Council of the Baltic Sea States
The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is a regional intergovernmental organisation working on three priority areas: Regional Identity, Safe & Secure Region and Sustainable & Prosperous Region. These three priority areas aim to address the themes of environment, economic development, entrepreneurship, education, culture, civil security, children's rights and trafficking in human beings.
 | |
| Abbreviation | CBSS |
|---|---|
| Formation | 1992 |
| Type | Regional/Intergovernmental Organization |
| Headquarters | Stockholm, Sweden |
Official language | English |
CBSS current Presidency | Lithuania |
Director General (Secretariat) | Ambassador Maira Mora |
Main organ | CBSS Secretariat |
| Website | www |


History
The CBSS was established by the region's Foreign Ministers in Copenhagen in 1992 as a response to the geopolitical changes that took place in the Baltic Sea region with the end of the Cold War. The CBSS founders were Hans-Dietrich Genscher, Uffe Ellemann-Jensen, Thorvald Stoltenberg, Lennart Meri, Janis Jurkans, Algirdas Saudargas, Henning Christophersen, Paavo Väyrynen, Andrei Kozyrev, Margaretha af Ugglas, and Krzysztof Skubiszewski.[1] Since its founding, the CBSS has contributed to ensuring positive developments within the Baltic Sea region and has served as a driving force for multilateral cooperation.
Since 1998 the CBSS has been served by a permanent international Secretariat that is located in Stockholm, Sweden and funded by the Member States. The highest institution of CBSS is the conference of foreign ministers, which convenes every two years.[1]
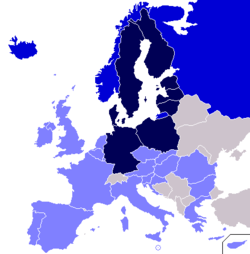
Member states
The CBSS has 11 member states as well as the European Union:
Observer states
11 other countries have observer status:[2]
Presidencies
The Council Presidency rotates between the eleven Member States on an annual basis. Each Presidency lays down a set of specific priorities to guide the works of the Council for the Presidency year and lasts for one year from 1 July until 30 June.[1]


























Structure
Committee of Senior Officials
The Committee of Senior Officials (CSO) consists of high-ranking representatives of the Ministries of Foreign Affairs of the 11 CBSS Member States as well as of a high-level representative of the European Union. The CSO serves as the main discussion forum and decision-making body for matters related to the work of the Council between Ministerial Sessions. The CSO monitors, facilitates and aims to coordinate the work of all CBSS structures.
The period chaired by each country rotates on an annual basis and follows the Council Presidency. The CSO Chairman is a representative, usually at ambassadorial level, appointed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the country which holds the Council Presidency.
A number of CBSS structures are operating under the auspices of the CSO.
In accordance with the Riga Declaration on the Reform of the CBSS from June 2008 one of the former working groups has been transformed into an Expert Group and the two other working groups have been dissolved.
The CSO monitors the work of the Expert Group on Nuclear and Radiation Safety, the Task Force against Trafficking in Human Beings (TF-THB), the Expert Group on Children at Risk, and coordinates the work undertaken in the agreed three long-term priorities 'Regional Identity', 'Sustainable & Prosperous Region' and 'Safe & Secure Region'.
Expert Groups
- CBSS Expert Group on Nuclear and Radiation Safety
- CBSS Expert Group on Maritime Policy
- CBSS Expert Group on Sustainable Development – manages Baltic 2030 Action Plan[4]
- CBSS Expert Group on Children at Risk
- The Task Force against Trafficking in Human Beings
Secretariat
A Permanent International Secretariat of the CBSS was established following a decision taken at the 7th Ministerial Session of the CBSS in 1998 in Nyborg, Denmark. The Secretariat was officially inaugurated at its premises on the island of Strömsborg in Stockholm on 20 October 1998. In November 2010, the Secretariat moved into its new premises located in Räntmästarhuset at Slussplan 9, Stockholm, Sweden.
The mandate of the Secretariat is as follows:
- to provide technical and organisational support to the Chairman of the CBSS and the structures and working bodies of the Council;
- to ensure continuity and enhanced coordination of CBSS activities;
- to implement the CBSS Information and Communication Strategy;
- to maintain the CBSS archives and information database;
- to maintain contacts with other organisations operating in and around the Baltic Sea region, the national authorities of Member States and the media.[1]
Strategic Partners
Since the 10th Ministerial Session of the CBSS in 2001, the Council has intensified efforts to coordinate CBSS activities with other organisations actively working to advance regional cooperation in the Baltic Sea Region. The CBSS has taken the initiative to organise annual coordination meetings, (organised and presided over by the CSO Chair), with the participation of Baltic Sea regional organisations, thus providing a more structured channel for involving the strategic partners to voice their concerns and coordinate their efforts with the CBSS and other organisations such as:
Long Term Priorities
In June 2014, the Council decided, after an evaluation and review of the CBSS five long-term priorities, to mainstream three renewed long-term priorities for the Council of the Baltic Sea States – Regional Identity, Sustainable & Prosperous Region and Safe & Secure Region.
- Regional Identity
- Goal: To foster a Baltic Sea Region identity and intensify contacts supporting its further development;
Objective: To develop the concept of Baltic Sea Region identity for and a sense of belonging to the Baltic Sea Region through engagement, participation and multilevel governance, in a community spirit and to create a notion of regional unity across borders by developing people-to-people contacts through dialogue, macro-regional networks and institutions;
- Sustainable and Prosperous Region
- Goals: To develop the Baltic Sea Region as a model region of sustainable societies able to manage and use resources efficiently, to tap the economic, technological, ecological and social innovation potential of the region in order to ensure its prosperity, environmental protection and social cohesion; To contribute to the eradication of obstacles hampering the comprehensive and sustainable development of the region;
Objectives: To improve the overall competitiveness of the Baltic Sea region through sustainable economic growth and labour markets, research and development, innovative infrastructure, an integrated maritime policy, transport and communications; To support the transition of the Baltic Sea region towards a competitive, green and low-carbon economy thereby ensuring sustainable development and inclusive growth; To support further action to reach a good environmental status and a healthy ecosystem supporting a prosperous Baltic Sea Region; To strengthen the region's capacity to adapt to climate change and the resilience capacity of ecosystems and societies; To ensure further mainstreaming of sustainable development at all levels and in all policy sectors, integrating economic, social and environmental aspects; To promote sustainable and green technologies and initiatives in order to protect the ecosystem and biodiversity of the Baltic Sea region;
- Safe and Secure Region
- Goal: To enhance societal security and safety in the Baltic Sea Region and to ensure that people of the Region are protected from and resilient to violence, accidents and emergencies through preparedness, and safeguarded against harm caused by criminal exploitation and human trafficking;
Objectives: To counteract all forms of trafficking in human beings, in the Baltic Sea Region via preventive and protective activities and projects based on a coherent and multidisciplinary approach; To promote comprehensive and sustainable child protection in order to prevent and respond to all forms of violence against children through a multi-sectorial approach and increased cooperation between relevant authorities and other stakeholders in the Baltic Sea Region; To strengthen societal resilience to disasters and hazards in all stages of crises through adequate prevention, preparedness, response and recovery; To enhance interoperability and strategic macro-regional cooperation enabling assistance and rapid response to cross-border accidents and emergencies, including disasters that may have cross-border consequences and impact;
See also
References
- http://www.cbss.org/council/
- "Annual Briefing of the CBSS Observer States". cbss.org. 13 November 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- "Danish Presidency 2019-2020". cbss.org. 2 July 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- "Baltic 2030". Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2017.