Overseas military bases of the United Kingdom
Overseas military bases of the United Kingdom enable the British Armed Forces to conduct expeditionary warfare. Bases tend to be located in or near areas of strategic or diplomatic importance, often used for the build-up or resupply of military forces, as was seen during the 1982 Falklands War and the use of RAF Ascension Island as a staging post. Most of the bases are located on British Overseas Territories or former colonies which retain close diplomatic ties with the UK.
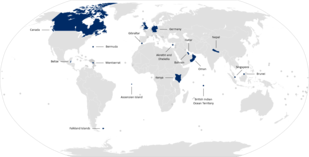
In total, the UK has 16 overseas military bases, second only to the United States. They often have been used by its allies, predominantly the US. A number of military operations would not have been possible without the strategic island of Diego Garcia in British Indian Ocean Territory. It was used for major operations during the War on Terror, Operation Granby (1991), Operation Herrick (2001–14; NATO), Operation Telic (2003–11), Operation Shader (2014–present), Operation Desert Storm (1991), Operation Desert Fox (1998), Operation Enduring Freedom (2001–14), Operation Iraqi Freedom (2003–11), and Operation Inherent Resolve (2014–present; NATO).
Overseas military installations
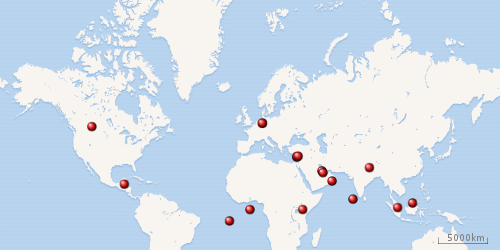 |
| Map of current military installations |
The British Armed Forces maintain a number of garrisons and military facilities around the world:
| Location | Details | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Ascension Island | RAF Ascension: The RAF maintains an airbase on Ascension Island; notable for use as a staging post during the 1982 Falklands War, the territory is also the site of a joint UK-US signals intelligence facility. | [1] |
| Bahrain | HMS Jufair: Britain's return East of Suez was marked with the establishment of a large Naval Support Facility. Officially opened in 2018, at the Bahraini port of Mina Salman, the base can support vessels up to the size of aircraft carriers. Bahrain is also home to the UK Maritime Component Command, which supports Royal Navy mine countermeasures vessels deployed in the Middle East. | [2] |
| Belize | British Army Training and Support Unit Belize (BATSUB): Used primarily for jungle warfare training, with access to 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2) of jungle terrain. Although British facilities were mothballed in the Strategic Defence and Security Review 2010, BATSUB is still seeing increased usage. | [3] |
| British Indian Ocean Territory | British Forces British Indian Ocean Territories: A Permanent Joint Operating Base. Although the Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia and airbase facilities on Diego Garcia are leased to the United States, the UK retains ownership and continual access. The small but permanent British garrison, known as Naval Party 1002, forms the civil administration on this British Overseas Territory. | [4] |
| Brunei | British Forces Brunei: A garrison made up of one battalion from the Royal Gurkha Rifles and No. 7 Flight AAC. Established in 1959, it also hosts routine jungle warfare courses for the British Army and Royal Marines. | [5] |
| Canada | British Army Training Unit Suffield: Home to a large contingent of in-service British Army vehicles, such as the Challenger 2 and Warrior IFV. It is the British Army's largest armoured warfare training facility, training up-to 5 battlegroups, each consisting of 1,400 personnel, every year. | [6] |
| Cyprus | British Forces Cyprus: A Permanent Joint Operating Base with significant garrisons in Akrotiri and Dhekelia, including RAF Akrotiri, the joint signals intelligence stations RAF Troodos and Ayios Nikolaos, and facilities to support two resident infantry battalions and supporting British Army units. | [4] |
| Falkland Islands | British Forces South Atlantic Islands: A Permanent Joint Operating Base. The British garrison is centred around RAF Mount Pleasant (the Mount Pleasant Complex) and includes commitments from all branches of the Armed Forces, most notably; No. 1435 Flight RAF (4 x Typhoons), No. 1312 Flight RAF (one Voyager and one Hercules), HMS Forth, and 1,000 British Army personnel. There are also early-warning and airspace-control radar stations at critical locations, and East Cove Military Port, a deep-water port operated by Naval Party 2010. | [4] |
| Germany | British Army Germany: Home of the 23 Amphibious Engineer Squadron and other supporting elements as well as depots and the Alpine Training Centre Hubertushaus in Oberstdorf. | |
| Gibraltar | British Forces Gibraltar: A Permanent Joint Operating Base. Britain has maintained a military presence in Gibraltar since its capture (1704) and the subsequent Treaty of Utrecht (1713). Facilities include (but are not limited to) the airbase RAF Gibraltar and the Port of Gibraltar. | [4] |
| Kenya | British Army Training Unit Kenya: Used primarily for the training of British infantry battalions in the arid and rugged terrain of the Great Rift Valley. Routine Royal Engineers and Royal Army Medical Corps exercises also carry out civil engineering projects and health care assistance to the local communities. | [7] |
| Nepal | British Gurkhas Nepal: The British Army maintains a small outpost in Nepal for recruitment purposes to the Brigade of Gurkhas. | [8] |
| Oman | UK Joint Logistics Support Base: A military logistics centre and training facility under construction in Duqm that will have a dry dock and be able to accommodate submarines and Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers. It could be linked to other Persian Gulf countries by the Gulf Railway. | [9] |
| Qatar | RAF Al Udeid: An outpost at Al Udeid Air Base serving as the headquarters for No. 83 Expeditionary Air Group and its operations across the Middle East. | |
| Singapore | Naval Party 1022: A Royal Navy repair and logistics support facility at Sembawang wharf in support of the Five Power Defence Arrangements. | [10] |
Locally raised units of British Overseas Territories
Four British Overseas Territories also maintain their own locally raised units for home defence and security:
| Location | Details | Official website |
|---|---|---|
| Bermuda | The Royal Bermuda Regiment: Formed in 1965. | www.bermudaregiment.bm |
| Falkland Islands | Falkland Islands Defence Force: Traces its origins back to 1847. The force consists of one light infantry company and trains once per week. It is manned entirely by the local population, following British Army doctrine, training and operations. | www.fig.gov.fk/fidf |
| Gibraltar | Royal Gibraltar Regiment: Raised in 1943. The regiment consists of one infantry battalion (1 x HQ company and 3 x infantry companies) and is regarded as a colonial force within the structure of the British Army. | royalgibraltarregiment.gi |
| Montserrat | Royal Montserrat Defence Force: Raised in 1899. |
See also
- Power projection
- List of overseas military bases by country
- List of Royal Navy shore establishments
- List of British Army installations
- List of Royal Air Force stations
- List of United States military bases
References
- "The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union" (PDF). Policy Department External Policies: 13–14. February 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- "Royal Navy's new Bahrain base seriously enhances Britain's ability to defend the Gulf". The Telegraph. 10 November 2016. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- "New Lease of Life for British Army Base in Belize". 7 April 2015. Archived from the original on 11 April 2015. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- Permanent Joint Operating Bases (PJOBs), www.gov.uk, 12 December 2012
- "The British Army in Brunei". www.army.mod.uk/. Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "The British Army in Canada". www.army.mod.uk/. Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "The British Army in Africa". www.army.mod.uk/. Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "British Gurkhas Nepal". www.army.mod.uk/. Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- "Defence Secretary strengthens ties between UK and Oman". Gov.uk. 28 August 2017. Retrieved 10 May 2018.
- Navy News (Magazine). United Kingdom: Royal Navy. June 2011. p. 11 Eastern Outpost. Retrieved 22 June 2016. ("The White Ensign is still flying above the operations of Naval Party 1022 (NP1022), based at Sembawang Wharves in Singapore.")
External links
- Overseas Military Bases of the United Kingdom (www.youtube.com)