List of military equipment used by Syrian opposition forces
List of military equipment[1][2] used by Syrian opposition forces in the Syrian Civil War. This list does not include equipment used by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and the Syrian Democratic Forces.
Sources
Large equipment like tanks and vehicles are generally captured from Syrian Army supplies, but small arms are likely a mixture of captured Syrian Army weapons, weapons imported by foreign combatants joining the opposition forces, or other sources. These include funding by private donors (notably from the Gulf region) and equipment supplied by friendly nations.
The U.S. supplied a considerable amount of weapons and ammunition, of both American and Soviet-type from Eastern Europe, to Syrian rebel groups under operation Timber Sycamore. For example, Jane's Defence Weekly reported that in December 2015 the U.S. shipped 994 tonnes of weapons and ammunition (including packaging and container weight).[3][4]
Small arms
| Model | Image | Caliber | Type | Origin | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pistols | ||||||
| TT-33 |  | 7.62×25mm Tokarev | Pistol | Commonly used by rebels, captured from the Syrian Arab Army. | ||
| Makarov PM |  | 9×18mm Makarov | Pistol | Commonly used by rebels, captured from the Syrian Arab Army. | ||
| M1911[5] |  | .45 ACP | Pistol | Rarely used by Syrian rebels | ||
| Browning Hi-Power | .jpg) | 9×19mm Parabellum | Pistol | Is an apparent popular pistol in Syria. | ||
| Kral Arms Canas[6] | N/A | 9 mm | Blank pistol | Blank pistol, possibly converted to fire live rounds. Only has been seen once in the war. | ||
| Rifles | ||||||
| Mosin–Nagant[7] | 7.62×54mmR | Bolt-action rifle | Seen common service by snipers, who usually put modern optics on it. The Mosin Nagant 1891/30 variant is used most but the M1944 (or Bulgarian 91/59 mosin nagant) carbine are also used, though to a lesser extent. | |||
| MAS-36[8] |  | 7.5×54mm French | Bolt-action rifle | Seen moderate usage by snipers through 2013-2014 in Aleppo when in July 2013, the FSA (probably 16th Division or some other branch of the FSA. 16th Division did use MAS-36s.)[9] captured large amounts of stockpiled MAS-36s from the Syrian Arab Army. Other rebel groups such as the Al-Tawhid Brigade also captured and used large amounts of MAS-36s captured from the Syrian Arab Army. Most rebel groups stopped using the MAS-36 around 2015 as ammo seemed to ran out.[10] | ||
| M1 Garand[11] | .30-06 Springfield | Semi-automatic rifle | Very limited usage. Questionable if it even is in Syria.[12] | |||
| SKS[13] Type 56 carbine[14] | 7.62×39mm | Semi-automatic rifle | Somewhat uncommon usage. Usually when it is used, it is seen being used by snipers attached with optics. Chinese copy of SKS. Used in the same way as the SKS. | |||
| Heckler & Koch G3[15][16] | 7.62×51mm NATO | Battle rifle | Sourced from Turkey and Saudi Arabia. Used as an DMR. Used very rarely. | |||
| FN FAL[16][17][18] |  | 7.62×51mm NATO | Battle rifle | Often used as Marksman Rifle and Operations Specialist Weapon, sourced from Libya and UAE. | ||
| M14 rifle[19] | 7.62×51mm NATO | Battle rifle | Rare. (Better source needed) | |||
| Assault rifles | ||||||
| StG 44[20][21][22] |  | 7.92×33mm Kurz | Assault rifle | On 8 August 2012, the FSA captured around 5,000 from a Syrian Arab Army storage container. | ||
| AK-47 | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | Isn't the most common gun in the war, but is used. The AKS-47 variant is also used.[23] | |||
| AKM | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | The AKMS variant is seen most (at least in the early part of the war), but the AKM is also seen. One of the most common weapons used in the Syrian Civil War. | |||
| Type 56 |  | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | Chinese variant of the Russian AK-47 and AKM. The Type-56 has been seen in use by various rebel groups. The Type-56-1 and Type-56-2 are also seen. | ||
| Zastava M70 | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | Yugoslavian variant of the Russian AK-47 and AKM. | |||
| PM md. 63 |  | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | Used commonly in the early part of the war. Isn't seen too commonly now. | ||
| AMD 65[24][25] |  | 7.62×39mm | Assault rifle | Isn't the most common gun in the war but is used occasionally. Seen more commonly in the early part of the war | ||
| vz. 58[26] |  | 7.62×39mm | Assault Rifle | Rare. Unknown how it got there. | ||
| AK-74 AKS-74[27] |  | 5.45×39mm | Assault rifle | Mostly used by opposition special forces and elite units. Isn't too common elsewhere. | ||
| AK-74M | 5.45×39mm | Assault rifle | Some modifited in bulpup configuration[27] | |||
| M16A1 M16A2[25] | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | Used by Division 30, the New Syrian Army,Al-Moutasem Brigade and Euphrates Shield rebels. The M16A1 was used commonly as a marksman rifle in the early parts of the war. | |||
| M4[28] |  | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | |||
| Norinco CQ[29] | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | "Where they are coming from is not certain. Iran is known to have purchased CQ rifles and produce it under license, but rifles similar to those seen in the Middle East have been seen and manufactured under license in Sudan, the National Interest report said." said by the Asia times. | |||
| FAMAS[30][31] |  | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | Seen once in 2013, possibly smuggled out of Lebanon. | ||
| Steyr AUG[17] |  | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | Origin unclear; serial numbers removed. Used by Syrian Opposition special forces[32][33] Sometimes used by Syrian rebels as a marksman rifle[34] | ||
| IMI Galil[25] |  | 5.56×45mm NATO | Assault rifle | Limited usage | ||
| Sniper rifles and anti-material rifles | ||||||
| Steyr SSG 69[35] | 7.62×51mm NATO | Sniper rifle | Is a common bolt action rifle use by Syrian rebels. | |||
| M14 EBR[36] |  | 7.62×51mm NATO | Designated marksman rifle | |||
| Dragunov SVD |  | 7.62×54mmR | Sniper rifle | The most common sniper rifle in the war. | ||
| Zastava M91 |  | 7.62×54mmR | Sniper rifle | |||
| PSL | 7.62×54mmR 7.62×51mm NATO | Designated marksman rifle | ||||
| OSV-96[37] |  | 12.7×108mm | Anti-materiel rifle | |||
| M99[38] | N/A | 12.7×108mm | Anti-materiel rifle | Supplied by Qatar.[39] Is one of the most common anti-material rifles used by Syrian rebels. | ||
| Sayad-2 |  | .50 BMG | Anti-materiel rifle | Unlicensed Iranian produced copy of the Steyr HS .50. Captured from the Syrian Army.[40] | ||
| PTRS-41[41] |  | 14.5×114mm | Anti-tank rifle | Used by rebels as an anti-material rifle, has seen very limited use. | ||
| Submachine guns | ||||||
| Sterling submachine gun[42] | 9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | Rare. Unknown how it got there. | |||
| Sten[43][25] |  |
9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | possibly leftover from the 1948 arab-israeli war | ||
| Sa vz. 23[25][44] | 7.62×25mm Tokarev | Submachine gun | ||||
| MAB 38[45] | 9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | Very rare. So rare indeed that only 1 has been seen in the war. As of 2017.[46] | |||
| Uzi[47][25] |  | 9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | |||
| MP-40[48] | 9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | "Few MP-40s have been seen during the Syrian civil war, and of those that have, they appeared a year or two into the conflict. There is a decent chance that these guns were not preexisting in the country at all, but rather brought in after the fighting started. The Saudi-Croatian deal is one possibility (MP-40s were seen during the 1990s fighting in the Balkans) as is Libya, which had bought some WWII-vintage MP-40s from Yugoslavia in the 1980s." From WWIIafterWWII[49] | |||
| Beretta M12[25] |  | 9×19mm Parabellum | Submachine Gun | |||
| Machine guns | ||||||
| RPD[50][51] |  | 7.62×39mm | Light machine gun | |||
| RPK[52] | 5.45×39mm | Light machine gun | ||||
| PKM | 7.62×54mmR | General-purpose machine gun | ||||
| MG-34[19] | 7.92×57mm Mauser | General-purpose machine gun | Captured from some Syrian stockpiles. Very rare usage but was one of the FSA's first machine guns looted from Syrian army warehouses.[53] | |||
| M240B[54] |  | 7.62×51mm NATO | General-purpose machine gun | Used by the NSA and al-Moutasem Brigade and Euphrates Shield forces | ||
| FN MAG[55] |  | 7.62×51mm | General-purpose machine gun | |||
| Ksp 58[25] | 7.62×51mm | General-purpose machine gun | ||||
| DShK[3] Type 54 HMG | 12.7×108mm | Heavy machine gun | Often mounted on technicals. Sometimes is planted in holes in walls or on flat surfaces when in lack of a tripod Chinese copy of DShK. | |||
| NSV[56] | 12.7×108mm | Heavy machine gun | Rarely used | |||
| W85[57] | .jpg) | 12.7×108mm | Heavy machine gun | Used very commonly.[58] Sometimes is planted in holes in walls or on flat surfaces when in lack of a tripod[59][60] | ||
| KPV[61] | 14.5×114mm | Heavy machine gun | Often mounted on technicals. | |||
| M2 Browning[62][63][64][54] |  | .50 BMG | Heavy machine gun | Used by US-backed FSA groups, including the al-Mu'tasim Brigade and the Hamza Division. | ||
| M1919 Browning[25][65] |  | .30-06 Springfield | Medium machine gun | Seen at least once in the war. It’s possible it was taken off a disabled Israeli vehicle during the Yom Kippur War or the 1980s fighting in Lebanon.[66] | ||
| Vickers machine gun[67] |  | .303 British | Heavy machine gun | Seen at least once in the war. May or may not be usable. | ||
Grenades, grenade launchers and explosives
| Model | Image | Diameter | Type | Origin | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1[68][69] |  | 55 mm | Hand grenade | The most common grenade used by the Free Syrian Army and other rebel groups. | |
| Mk 2 grenade[70] | 59 mm | Hand grenade | |||
| M26 grenade |  | 57 mm | Hand grenade | (Citation needed) | |
| RGD-5[71] |  | 58 mm | Hand grenade | The second most common grenade. | |
| OHG-92[72] |  | 65mm[73] | Hand grenade | Grenades originally delivered to the United Arab Emirates in 2003–2004 and then given to Jordan in 2004. Unclear how the hand grenades reached the Syrian rebels.[74] | |
| AGS-17[75] |  | 30×29mm grenade | Automatic grenade launcher | ||
| Type 87 |  | 35×32mm grenade | Automatic grenade launcher | (Citation needed) | |
| Mark 19 grenade launcher |  | 40×53mm grenade | Automatic grenade launcher | Supplied by the USA. | |
| RBG-6[76][77][78] |  | 40×46mm grenade | Grenade launcher | Croatian-produced copy of South African Milkor MGL. Supplied by Saudi Arabia.[79] | |
| Arsenal MSGL[80] |  | 40×46mm grenade | Grenade launcher | ||
| FN 303 | 18 mm | Riot gun | Used by Free Syrian Police. | ||
| IED[81] |  | Improvised explosive device | |||
| Molotov cocktail[81] |  | Incendiary device |
Anti-tank weapons
| Model | Image | Diameter | Type | Origin | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder-fired missiles | ||||||
| SPG-82[82] | 82 mm | Anti-tank rocket launcher | ||||
| RPG-2 |  | 82 mm | Recoilless rifle[83] | Although the 104th Brigade of the Syrian Republican Guard had used them,[84] there is no proof of the Syrian Opposition using RPG-2s. Syrian rebels did use Chinese Type-69 RPGs which could be mistaken as the RPG-2.[85] | ||
| RPG-7[3] |  | 40 mm (launcher only, warhead diameter varies) | Rocket-propelled grenade | Very common, the most common anti-tank gun in Syria. | ||
| RPG-18[86] | 64 mm | Rocket-propelled grenade | ||||
| RPG-22[77] |  | 72.5 mm | Rocket-propelled grenade | Supplied by Saudi Arabia.[79] | ||
| RPG-26[87] |  | 72.5 mm | Rocket-propelled grenade | |||
| RPG-29[88] | 105 mm | Rocket-propelled grenade | ||||
| RPG-75[89] | 68 mm | Rocket-propelled grenade | ||||
| M72 LAW[18] |  | 66 mm | Anti-tank rocket launcher | Turkish HAR-66 (LAW copy) supplied by Turkey | ||
| M79 Osa[77][90] |  | 90 mm | Anti-tank rocket launcher | Supplied by Saudi Arabia.[79] | ||
| RBR-120 mm M90[91] |  | 120 mm | Anti-tank rocket launcher | |||
| Anti-tank guided weapons | ||||||
| 9M14 Malyutka[92][93] | 125 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Designated AT-3 Sagger by NATO. | |||
| 9K111 Fagot[3][94][93] |  | 120 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Designated AT-4 Spigot by NATO. | ||
| 9M113 Konkurs[3][95][93] |  | 135 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Captured from the Syrian Army and supplied by Saudi Arabia.[96] Designated AT-5 Spandrel by NATO. | ||
| 9K115 Metis[93] |  |
130 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Designated AT-7 Spriggan by NATO. | ||
| 9K115-2 Metis-M[97][93] |  | 130 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Designated AT-13 Saxhorn-2 by NATO. | ||
| 9M133 Kornet[98][93] | 152 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Designated AT-14 Spriggan by NATO. | |||
| HJ-8[99][100] | 120 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Supplied by Qatar from Sudan.[101] | |||
| MILAN[102][93] |  | 115 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Captured from the Syrian Army and YPG.[103] Some supplied by Qatar or from Libyan National Army stocks.[104] | ||
| BGM-71 TOW[105][93] |  | 152 mm | Wire-guided anti-tank missile | Allegedly supplied by the U.S., but origin remains "unclear"; serial numbers removed.[106] The TOW missile system has seen extensive use during the Hama Offensive by Syrian opposition forces, mainly against armoured vehicles from both the SAA and NDF. | ||
Anti-aircraft weapons
| Model | Image | Diameter | Type | Origin | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Towed anti-aircraft guns | ||||||
| ZU-23-2[107][93] |  | 23 mm | Autocannon | Often mounted on technicals. | ||
| 37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K)[108] |  | 37 mm | Autocannon | Mounted on technicals. | ||
| 57 mm AZP S-60[109] |  | 57 mm | Autocannon | |||
| ZPU[81][93] |  | 14.5×114mm | Anti-aircraft gun | Based on the Soviet 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine gun. Often mounted on technicals. | ||
| ZPU-4[93] |  | 14.5×114mm | Anti-aircraft gun | Mostly mounted on Technicals. | ||
| ZPU-1[93] |  | 14.5×114mm | Anti-aircraft gun | mounted on Technicals. | ||
| Self-propelled air defense | ||||||
| ZSU-23-4 "Shilka"[110][93] |  | 23 mm | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | Often used against ground targets in urban environments. | ||
| 9K33 Osa[111] |  | 209.6 mm 9M33 missile | Amphibious SAM system | Two captured from the Syrian Armed Forces and used by Jaysh al-Islam and Jaysh al-Ahrar. | ||
| Man-portable air-defense systems | ||||||
| FN-6[112] | 72 mm | Supplied by Qatar.[113] | ||||
| 9K32 Strela-2[114] |  | 72 mm | Man-portable air-defense system | Designated SA-7 Grail by NATO. | ||
| 9K310 Igla-1[115] |  | 72 mm | Man-portable air-defense system | Designated SA-16 Gimlet by NATO. | ||
| 9K338 Igla-S[116] | .jpg) | 72 mm | Man-portable air-defense system | Designated SA-24 Grinch by NATO. | ||
| FIM-92 Stinger[117] |  | 100 mm | Turkey reportedly helped to transport to a limited amount of FIM-92 Stingers to the Free Syrian Army | |||
Artillery and Mortars
| Model | Image | Caliber | Type | Origin | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortars | ||||||
| 82-BM-37[93] |  | 82 mm | Infantry mortar | |||
| 2B9M Vasilek[118] | 82 mm | Gun-mortar | Possible Chinese copy (W99). At least one in use by Ansar al-Sham. Unclear origin. Also being used by Syrian Turkmen Brigade.[119][118] | |||
| M1938 mortar[93] | .jpg) | 120 mm | Infantry mortar | |||
| 120-PM-43 mortar |  | 120 mm | Infantry mortar | |||
| Improvised mortars | N/A | Various | Improvised mortar | |||
| Field artillery | ||||||
| 10.5 cm leFH 18M |  | 105 mm | Howitzer | Seen occasional service with rebel groups during the Syrian Civil War, in July 2013 and May 2015. | ||
| 122 mm howitzer M1938 (M-30)[93] |  | 122mm | Howitzer | Captured during Ramouseh Artillery Base assault by Jaish al Fateh | ||
| D-30[93] |  | 122 mm | Howitzer | Captured from the Syrian Army | ||
| "Hell cannon"[120] | N/A | Various | Improvised howitzer | Improvised howitzer that fires propane gas cylinders. Originated with the Ahrar al-Shamal Brigades, now used widely. | ||
| M-46[61] |  | 130 mm | Field gun | |||
| 180 mm gun S-23[121] | 180mm | Heavy Gun | Captured during Ramouseh Artillery Base assault by Jaish al Fateh | |||
| 152 mm howitzer 2A65[93] |  | 152mm | Howitzer | |||
| Self-propelled artillery | ||||||
| 2S1 Gvozdika[122][93] |  | 122 mm | Self propelled howitzer | Armed with D-30 howitzer. | ||
| 2S3 Akatsiya[123] |  | 152.4 mm | Self propelled howitzer | Armed with D-22 howitzer. | ||
| Recoilless rifles | ||||||
| B-10[93] Type 65 |  | 82 mm | Recoilless rifle | Chinese copy of B-10. | ||
| M60[77] | 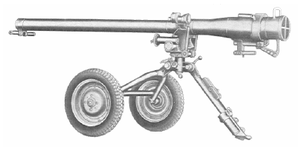 | Recoilless rifle | Supplied by Saudi Arabia.[79] | |||
| M40[124] |  | 105 mm | Recoilless rifle | Possible Iranian copy. | ||
| Carl Gustav 84mm[125] |  | 84 mm | Recoilless rifle | |||
| SPG-9[93] |  | 73 mm | Recoilless rifle | |||
| Rocket artillery | ||||||
| Type 63[97][93] | 106.7 mm | Multiple rocket launcher | Possible Iranian copy.[126] | |||
| RAK-12[127][128][129] |  | 128 mm | Multiple rocket launcher | Croatian built version of Yugoslavian M-63 Plamen with 12 rocket tubes instead of the original 32. Supplied by Saudi Arabia.[79] | ||
| Katyusha[130][131][132] | N/A | Multiple Rocket Launcher | ||||
| BM-21 Grad[133][134][93] |  | 122 mm | Multiple rocket launcher | Initially captured from the Syrian Army,[135] later supplied by Saudi Arabia from Bulgaria and Poland.[136] | ||
| Grad-P |  | 122 mm | Light portable rocket system | |||
| Improvised rocket launchers[81] |  | Various | Rocket launcher | |||
| Khaibar | N/A | 302 mm | Multiple rocket launcher | |||
Tanks and armoured vehicles
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-54[137][93] |  | Medium tank Main battle tank | Captured from the Syrian Army, at least one operated by the al-Tawhid Brigade and the Conquest Brigade as of September 2013. | |
| T-55 [138][93] |  | Medium tank Main battle tank | Captured from the Syrian Army. | |
| T-62[139] |  | Main battle tank | Captured from the Syrian Army. One of the most used tanks used by Syrian rebels. | |
| T-72[140] |  | Main battle tank | Captured from the Syrian Army. At least 8 operated by Jaysh al-Islam. Liwa Dawood had another 6, now owned by ISIL.[141] | |
| T-90[142] |  | Main battle tank | 1 operated by Harakat Nour al-Din al-Zenki, captured from the Syrian Army. | |
| BMP-1[93] |  | Infantry fighting vehicle | Captured from the Syrian Army. | |
| BVP-1 AMB-S [143] | Field ambulance | Captured from the Syrian Army. | ||
| BMP-2 |  | Infantry fighting vehicle | Two BMP-2s were captured from Syrian Army when FSA overran Aleppo's Infantry School and another was destroyed in the fight for Aleppo's Central Prison.[144] | |
| BTR-60PB[145] | Wheeled amphibious armoured personnel carrier | Captured from the Syrian Army. | ||
| BRDM-2[146] |  | Amphibious armoured scout car | Captured from the Syrian Army. | |
| Humvee |  | Armored car | Some captured from ISIS and YPG/SDF. | |
| Improvised fighting vehicles |  | Improvised fighting vehicle | Examples are the Sham 1 armored pickup truck and the Sham 2 armored car used by the Al-Ansar Brigade.[147] | |
| Streit Cougar | Infantry mobility vehicle | |||
| Streit Typhoon | MRAP | |||
| Safir | Off-road military light utility vehicle |
References
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aS-fjNFnNPk
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ld9Th3Ivfss
- Jeremy Binnie, Neil Gibson (8 April 2016). "US arms shipment to Syrian rebels detailed". Jane's Defence Weekly. IHS. Archived from the original on 2016-12-05. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- Malone, Paul (10 July 2016). "Save us from the Dr Strangeloves". Canberra Times. Archived from the original on 2016-10-10. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-10-19. Retrieved 2018-11-10.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Photo of Syrian rebel with Kral Av Canas". Archived from the original on 2014-12-25. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "WWII Weapons In The Syrian Civil War - The Firearm Blog". 26 June 2015. Archived from the original on 2015-06-27. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j8qFTTZClMk
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-08-25. Retrieved 2017-07-12.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "Syrian Uprising - Photos & Videos - no discussion, no conversation - Page 356". Archived from the original on 2014-11-09. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Photo of Type 56 carbine in al-Qsair". Archived from the original on 2014-11-09. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- PARABELLUM (8 June 2014). "The HK G3 in Syria". Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2017 – via YouTube.
- "Arming the Free Syrian Army". The American Spectator. 6 December 2012.
- "Is Syria's balance of firepower close to a tipping point?". The Guardian. 9 August 2012. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2016-12-17.
- "Insight - Syria rebels get light arms, heavy weapons elusive". Reuters. 13 July 2012. Archived from the original on 2014-10-20. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
- MG-34 & M14 at 1:39. Archived 2016-05-27 at the Wayback Machine 23 January 2014. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- "Free Syrian Army captures 5000 Stg 44s". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Sturmgewehr 44 used by Syrian Rebels Archived 2013-05-13 at the Wayback Machine – The Firearm Blog, August 22, 2012
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l7i-HZS0x0Q
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2018-04-10. Retrieved 2018-04-10.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- https://silahreport.com/2019/09/13/syrian-war-trophies-of-russian-armed-forces/
- "Video showing an FSA training camp with FSA soldiers training with vz. 58s". YouTube. Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- https://www.calibreobscura.com/idlibi-innovation-bullpup-kalashnikovs-of-syria/
- https://www.military.com/video/guns/machine-guns/syrian-rebel-sports-a-nice-m4/1653045833001
- https://www.asiatimes.com/2019/10/article/more-chinese-weaponry-turning-up-in-mideast/
- "Video showing a FSA member carrying a FAMAS F1 rifle in Syria". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-07-22. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=brTsRkE06RQ
- Spleeters, Damien (17 March 2013). "Austrian Steyr AUG A1. No serial numbers could be documented". Archived from the original on 21 January 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- OGN TV (2017-03-22), OGN - Russian force of Muslims in Syria, archived from the original on 2017-08-16, retrieved 2017-03-22
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0VCX5iNfEOA&feature=youtu.be
- "Picture showing an FSA member using a Steyr SSG 69".
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJGp2kth-Ec
- Brown Moses. "Video footage of rebels using OSV-96". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "More Chinese M99 12.7mm Anti-Material Rifles In Syria". State Of Tactical. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Timothy Yan. "The Chinese M99 50-caliber Anti-material Rifle". The Bangswitch. Archived from the original on 2014-07-22. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "Syria's HS.50s". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9nJMA5XvUbE
- https://www.facebook.com/iwantedagunpagesoimadeone/photos/a.247049835659364.1073741831.245858932445121/503550510009294/?type=3&theater
- "Footage of weapons which were handed over by rebels to the Syrian Arab Army in Southern Damascus". 12 May 2018.
- "معسكر أسود الحرب 2 ـ الإصدار الثاني".
- Johnson, Steve (2012-08-10). "Nifty Beretta Model 1938 in Syria". The Firearm Blog. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-01-28.
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "Uzi seen in the hands of Syrian rebel fighters". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2013-12-17. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "MP40 seen in the hands of Syrian rebel fighters". The Firearm Blog. Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RVmkB416goM
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=--wUGmoeaCc
- https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-syrian-rebels-from-the-katiba-al-wahad-unit-of-the-lewah-al-wad-53286213.html
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "Mutassim Brigade witnessing violent clashes while in the village of al-Tat Homs against Daesh". Youtube. 3 April 2016. Archived from the original on 2017-10-10. Retrieved 2016-04-04.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WKbDEkNuA5Y
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-S1FAijnmSs
- "These Are not the DShKs you're looking for: Part 2, the W85 Heavy Machine Gun - Guns & Tech". 9 September 2016. Archived from the original on 2017-05-26. Retrieved 2017-05-29.
- https://www.asiatimes.com/2019/10/article/more-chinese-weaponry-turning-up-in-mideast/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6_3NIUdiGHc
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ISNhv0AT74U
- Brown Moses. "Brown Moses Blog". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- War Clashes (30 November 2016). "Syria War 2016 - FSA in Heavy Intense Firefights Against ISIS in Aleppo Governorate" – via YouTube.
- War Clashes (2 November 2016). "Syria War 2016 - Battle of Aleppo: Heavy Clashes and Intense Urban Fighting". Archived from the original on 2018-02-16. Retrieved 2017-05-26 – via YouTube.
- War Clashes (2 November 2016). "Syria War 2016 - Battle of Aleppo: Heavy Clashes and Intense Urban Fighting". Archived from the original on 2018-02-16. Retrieved 2017-05-26 – via YouTube.
- "Footage of weapons which were handed over by rebels to the Syrian Arab Army in Southern Damascus". 12 May 2018.
- "Syrian Civil War: WWII weapons used". November 2019. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2019-12-15.
- "Footage of weapons which were handed over by rebels to the Syrian Arab Army in Southern Damascus". 12 May 2018.
- "معركة توحيد الصفوف الضرب بالمقنبل على الدشم المقابلة للباب الرئيسي للثكنة 29-9-2013". YouTube. 22 March 2017. Retrieved 2019-12-20.
- "Footage of weapons which were handed over by rebels to the Syrian Arab Army in Southern Damascus". 12 May 2018.
- "Mk 2 grenade in safehouse". Archived from the original on 2014-11-09. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Footage of weapons which were handed over by rebels to the Syrian Arab Army in Southern Damascus". 12 May 2018.
- "Swiss Hand Grenades in Syria". Archived from the original on 2015-01-21. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- "OHG-92 Specifications". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- Wezeman, Pieter D. (2013). SIPRI Yearbook 2013: Armaments, Disarmament and International Security. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 269–273. ISBN 978-0-19-967843-3.
- Brown Moses. "The FSA Captures An Unusual Weapon". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- AMGAD HARERE (13 January 2013). "درعا مدينة بصر الحرير اشتباكات عنيفة بين ابطال الجيش الحر وكتائب الاسد لليوم الثامن عشر على التوالي في محاولة استعادة السيطرة على المدينة م" – via YouTube.
- Brown Moses. "Evidence Of Multiple Foreign Weapon Systems Smuggled To The Syrian Opposition In Daraa". Archived from the original on 2014-10-18. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Jihadists Northern Hama offensive | March 22nd 2017". YouTube. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
- Richard Spencer. "US and Europe in 'major airlift of arms to Syrian rebels through Zagreb'". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "Bulgarian Arsenal MSGL grenade launcher in Syria & Iraq – Armament Research Services". armamentresearch.com. Archived from the original on 2017-05-27. Retrieved 2017-05-29.
- DIY weapons of the Syrian rebels. Archived 2014-12-28 at the Wayback Machine 20 February 2013. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- World Conflict Films (16 September 2015). "SPG-82 Used By Rebels In Syria". Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2017 – via YouTube.
- "Modern Firearms - RPG-2". Archived from the original on 2015-02-15. Retrieved 2014-12-28.
- "La 104ème brigade de la Garde républicaine syrienne, troupe d'élite et étendard du régime de Damas". France-Soir (in French). 20 March 2017. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2019.
- "DIY Rebel RPG in East Ghouta, Syria 29 March 2017". 29 March 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2020 – via Reddit.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-08-23. Retrieved 2017-08-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "RPG-26 used by Syrian rebels". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-06-24. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Video footage of RPG-29 used by Syrian rebels". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2015-12-27. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "RPG-75 in Syria". Archived from the original on 3 May 2015. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Brown Moses. "Video footage of Jabhat al-Nusra with M79 Osa". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Video of captured RBR-120 mm at 2:55". Archived from the original on 2014-07-28. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "9K11 Malyutka/AT-3 Sagger sighted with Syrian rebels". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-05-09. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Military Balance 2019. IISS. 2019. p. 370. ISBN 978-1857439007.
- "Hundreds of anti-tank guided missiles captured in Damascus Governorate". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "9M113 Konkurs/AT-5 Spandrel sighted with Syrian rebels". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-06-03. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "New Saudi-supplied missiles boost rebels in south Syria". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2014-11-26. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- Brown Moses. "The Syrian Opposition's Latest Missiles and Rockets". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Syrian FSA firing a Kornet". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-05-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- SyrianCivilWarVideo (1 March 2014). "Syrian rebels assembling and launching HJ-8 ATGM" – via YouTube.
- Oryx. "Footage of HJ-8 in the hands of Syrian rebels". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "The HJ-8, a new weapon on the Syrian battlefield". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- Syrian rebels captured ammunition depot with Milan / Konkurs anti-tank missiles and rockets Archived 2013-08-10 at the Wayback Machine - Armyrecognition.com, 5 August 2013
- "Syrian MILANs". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-12-01. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "Syrian MILANs (2), MILANs coming from abroad?". Oryx Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "Syrian rebels who received first U.S. missiles of war see shipment as 'an important first step'". The Washington Post. 28 April 2014. Archived from the original on 2017-08-23. Retrieved 2017-09-03.
- "Syrian rebels who received first U.S. missiles of war see shipment as 'an important first step'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2014-12-01. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "Video footage of a truck-mounted ZU-23-2". YouTube. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "YouTube".
- "Video showing 57 mm AZP S-60 used by Syrian rebels". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-05-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Video of rebels using ZSU-23-4 Shilka". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2014-09-15. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Liwa al-Islam and her 9K33 Osa Archived 2013-11-06 at the Wayback Machine 31 July 2013. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- "Chinese missiles steal spotlight after downing Syria army helicopters". Global Times. 13 March 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-03-17. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
- C. J. Chivers and Eric Schmitt. "Arms Shipments Seen From Sudan to Syria Rebels". New York Times. Archived from the original on 2017-10-12. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- Brown Moses. "Videos Show Complete SA-7 MANPADS Reportedly Looted From The 46th Regiment Base". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Brown Moses. "Video Shows A SA-16 Surface-To-Air Missile Fired By The Syrian Opposition". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Video footage of Syrian rebels with SA-24". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2013-06-18. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Syrian Rebels Claim to Have Brought Down a Jet". The New York Times. 13 August 2012. Archived from the original on 16 August 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- "2B9M Vasilek automatic mortar in service with Ansar al-Sham in Syria". Archived from the original on 2015-01-16. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- Military Balance 2017
- Brown Moses. "DIY Weapons in Syria". Archived from the original on 2014-12-16. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Morant Mathieu on Twitter".
- Brown Moses. "Video footage of rebels using 2S1 Gvozdika self-propelled howitzer". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Syrian 2S3 M-1973 152 mm Akatsiya". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- "Video footage of M40 recoilless gun in Syria". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-05-05. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Syria Rebel with Carl Gustav 84mm". Archived from the original on 2016-04-17. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Brown Moses. "The Syrian Opposition's Latest Missiles and Rockets". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- Hamilton's Military Channel (25 May 2013). "FSA Fires RAK-12 Multiple Rocket Launchers in Syria" – via YouTube.
- "Video footage of RAK 12 Multiple Rocket Launchers in Syria". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2015-01-10. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Croatian RAK-12 in Syria". Military In the Middle East. Archived from the original on 2014-08-18. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Syria War (29 June 2013). "Syria - FSA Katyusha Missile Target Hezbollah" – via YouTube.
- Syria War (5 July 2013). "18+ Syria - Rebel Katyusha Rockets Target Assad Shabiha in Capitol Damascus 4-July-13 - YouTube". Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2017 – via YouTube.
- BeeteleN ewszz (22 October 2013). "KATYUSHA ROCKETS LAUNCHED BY FSA FIGHTERS HD]" – via YouTube.
- Conflict News (19 October 2016). "Syria-Aleppo: FSA target Regime HQ on Shaykh Yusuf hill with Grad" – via YouTube.
- "Syria's Descent: what weapons do the rebels have?". Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 2013-09-20.
- "Syrian rebels seize anti-tank missiles in raid on army base". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2014-12-28. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- "New rebel alliance attacks Syrian regime with foreign rockets". The New Arab. 30 September 2016. Archived from the original on 2017-10-10. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- Tell Rifaat Information Office (13 September 2013). "A T-54 tank seen during a joint military parade between the Tawhid Brigade and the Conquest Brigade in Tell Rifaat". Archived from the original on 2017-05-21. Retrieved 2017-05-21.
- "Video footage of rebel T-55 tank". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2016-03-07. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- Brown Moses. "Video footage of Free Syrian Army using T-62 tank". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Picture of a captured T-72 tank used by rebels". Archived from the original on 2013-07-08. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
- Oryx. "Syria's Steel Beasts: The T-72". Bellingcat. Archived from the original on 2015-06-27. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- @QalaatAlMudiq (10 June 2016). "Huge. Among the spoils Zinki made in Mallah: a T-90 seized from pro-Regime forces. N. #Alepp" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- Thiqa Agency. "وكالة ثقة - كلمة لقائد جيش المجاهدين المقدم أبوبكر في الخطوط الأولى بجبهة الملاح". Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- Oryx. "Onwards to the front, Syria's BMPs". Oryx. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- "بعض من الغنائم داخل الكتائب التي تم السيطرة عليها في مدينة نوى بمحافظة درعا - YouTube". YouTube. Archived from the original on 2015-07-31. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- "Video of BRDM-2 captured by rebels". Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- More Syrian rebel DIY weapons. Archived 2014-12-28 at the Wayback Machine 20 February 2013. Retrieved 4 January 2014.