Yes, but this would be difficult to do without it being discovered.
From a purely technical standpoint you're correct, there's nothing stopping a nation-state from compelling a Certificate Authority under their jurisdiction from issuing them a fraudulent certificate, and most TLS clients (including web browsers) will silently accept that certificate without warning the user.
However, there are several factors which make this method completely infeasible for governments to use for mass surveillance, and risky even for targeted attacks.
The risk of discovery
First, it's important to note that if a CA were ever discovered to have issued fraudulent certs like this, especially for the purposes of allowing governments to conduct MITM attacks, that CA would almost certainly have their root certificates distrusted by browser vendors and other trust stores. That would put that CA out of business, and render the fraudulent certificates useless. So if a nation state wanted to compel a CA to issue fraudulent certs in this way they'd have to do so secretly, without the public being aware of it. In practice, that would be very difficult.
Discovery through Linus's Law
In the case of mass surveillance, using fraudulent certificates without being discovered would be nearly impossible. Even if web browsers didn't automatically detect that their connection was being hijacked by a fraudulent certificate (we'll cover some ways that could happen in a moment), those certificates would still necessarily be different from the ones issued to the legitimate site operators, and could therefore be detected manually. If millions of users were all being served fraudulent certificates, it's almost certain that somone would notice (maybe the site operators themselves) and the whole scheme would quickly be uncovered. It's essentially Linus's Law ("given enough eyeballs, all bugs are shallow") applied to TLS certificates.
For targeted attacks against individual users, using fraudulent certificates without being discovered is much more feasible. Only the targeted users would have an opportunity to notice that the certificates had changed, and the average user is very unlikely to even check for something like that. There is still a significant risk the fraudulent certificates would be detected through other means, however.
Discovery through HPKP
The most likely way that an average user might detect that they're using a fraudulently issued certificate is by visiting a site which uses HTTP Public Key Pinning (HPKP). HPKP is a feature of modern browsers that lets sites tell a browser "future visits to this site should only be secured using one of these known keys". If a user previously visited a site before the government started spying on them, a later visit would result in a warning message if the site presented a fraudulent certificate. This might raise the user's suspicions, and if they were to investigate why the warning message was appearing, they might discover and report the fraudulent certificate.
Discovery through leaks
It's also possible that the government agency, the CA, or one of their employees might leak the fraudulent certificates to a third party. You might assume this is unlikely, but such leaks are always a possibility, and the fraudulent certificates themselves are strong cryptographic proof that the CA that issued them is somehow compromised, so even a completely anonymous leaker would have no trouble convincing security experts of the legitimacy of their story.
The future: Certificate Transparency
But what if the nation-state only targets a small number of users, avoids spying on sites which use HPKP, and is careful to ensure that nobody leaks the fraudulent certificates to the public? Then they'd be able to get away with it, right? At the moment; yes, probably. However, there is one other way fraudulently-issued certificates might be discovered which will make this much harder in the near future: Certificate Transparency.
Certificate Transparency (CT) is a publicly-auditable logging system for TLS certificates which CAs may use to log all certificates they sign. If a fraudulent certificate were submitted to a CT log, it's likely that someone would notice. For now, it'd be easy for a government to avoid detection by simply not submitting the certificate to a log, but starting in April 2018 at least one browser (Chrome) is going to start enforcing logging for all new certificates. This means that at least 2 trusted logs would need to cryptographically sign a statement claiming they've logged a given certificate in order for it to be considered valid.
Browsers and other third-party auditors will hold the CT logs to their word by periodically checking that the certificates they claim to have logged really are in the log (though Chrome has not yet implemented this), and that the logs are consistent for all parties viewing them. (So a Certificate Transparency log can't just tell the client it logged a certificate, but pretend that certificate doesn't exist when contacted by a third party.)
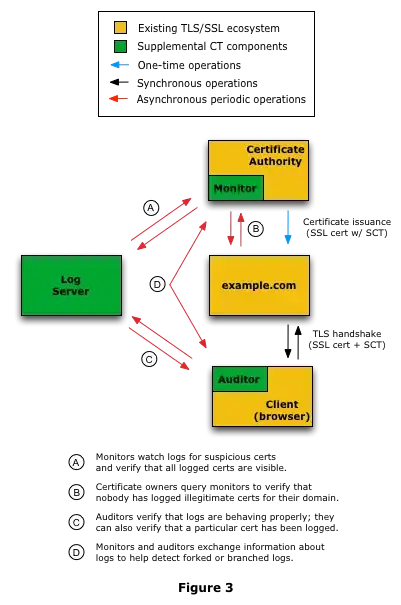
Image source: https://www.certificate-transparency.org/how-ct-works#TOC-Typical-System-Configuration
In order to bypass these checks, a nation-state would need to compromise or coerce multiple Certificate Transparency logs and independent third-party auditors and monitors, some of which might be outside their jurisdiction, all without any of those parties leaking the nation-state's actions to the public. This would be very difficult. Difficult enough, in fact, that even a nation-state would most likely give up at this point and start considering completely different methods for surveilling their targets instead.
To summarize
Yes a government could coerce a CA into issuing them fake certificate for a site. But in order for this to work, they'd have to keep the fact that they'd obtained the certificate a secret. This means they'd have to keep their surveillance targeted at a relatively small number of users, avoid spying on sites that use HPKP, make sure nobody leaks any of their certs to the public, and, starting in April 2018, compromise a significant number of certificate transparency logs and third-party monitors and auditors all at once. In short, it's not very likely.
