.
At the end of the negotiation, both sides generate a session key for encrypting communication.
I think that wireshark, with server's private key can pick this session key during the handshake.
Cedric.
Clients private key is used only when using client certificate authentication and there it is used only for signing, not decryption. (if using RSA/DSA keys)(If using static DH, it could be possible, but static DH is not supported by any TLS servers or clients)
Assuming an appropriate setup of the SSL/TLS parameters on the side of the server (or theoretically client, but that is harder and doesn't have to always work) having the servers private key should still not allow you to decrypt any traffic unless you are performing an active attack.
It really depends on if Forward Security (FS) was negotiated between client and server. There's no guarantee that the client negotiates a forward security algorithm. IE is notoriously bad at choosing a FS algorithm, and relies on the server to prioritize the various options. So if you're very careful in setting up your SSL options on the server, AND your server supports prioritizing one algorithm over another, then it's possible to get Forward Security negotiated on even IE.
(Qualsys has an excellent tool that simulates major browser negotiation with websites.) https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/index.html
Essentially all the other major browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc) generally choose forward security if the server supports it, so decryption with just the private key of the server isn't possible.
Raz's answer gives a very good overview of your particular situation. It should however be mentioned that, if the server's private key allows you to actually decrypt the communication without performing a MITM attack your SSL/TLS is set up badly.
Assuming an appropriate setup of the SSL/TLS parameters on the side of the server (or theoretically client, but that is harder and doesn't have to always work) having the servers private key should still not allow you to decrypt any traffic unless you are performing an active attack.
Using DHE (Diffie-Hellman exchange) or ECDHE (the same above elliptic curves) for key exchange (actually exchanging the master secret from which the keys are generated) brings a marked increase in security at almost no cost to performance or usability.