40
2
Your task is simple: given two integers a and b, output ∏[a,b]; that is, the product of the range between a and b. You may take a and b in any reasonable format, whether that be arguments to a function, a list input, STDIN, et cetera. You may output in any reasonable format, such as a return value (for functions) or STDOUT. a will always be less than b.
Note that the end may be exclusive or inclusive of b. I'm not picky. ^_^
Test cases
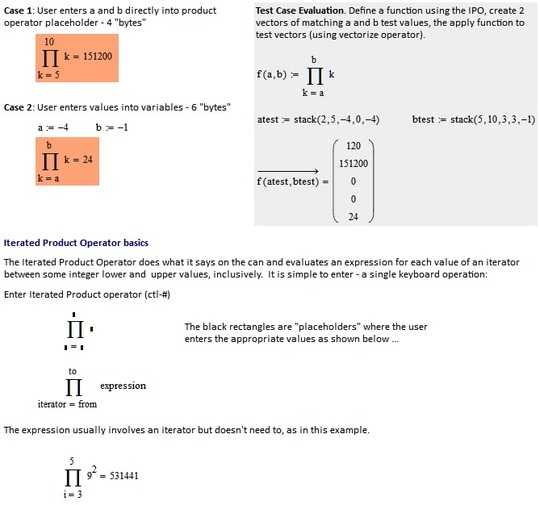
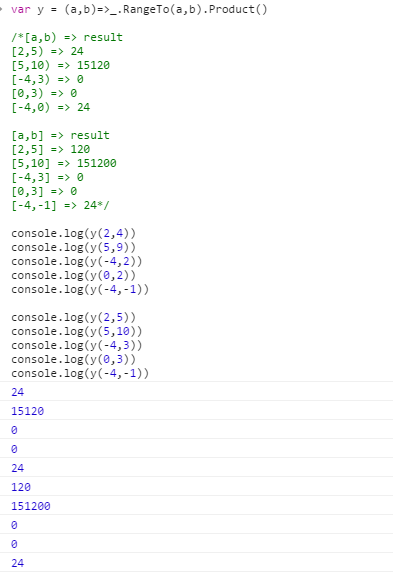
[a,b) => result
[2,5) => 24
[5,10) => 15120
[-4,3) => 0
[0,3) => 0
[-4,0) => 24
[a,b] => result
[2,5] => 120
[5,10] => 151200
[-4,3] => 0
[0,3] => 0
[-4,-1] => 24
This is a code-golf, so the shortest program in bytes wins.
Leaderboard
The Stack Snippet at the bottom of this post generates the catalog from the answers a) as a list of shortest solution per language and b) as an overall leaderboard.
To make sure that your answer shows up, please start your answer with a headline, using the following Markdown template:
## Language Name, N bytes
where N is the size of your submission. If you improve your score, you can keep old scores in the headline, by striking them through. For instance:
## Ruby, <s>104</s> <s>101</s> 96 bytes
If there you want to include multiple numbers in your header (e.g. because your score is the sum of two files or you want to list interpreter flag penalties separately), make sure that the actual score is the last number in the header:
## Perl, 43 + 2 (-p flag) = 45 bytes
You can also make the language name a link which will then show up in the snippet:
## [><>](http://esolangs.org/wiki/Fish), 121 bytes
var QUESTION_ID=66202,OVERRIDE_USER=44713;function answersUrl(e){return"https://api.stackexchange.com/2.2/questions/"+QUESTION_ID+"/answers?page="+e+"&pagesize=100&order=desc&sort=creation&site=codegolf&filter="+ANSWER_FILTER}function commentUrl(e,s){return"https://api.stackexchange.com/2.2/answers/"+s.join(";")+"/comments?page="+e+"&pagesize=100&order=desc&sort=creation&site=codegolf&filter="+COMMENT_FILTER}function getAnswers(){jQuery.ajax({url:answersUrl(answer_page++),method:"get",dataType:"jsonp",crossDomain:!0,success:function(e){answers.push.apply(answers,e.items),answers_hash=[],answer_ids=[],e.items.forEach(function(e){e.comments=[];var s=+e.share_link.match(/\d+/);answer_ids.push(s),answers_hash[s]=e}),e.has_more||(more_answers=!1),comment_page=1,getComments()}})}function getComments(){jQuery.ajax({url:commentUrl(comment_page++,answer_ids),method:"get",dataType:"jsonp",crossDomain:!0,success:function(e){e.items.forEach(function(e){e.owner.user_id===OVERRIDE_USER&&answers_hash[e.post_id].comments.push(e)}),e.has_more?getComments():more_answers?getAnswers():process()}})}function getAuthorName(e){return e.owner.display_name}function process(){var e=[];answers.forEach(function(s){var r=s.body;s.comments.forEach(function(e){OVERRIDE_REG.test(e.body)&&(r="<h1>"+e.body.replace(OVERRIDE_REG,"")+"</h1>")});var a=r.match(SCORE_REG);a&&e.push({user:getAuthorName(s),size:+a[2],language:a[1],link:s.share_link})}),e.sort(function(e,s){var r=e.size,a=s.size;return r-a});var s={},r=1,a=null,n=1;e.forEach(function(e){e.size!=a&&(n=r),a=e.size,++r;var t=jQuery("#answer-template").html();t=t.replace("{{PLACE}}",n+".").replace("{{NAME}}",e.user).replace("{{LANGUAGE}}",e.language).replace("{{SIZE}}",e.size).replace("{{LINK}}",e.link),t=jQuery(t),jQuery("#answers").append(t);var o=e.language;/<a/.test(o)&&(o=jQuery(o).text()),s[o]=s[o]||{lang:e.language,user:e.user,size:e.size,link:e.link}});var t=[];for(var o in s)s.hasOwnProperty(o)&&t.push(s[o]);t.sort(function(e,s){return e.lang>s.lang?1:e.lang<s.lang?-1:0});for(var c=0;c<t.length;++c){var i=jQuery("#language-template").html(),o=t[c];i=i.replace("{{LANGUAGE}}",o.lang).replace("{{NAME}}",o.user).replace("{{SIZE}}",o.size).replace("{{LINK}}",o.link),i=jQuery(i),jQuery("#languages").append(i)}}var ANSWER_FILTER="!t)IWYnsLAZle2tQ3KqrVveCRJfxcRLe",COMMENT_FILTER="!)Q2B_A2kjfAiU78X(md6BoYk",answers=[],answers_hash,answer_ids,answer_page=1,more_answers=!0,comment_page;getAnswers();var SCORE_REG=/<h\d>\s*([^\n,]*[^\s,]),.*?(\d+)(?=[^\n\d<>]*(?:<(?:s>[^\n<>]*<\/s>|[^\n<>]+>)[^\n\d<>]*)*<\/h\d>)/,OVERRIDE_REG=/^Override\s*header:\s*/i;body{text-align:left!important}#answer-list,#language-list{padding:10px;width:290px;float:left}table thead{font-weight:700}table td{padding:5px}<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/2.1.1/jquery.min.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="//cdn.sstatic.net/codegolf/all.css?v=83c949450c8b"> <div id="answer-list"> <h2>Leaderboard</h2> <table class="answer-list"> <thead> <tr><td></td><td>Author</td><td>Language</td><td>Size</td></tr></thead> <tbody id="answers"> </tbody> </table> </div><div id="language-list"> <h2>Winners by Language</h2> <table class="language-list"> <thead> <tr><td>Language</td><td>User</td><td>Score</td></tr></thead> <tbody id="languages"> </tbody> </table> </div><table style="display: none"> <tbody id="answer-template"> <tr><td>{{PLACE}}</td><td>{{NAME}}</td><td>{{LANGUAGE}}</td><td>{{SIZE}}</td><td><a href="{{LINK}}">Link</a></td></tr></tbody> </table> <table style="display: none"> <tbody id="language-template"> <tr><td>{{LANGUAGE}}</td><td>{{NAME}}</td><td>{{SIZE}}</td><td><a href="{{LINK}}">Link</a></td></tr></tbody> </table>
2I'm answering this in TI-BASIC tomorrow. – SuperJedi224 – 2015-12-10T02:48:28.700
@SuperJedi224 Good luck ;) – Conor O'Brien – 2015-12-10T02:48:56.463
Can the input be taken as
b, a? – FlipTack – 2017-02-12T20:01:02.423@FlipTack yes you can – Conor O'Brien – 2017-02-12T20:03:07.273