
Patching a 125 2 stroke fuel tank
Motorcycles (also called bikes and motorbikes) are motor vehicles with two or—in the case of motorized tricycles or trikes—three wheels. Motorcycles have been designed for a wide variety of functions, including commuting, off-road riding, long-distance travel, and racing. The three main types of motorcycles include street bikes, off-road bikes, and dual-purpose bikes. Street motorcycles include scooters, mopeds, and cruisers. Off-road motorcycles include motocross bikes, which are usually not street legal. Dual-purpose motorcycles are made to withstand off-road conditions but are also street legal.
In 1885, Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach designed the first internal combustion, petroleum-fueled motorcycle, which they called the Daimler Reitwagen (meaning “riding car” in German). The Butler Petrol Cycle, which was the first commercial design for a motorized cycle, was designed in 1884 and had three wheels for stability. Series motorcycle production began in 1894. Production greatly increased during the first World War, since motorcycles introduced a faster alternative for delivering messages.
In 2014, Honda, Yamaha, and Hero MotoCorp were the top three international motorcycle manufacturers by volume. Motorcycles are especially popular in developing countries because of their impressive fuel economy and lower prices.
Generally, motorcycles have steel or aluminum frames, disk brakes, and telescoping forks for steering and holding the front wheel in place. Motorcycles are usually powered by petrol-powered engines typically with one to four cylinders (though sometimes up to eight cylinders). The engine is connected to manual transmissions, which drive the rear wheel of the motorcycle by a belt, driveshaft, or chain. Repair on motorcycles is often performed with a motorcycle lift.
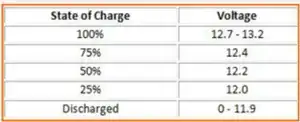
The larger and more modern the motorcycle engine, the longer it is likely to last with a good maintenance routine. For example, a small 250cc engine on a 1995 Kawasaki Ninja may only last for about 20,000 miles before replacement is necessary. However, a 1000cc 2011 Honda CBR1000RR can last up to 100,000 miles.
Motorcycles are generally easier to maintain than cars, regardless of your mechanical experience. Motorcycles are smaller and generally require less maintenance than cars and include fewer parts which are more accessible. The average amount a person spends to maintain a motorcycle is around $200-$300 each year (compared with the $800-$900 per year spent by the average car owner).
The cost of fixing a flat or leaking tire depends on the damage. If the puncture is caught early, the repair should cost around $15 to $30. However, run-flat tires often require complete replacement. Tire plug kits are generally priced between $10 to $20, so it is relatively inexpensive to complete the repair yourself. If you use tire sealant on a punctured tire, it is only expected to last for 50 to 100 miles.
Generally, moped brake handles are made of low-cost pot metal (poured into a mold). So, if the handle breaks, it is more than likely broken in pieces and will need to be welded back together. If you have access to welding equipment, it may be possible to weld the handle back together. However, for people without welding equipment, it is likely less expensive to simply buy a new handle.
When getting your motorcycle’s brakes serviced, the rotors will be more expensive than the brake pads. So, it is recommended to avoid harsh and sudden stops to reduce wear on your brakes. Brake pads are generally between $30 and $50 per set. For rotors, however, expect to pay a couple of hundred dollars per brake pad set.
The standard suggestion is to replace the oil in your motorcycle around every 3,700 miles. If your motorcycle uses synthetic oil, you can get closer to 5,000 miles without performing an oil change. If you use conventional oil, however, the number is closer to 3,000 miles between each oil change.