Charles G. Boyd
Charles Graham Boyd (born April 15, 1938) is a retired four-star general of the United States Air Force. Boyd is a highly decorated combat pilot who served in Vietnam and is the only Vietnam War prisoner of war (1966–1973) to reach the four-star rank (1992). His final Air Force assignment was as deputy commander in chief, U.S. European Command, Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Germany. He retired from the Air Force in 1995 and has remained active in the national security realm, including as a program director of the Council on Foreign Relations and as president of Business Executives for National Security. He is a member of the guiding coalition of the Project on National Security Reform.
Charles G. Boyd | |
|---|---|
 General Charles G. Boyd | |
| Birth name | Charles Graham Boyd |
| Born | April 15, 1938 near Rockwell City, Iowa, U.S. |
| Allegiance | United States of America |
| Service/ | United States Air Force |
| Years of service | 1959 – 1995 |
| Rank | |
| Commands held | Air University |
| Battles/wars | Vietnam War |
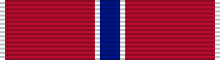
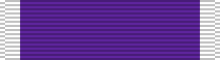
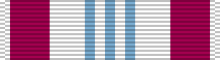
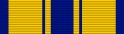
| Awards | Air Force Cross Air Force Distinguished Service Medal Silver Star (2) Legion of Merit (3) Distinguished Flying Cross Bronze Star with "V" device (3) Purple Heart (3) |
| Spouse(s) | Jessica Mathews |
| Other work | Council on Foreign Relations Business Executives for National Security |
Biography
Charles Graham Boyd was born on April 15, 1938 near Rockwell City, Iowa.[1] He entered the United States Air Force in April 1959.[2]
Education
Boyd received his Bachelor of Arts degree from the University of Kansas in 1975, and earned his Master of Arts degree from the same in 1976. His military education included attending the Air War College, Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama in 1977. In 1986, he participated in the Program for Senior Executives in National and International Security at Harvard University.
Air Force career
Boyd was commissioned as a second lieutenant through the aviation cadet program in July 1960 and served in a variety of assignments in Europe, the Pacific, and the Continental United States. A command pilot, with over 2,400 flight hours, he flew F-100s and F-105s in Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War. He was shot down on April 22, 1966[1] while on his 105th mission.[3] From 1966 to 1973[4] (2,488 days),[3] he was a prisoner of war,[4] interned in various prisons in North Vietnam.[5] During his captivity, Boyd was one of 52 Americans forced to participate in the Hanoi March, a propaganda event held in July 1966 in which U.S. prisoners of war were marched through the streets of Hanoi and brutally beaten by North Vietnamese civilians. He was released on February 12, 1973 as a part of Operation Homecoming.[1]
Boyd was vice commander of Strategic Air Command's 8th Air Force, director of plans at Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Washington, D.C., and commander of Air University, with headquarters at Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama, before becoming deputy commander in chief, U.S. European Command, Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Germany, which was his final assignment.
His Air Force assignments include:[2]
- April 1959–July 1960, student, undergraduate pilot training, Aviation Cadet Program, Greenville Air Force Base, Mississippi
- July 1960–January 1961, student, F-100 combat crew training, Luke Air Force Base, Arizona, and Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada
- July 1961–October 1963, F-100 fighter pilot, 510th Tactical Fighter Squadron, Clark Air Base, Republic of the Philippines
- October 1963–August 1964, F-105 fighter pilot, 355th Tactical Fighter Wing, George Air Force Base, California
- August 1964–November 1965, F-105 fighter pilot, 355th Tactical Fighter Wing, McConnell Air Force Base, Kansas
- November 1965–April 1966, F-105 fighter pilot, 388th Tactical Fighter Wing, Royal Thai Air Force Base, Thailand
- April 1966–February 1973, interned in various prisons throughout North Vietnam
- February 1973–August 1973, repatriation orientation
- August 1973–June 1975, undergraduate student, Air Force Institute of Technology, University of Kansas
- June 1975–June 1976, graduate student, Air Force Institute of Technology, University of Kansas
- August 1976–May 1977, student, Air War College, Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama
- June 1977–June 1979, special assistant to the chief of staff, Allied Forces Southern Europe, and executive officer to the chief of staff, Allied Air Forces, Southern Europe, Naples, Italy
- June 1979–September 1980, chief, Western Hemisphere Division, Directorate of Plans, Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Washington, D.C.
- September 1980–June 1982, deputy assistant director for Joint and National Security Council matters, Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Washington, D.C.
- June 1982–July 1984, assistant director for Joint and National Security Council matters, Headquarters U.S. Air Force
- July 1984–December 1986, deputy chief of staff for plans and programs, Headquarters U.S. Air Forces in Europe, Ramstein Air Base, West Germany
- December 1986–June 1988, vice commander, 8th Air Force, Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana
- June 1988–August 1989, director of plans, Office of the Deputy Chief of Staff, Plans and Operations, Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Washington, D.C.
- August 1989–January 1990, assistant deputy chief of staff for plans and operations, Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Washington, D.C.
- January 1990–October 1992, commander, Air University, Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama
- October 1992–August 1995, deputy commander in chief, U.S. European Command, Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Germany
His promotions and dates of rank are:[2]
- Second Lieutenant: July 22, 1960
- First Lieutenant: January 22, 1962
- Captain: January 22, 1965
- Major: December 1, 1970. He was promoted to major while a prisoner of war in Vietnam.
- Lieutenant Colonel: May 1, 1975
- Colonel: December 1, 1979
- Brigadier General: April 1, 1985
- Major General: November 1, 1987
- Lieutenant General: January 3, 1990
- General: December 1, 1992. General Boyd is the only Vietnam War POW to reach the four-star rank.[3]
Military awards and decorations
General Boyd's major military awards and decorations include:[2]


Post-military career
Following his retirement from the Air Force in 1995, Boyd served as strategy consultant to Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, Newt Gingrich. From July 1998 he was executive director of the U.S. Commission on National Security for the 21st Century, whose final report in January 2001 predicted a growing threat to the United States from terrorism. He has also served as senior vice president and Washington program director of the Council on Foreign Relations.[3]
From May 1, 2002 until December 31, 2009, he was the president and CEO of Business Executives for National Security (BENS), a national security public interest group. From December 14–17, 2009, Boyd led a delegation from BENS to Pyongyang, North Korea, to discuss economic issues with officials from the Democratic People's Republic of Korea government.[6] Boyd remains involved with BENS as a member of the Board of Directors.[7]
He is a member of the board of directors at defense electronics firm, DRS Technologies; graphics software firm, Forterra Systems; and venture capitalists In-Q-Tel, who support the work of the Central Intelligence Agency.
Family
His second wife is Jessica Tuchman Mathews,[3] former president of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.[8] General Boyd's first wife, Millicent Sample Boyd (April 23, 1938–April 11, 1994) is buried in Arlington National Cemetery.[5]
Notes
- "Bio: Boyd, Charles G." POW Network. Retrieved November 22, 2008.
- "General Charles G. Boyd". U.S. Air Force Military Biographies. 2004.
- "Charles G. Boyd". BENS Leadership. Business Executives for National Security. Archived from the original on 2009-12-26.
- "NAM-POW Medals". Veterans Tributes. November 6, 2008. Retrieved November 22, 2008.
- "Charles Graham Boyd, General, United States Air Force". ArlingtonCemetery.net. Retrieved November 22, 2008.
- "Sojourn of US Businessmen Delegation in Pyongyang". KCNA. Archived from the original on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2009-12-17.
- "Highlights". BENS. Archived from the original on 2009-10-10. Retrieved 2010-02-22.
- "Jessica Tuchman Mathews, President". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Archived from the original on March 15, 2006. Retrieved November 23, 2008.
References
- "General Charles G. Boyd". U.S. Air Force Military Biographies. HighBeam Research. January 1, 2004. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- "Bio: Boyd, Charles G." POW Network. Retrieved November 22, 2008.