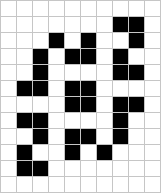
Triple pseudo still life
Triple pseudo still life[1] is the smallest pseudo still life that can be decomposed into three stable subpatterns (shown below; note that the first and third are themselves pseudo still lifes), but cannot be decomposed into two stable subpatterns.[2] It was found by Gabriel Nivasch in July 2001. It consists of a single block surrounded by two hook with tails and two snakes.
| Triple pseudo still life | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| View static image | |||||||||||
| Pattern type | Pseudo still life | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cells | 32 | ||||||||||
| Bounding box | 8×10 | ||||||||||
| Discovered by | Gabriel Nivasch | ||||||||||
| Year of discovery | 2001 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Uniqueness
Nathaniel Johnston showed on May 25 2017, via an exhaustive computer search using Simon Ekström's still life searcher, that the triple pseudo still life is the unique pseudo still life of 32 or fewer bits requiring a decomposition into 3 or more pieces.[3]
Image gallery
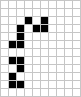 The first stable subpattern. |
 The second stable subpattern. |
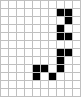 The third stable subpattern. |
gollark: They are in general. My thing just has the program counter be the last region of memory.
gollark: Not currently. I was going to add `IMOV` or something, but forgot. You can technically just do self-modifying code quite easily anyway.
gollark: It's basically a register machine, except it's memory.
gollark: Memory locations.
gollark: I REFUSE to stackize this.
See also
References
- Mark D. Niemiec (February 19, 2015). "29 Pseudo-still-lifes 26 bits and larger". Retrieved on April 3, 2016.
- Nivasch, Gabriel (July, 2001). "Still lifes". Retrieved on March 23, 2016.
- Nathaniel Johnston (May 25, 2017). Re: Enumerating Still Lifes (in C) (discussion thread) at the ConwayLife.com forums
This article is issued from Conwaylife. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.