Introduction
Warning: Obtaining unauthorized access to another's computer system or systems is illegal under the Computer Fraud & Abuse Act.
The following guide was made with the purpose of educating others on cyber security tools, technologies, and techniques with the intention of educating others on better protecting their own technologies and data. Please use the knowledge gained from this guide responsibly.
This guide will walk you through how to use Kali's Aircrack-ng to recover the password to a wireless network.
What you'll need before you start
Ideally you will need the following before you start this guide...
- A Wi-Fi network adapter that supports monitor mode
- The Kali Linux OS with Aircrack-ng installed (Learn how to install Kali onto a VM here)
- A password dictionary (wordlist)
How do I install Aircrack-ng?
Normally, if you installed Kali Linux normally you should already have Aircrack-ng pre-installed onto your machine. However, you can install the Aircrack-ng tool by using the command sudo apt install aircrack-ng
-
-
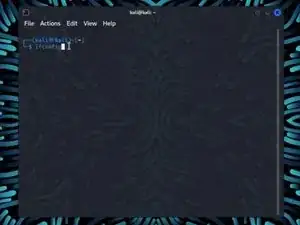
Enter the command ifconfig. This will show all your networking interfaces connected to your device.
-
-
-
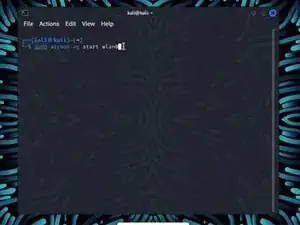
Enter the command sudo airmon-ng start wlan0
-
If your network adapter supports Monitor Mode then you should see (monitor mode enabled) at the bottom of the screen.
-
-
-
Find your network under the ESSID column.
-
Take note of the following information in your networks row. Channel (CH), BSSID.
-
-
-
Use the command sudo airodump-ng -c *Channel Number* -w *ESSID Name* —bssid *BSSID Numbers* wlan0 to start capturing your networks packets
-
-
-
Without closing your previous terminal, open a new terminal with Ctrl + Alt + T
-
Enter the command aireplay-ng -0 *RXQ Number* -a *BSSID Number* wlan0
-
Once you de-authenticate your clients you should have your WPA handshake in the upper right hand corner where it says WPA handshake.
-
Once you have your handshake, take note of it and end both processes with Ctrl + C
-
-
-
Use your wordlist to decrypt your handshake with the command aircrack-ng -w *your word list*.txt kali-01.cap
-
Using Aircrack-ng to recover Wi-Fi passwords can be effective under certain conditions. However, it's important to remember that attempting to crack someone's Wi-Fi password without their explicit permission is illegal and extremely unethical. If you find that your network is vulnerable to attacks from Aircrack-ng, consider looking at the tips in the following Bluf.
Bluf: Protecting a Wi-Fi Network from Attacks
To protect your Wi-Fi network from attacks that use Aircrack-ng, consider implementing the following security measures to your network.
- Strong Encryption: Use WPA3 or WPA2 with a strong, unique password to enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network.
- Regular Password Updates: Keep the password to your Wi-Fi password updated regularly to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- MAC Address Filtering: Enable MAC address filtering to allow only specific devices to connect to your network.
- Disable WPS: Disable Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) as it can be susceptible to brute-force attacks.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keep your router's firmware up to date to ensure it has the latest security patches.
- Network Segmentation: Separate guest networks from your main network to limit potential exposure. This is more applicable to enterprise-grade networks, but segmenting your network will prevent users from accessing any device connected to your network.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Consider using an IDS to monitor suspicious activity on your network.
The most important thing you should take away from this guide is to remember to use this information responsibly. Obtaining unauthorized access to another's computer system or systems is illegal under the Computer Fraud & Abuse Act.
Please use the knowledge gained from this guide responsibly.