42
2
Starting with a positive integer N, find the smallest integer N' which can be computed by repeatedly dividing N by one of its digits (in base-10). Each selected digit must be a divisor of N greater than 1.
Example #1
The expected output for N = 230 is N' = 23:
Example #2
The expected output for N = 129528 is N' = 257:
Beware of non-optimal paths!
We could start with 129528 / 9 = 14392, but that would not lead to the smallest possible result. The best we can do if we first divide by 9 is:
Rules
- Input can be taken in any reasonable format (integer, string, array of digits, ...).
- This is code-golf, so the shortest answer in bytes wins!
Test cases
1 --> 1
7 --> 1
10 --> 10
24 --> 1
230 --> 23
234 --> 78
10800 --> 1
10801 --> 10801
50976 --> 118
129500 --> 37
129528 --> 257
8377128 --> 38783
655294464 --> 1111
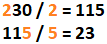
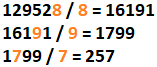
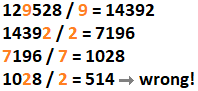
1I wonder if this series (1, 1, ..., 10, 11, 1, 13, ..., 1, ...) has an OEIS entry – Draco18s no longer trusts SE – 2017-12-28T01:48:10.350
It doesn't (yet), AFAICS. – GNiklasch – 2017-12-29T15:18:55.443