San Francisco Belt Railroad
The San Francisco Belt Railroad was a short-line railroad along the Embarcadero in San Francisco, California. It began as the State Belt Railroad in 1889, and was renamed when the city bought the Port of San Francisco in 1969. As a state owned enterprise, the railroad asserted several unsuccessful claims to immunity from federal regulation.[1] The railroad ceased operation in 1993.[2]
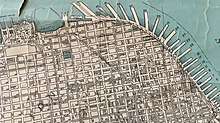
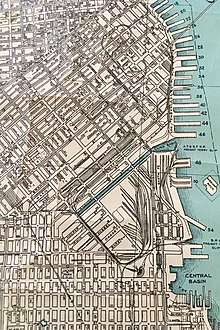

The railroad connected the Port of San Francisco to many waterfront docks and to industries and warehouses which were adjacent to the waterfront. In its early years, it operated dual-gauged track to accommodate the North and South Pacific Coast Railroads.[3] It would eventually have 67 miles (108 km) of trackage and general offices in the Ferry Building. Its function was to switch railroad cars from four major railroads to points along its system and vice versa. At the southern portion of the line, a track along King Street (passing the location now occupied by Oracle Park) connected with the Southern Pacific. San Francisco Municipal Railway's "E" Embarcadero line now traverses this route. A train ferry slip at Pier 43 allowed interchange with the Northwestern Pacific, the Western Pacific, and the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. To reach its northern terminus in the Presidio, the line passed through Fisherman's Wharf, Aquatic Park, and Fort Mason Tunnel.
The San Francisco Bay Railroad is the successor to the Belt Railroad and received approval to operate the remaining five miles of track in 2000.[4]
The former roundhouse has been converted to commercial business but exists in a recognizable form on the Sansome St, Lombard St, The Embarcadero, and Chestnut St block.
Locomotives
During its years of operation the railroad had 12 steam locomotives and 6 ALCO diesel engines:[5]
| Number | Arrangement | Year, Builder | Number | Arrangement | Year, Builder | Number | Model | Year, Builder | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governor Markham | 2-4-2T | 1891, Baldwin | Number 7 | 0-6-0 | 1914, Alco-Brooks | Number 20 | S2 | Alco | ||
| Number 2 | 0-4-2T | 1901, Baldwin | Number 8 | 0-6-0 | 1916 | Number 21 | S2 | Alco | ||
| Number 3 | 0-4-2T | 1904, Baldwin | Number 9 | 0-6-0 | 1920, Alco-Brooks | Number 22 | S2 | 1944, Alco | ||
| Number 4 | 0-6-0 | 1906, Vulcan | Number 10 | 0-6-0 | 1923, Baldwin | Number 23 | S2 | 1944, Alco | ||
| Number 5 | Number 11 | 0-6-0 | 1927 | Number 24 | S2 | 1945, Alco | ||||
| Number 6 | 0-6-0 | 1913, Baldwin | Number 12 | Number 25 | S2 | Alco |

Over the years, the belt railroad's tracks hosted several noteworthy locomotives and trains. In 1949, the California Zephyr was positioned near the Ferry Building for its inaugural ceremony. In 1971, the Flying Scotsman concluded its American tour by shuttling back and forth on a stretch of track adjacent to the Embarcadero and near Fisherman's Wharf. Owner Alan Peglar ran out of funds and the locomotive spent most of 1972 stored at an army base in Stockton, California. In 1975, the American Freedom Train pulled by ex-Southern Pacific Daylight locomotive #4449 visited San Francisco. For public viewing, the train's cars were switched to the Presidio by the belt line. The locomotive itself remained on display at Aquatic Park near the foot of Hyde Street. In 1987, the tracks along the Embarcadero just south of Sansome Street hosted a rail fair. Diesel locomotives and steam locomotives including V&T's J.W. Bowker (2-4-0 locomotive) were on display.
Steam Locomotive Number Four
Currently Locomotive #4 is being restored by the San Francisco Trains group, with larger plans to change the old Bayshore Roundhouse, originally owned by Southern Pacific, to a historic community destination. Due to work on the Roundhouse, it has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
See also
- Fred E. Stewart, former superintendent
References
- See e.g. California v. Taylor, 353 U.S. 553, 1 L. Ed. 2d 1034, 77 S. Ct. 1037 (1957).
- "The State Belt Railroad - Switching Freight on San Francisco's Embarcadero". Golden Gate Railroad Museum. Archived from the original on 10 February 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2020.CS1 maint: unfit url (link)
- Harrison, Greg. "The San Francisco Belt Railroad". AbandonedRails.com. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "San Francisco Bay Railroad Company SFB #543". Union Pacific Railroad. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "The State Belt Railroad of California". Retrieved 22 December 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to San Francisco Belt Railroad. |
- Abandoned tracks of the San Francisco Belt Railroad
- San Francisco Trains - State Belt Railroad
- "History of the San Francisco Belt Railroad". San Francisco Bay Railroad. Retrieved 1 March 2018.