Fish that survive on land
Fish that survive on land or amphibious fish include many organisms of past and present that evolved and adapted to spend time out of water and breathe air. Studying extant (still living, not extinct) fish and fossils from extinct specimen of these taxa helps evolutionary biologists understand how ancestral land vertebrates existed.
| We're all Homo here Evolution |
| Relevant Hominids |
| A Gradual Science |
| Plain Monkey Business |
v - t - e |
“”A fish definitely did not crawl out and evolve lungs and limbs. |
| —Professor Elizabeth L. Brainerd, Brown University[1] |
“”I tell people they’re fish that can’t swim. |
| —Rachel Arnold[2] |
Having air-breathing capacity is useful for fish that live in hypoxic (low-oxygen) environments; it allows them to gulp air from the surface without ever going on land. Air breathing has evolved in some form at least 38 separate times independently among fishes, according to Elizabeth Brainerd.[1][3]
Having leg-like appendages is also useful to fish in some environments. Frogfishes (family Antennariidae) and handfishes (family Brachionichthyidae) are poor swimmers and use their fins to walk along the sea floor.[2]
Mudskippers
The mudskippers are fish that spend more time on land than in water with pectoral fins adapted for hopping on land and get their food in the air. Mudskippers can even climb trees; some have suckers on their fins to help them climb. They breathe through their skin and also their gills which are kept moist with water stored in in a specialised organ. Mudskippers mainly return to water to keep their gills moist.[4][5][6]
Climbing perch
Climbing perch (family Anabantidae) are a diverse group of East Asian and African fish that live in oxygen poor water and are adapted to air breathing, indeed the fish suffocate without access to air. A specialized organ for air exchange called the labyrinth organ has evolved out of modified gill tissue. Climbing perch (not true perch) have varied shapes and some rear their young in a bubble nest that keeps the fry near the surface till the labyrinth organ has developed. Climbing perch come out onto land during rainy weather using their gill covers and fins as limbs and their tails for propulsion. When moving on land then they look for new watery places to live. Like the walking catfish discussed below they survive in a similar way to the Palaeozoic Tiktaalik and like the walking catfish can become invasive.[7][8][9][10][11]
Mangrove rivulus
The Mangrove rivulus (Kryptolebias marmoratus) is a fish that can live out of water for months at a time breathing air through its skin. This fish is yet another example showing how fish are capable of evolving into land animals. These fish live in mangrove swamps which from time to time dry out. When this happens the fish seek moist, sheltered places like hollow tree logs or leaf litter and stay there till conditions improve. Another odd feature of these fish is that they can reproduce without sex, producing clones of themselves.[12][13][14][15]
European and American eels
Eels normally live in water but can travel over land if they need to do this in the course of their migration.[16][17] Out-of-water eels breathe through their skins.[18]
Walking catfish
The Walking catfish (Clarias batrachus) is yet another fish that can live on land and like climbing perch it survives in a similar way to the Palaeozoic Tiktaalik. The walking catfish normally lives in the type of water that can dry up and when this happens the fish moves out onto dry land using its rigid pectoral fins as stilts. Walking catfish literally walk till they find water where they can live. These fish have a specialised air breathing apparatus in their gills. In humid conditions the walking catfish can survive for hours out of water and shoals of these fish walking on roads sometimes force motorists to stop driving.[19]
The walking catfish survives and reproduces so effectively that when introduced in the wrong places it can become a pest. There are problems in Florida,[20] and trouble could develop in the UK.[21]
Lungfish
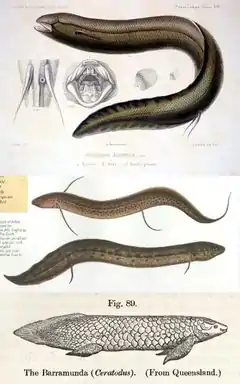
The lungfish and birchirs, together with the Coelacanth, are the closest living relative of land vertebrates. They breathe through lungs like our lungs and can survive in brackish water with low oxygen content due to this. When their water dries up lungfish can remain dormant in burrows breathing air for years.
Blue Dwarf Snakehead
The Blue dwarf snakehead fish (Channa sp.) was recently found in West Bengal, India by the World Wildlife Fund. The Blue Dwarf Snakehead fish has gills, but can also directly breathe air and survive on land for 4 days.[22]
Palaeozoic fish
Before the fish evolved to become amphibians there were plants and invertebrates on land but nothing needed to evolve defences against vertebrate methods of feeding. Therefore it is likely any fish that could survive in brackish water, in shallow water or on land even for a short time could get plenty of food that was easy to take. This could apply to carnivores or herbivores and could have been a factor in fish evolving to live on land.
See Tiktaalik and Ichthyostega for examples.
Creationist responses
All this has proponents of evolution saying "Look! See!" and creationists responding "er... look over there, a Crocoduck!" *flees*
Alternatively a favoured creationist response is to repeat continually something like, "A fish couldn't possibly survive with half a lung and half a gill"[23] while ignoring the evidence. Florida, where the walking catfish is a problem, is in the Bible Belt. Therefore ignoring this evidence could become progressively harder for Bible Belt Christians as the fish spreads – that fish really is a pest.
See also
- Amphistium and Heteronectes
- Transitional fossils
- List of transitional fossils
- Suboptimal design (amniote gill bars and aquatic air breathing) — the consequences of land animals having evolved from animals with gills
References
- Slow, cold reptiles may breathe like energetic birds: One-way airflow, thought to exist only in birds, may keep several reptiles going by Susan Milius (1:11pm, October 19, 2015) Science News.
- These fish would rather walk: Slowpokes of the sea, frogfish and handfish barely manage to swim by Susan Milius (8:00am, September 23, 2015) Science News.
- K.P. Dial, N. Shubin and E.L. Brainerd, Eds. Great Transformations in Vertebrate Evolution. University of Chicago Press, 2015. ISBN 022626825X.
- Mudskippers: Walking Fish
- Mudskippers
- Giant Mudskippers
- Climbing perch
- The Labyrinth Fishes
- Anabantidae — Labyrinth Fishes
- The Climbing Perch
- Climbing perch
- BBC Nature: Shells, trees and bottoms — Strange places fish live
- Reuters: Tropical fish can live for months out of water November 15, 2007
- Fish Lives in Logs, Breathing Air, for Months at a Time
- Fish Lives in Logs, Breathing Air, for Months at a Time
- European eel
- Common Common eel crossing land
- Eel-tastic
- Walking catfish
- Introduced Species Summary Project
- Walking catfish spotted in the Thames by angler
- http://www.fishchannel.com/fish-news/2015/10/dwarf-snakehead-fish-discovered-in-india-trending.aspx
- http://creation.com/something-fishy-about-lungs