2015–2017 youth suicides in Hong Kong
Youth Suicide trend in Hong Kong (Chinese: 香港學生連續自殺事件) refers to the succession of suicide committed by Hong Kong primary, secondary and post-secondary students from 2015 to 2017. The suicide cases are not connected, but the frequency of suicides aroused public's attention to the mental health and academic pressure of Hong Kong students.
| 2015–2017 youth suicides in Hong Kong | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 香港學生連續自殺事件 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 香港学生连续自杀事件 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
General Background
Statistics
Since the commencement of the 2015 school year, a spate of suicides among students began to take place, over 70 suicide cases were reported from 2015 to 2017. The alarming frequency of youth suicide is very worrying as it reached a record high, raising concerns that students in Hong Kong face too much academic stress. Based on records from the Coroner's Court,[1] there were 70 suicide incidents of youths aged 15–24 in 2015, among them 23 were full-time students.
Under sensational reports by the media, suicide can be contagious and intensify copycat effect, thus leading to more deaths. The distribution of deaths is shown below:[2]
| School Year | Primary and Secondary | Post-secondary |
|---|---|---|
| 2015–2016 | 22 | 16 |
| 2016–2017 | 17 | 15 |
| 2017–2018 | 13 | 12 |
It is worth to note that the current data on primary and secondary suicide cases also reveal a significant association between gender and mental illness, with male suicide rates outnumbering its female counterparts in Hong Kong. The Final Report published by the Committee on Prevention of Student Suicides (Chinese: 防止學生自殺委員會) suggested the reason may be unwillingness amongst men to talk openly with health care professions and treat mental disorders, while females are more likely to seek help.[3]
List of suicide case
Template:動態列表 the related suicide cases are listed as below:
Academic year 2014-2015
| student | age | grade (school) |
date | reference |
| Chan | 15 | secondary 3 | 15 October 2014 | [4] |
| Wong | 19 | secondary 6 | 9 March 2015 | [5] |
| Chan | 22 | Bachelor degree year 5 (Education University of Hong Kong) | 24 March 2015 | [6] |
Academic year 2015-2016
| Student | Age | Grade (School) |
Date | Reference |
| Chan | 21 | Associate degree | 26 July 2015 | [7] |
| Chow | 17 | Secondary 5 | 2 August 2015 | [8] |
| Boy | 19 | Studying overseas | 12 August 2015 | [9] |
| Chan | 21 | Bachelor degree (Hong Kong Chinese University) | 7 September 2015 | [10] |
| Chan | 11 | Secondary 1 | 10 September 2015 | [11] |
| Chu | 13 | Secondary 1 | 23 September 2015 | [12] |
| Lam | 15 | gap year | 23 October 2015 | [13] |
| Ng | 17 | Post-secondary IVE | 24 October 2015 | [14] |
| Wong | 21 | University (Hong Kong Shue Yan University) | 4 November 2015 | [15] |
| Ng | 21 | Bachelor degree 2 (Hong Kong Polytechnic University) | 4 November 2015 | [16] |
| Leung | 18 | Bachelor degree 1 (Hong Kong Chinese University) | 19 November 2015 | [17] |
| Tse | 21 | Diploma (VTC) | 14 December 2015 | [18] |
| Chan | 22 | Bachelor degree 4 (Hong Kong Chinese University) | 15 December 2015 | [19] |
| Wong | 15 | Secondary 4 | 16 December 2015 | [20] |
| Cheung | 18 | Secondary 6 | 28 December 2015 | [21] |
| Ho | 15 | Secondary 4 (CNEC Lee I Yao Memorial Secondary School) | 4 January 2016 | [22] |
| Siu | 19 | Bachelor degree 1 (Hong Kong Shue Yan University) | 6 January 2016 | [23] |
| Lee | 20 | Secondary 6 | 17 January 2016 | [24] |
| Lam | 14 | Grade 9 (Secondary 3) (Hong Kong International School) | 18 January 2016 | [25] |
| Wong | 21 | Bachelor degree 4 (Hong Kong Chinese University) | 20 January 2016 | [26] |
| Lai | 12 | Secondary 1 | 12 February 2016 | [27] |
| Ng | 16 | Secondary 5 | 18 February 2016 | [28] |
| Cheung | 20 | Bachelor degree 3 (Hong Kong Chinese University) | 5 March 2016 | [29] |
| Chow | 15 | Secondary 4 (St. Bonaventure College and High School) | 7 March 2016 | [30] |
| Ng | 12 | Secondary 1 (Buddhist Sum Heung Lam Memorial College) | 8 March 2016 | [31] |
| So | 20 | Bachelor degree 3 (University of Hong Kong) | 8 March 2016 | [32] |
| Cheung | 20 | Studying overseas | 11 March 2016 | [33] |
| Tam | 11 | Primary 6 | 12 March 2016 | [34] |
| Yip | 21 | Bachelor degree 3 (Hong Kong Polytechnic University) | 13 March 2016 | [35] |
| Chau | 22 | Bachelor degree 4 (Hong Kong Polytechnic University) | 26 March 2016 | [36] |
| Kwan | 17 | Grade 11 (Secondary 5) (Po Leung Kuk Choi Kai Yau School) | 27 March 2016 | [37] |
| Yeung | 20 | DSE Retaker | 4 April 2016 | [38] |
| Siu | 17 | Secondary 4 | 13 April 2016 | [39] |
| So | 22 | Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts year 4 | 14 April 2016 | [40] |
| Tse | 16 | Secondary 3 | 19 April 2016 | [41] |
| Wong | 18 | Studying overseas | 24 April 2016 | [42] |
| Lau | 18 | DSE | 10 June 2016 | [43] |
| Ng | 20 | DSE | 17 June 2016 | [44] |
| Wong | 14 | Grade 10 (Secondary 4) (Yew Chung International School) | 23 June 2016 | [45] |
| Tse | 19 | Diploma (Community College of City University (城大專上學院)) | 22 July 2016 | [46] |
Academic year 2016-2017
| Student | Age | Grade (School) |
Date | Reference |
| Lee | 17 | Secondary 5 (中華基督教青年會中學) | 2016/8/5 | [47] |
| Cheung | 22 | Bachelor degree 3 (香港中文大學) | 2016/8/26 | [48] |
| Boy | 20 | Bachelor degree 2 (香港專業教育學院) | 2016/9/13 | [49] |
| Leung | 20 | Secondary 6 graduate (新界鄉議局元朗區中學) | 2016/9/28 | [50] |
| Wong | 16 | VTC student | 2016/10/4 | [51] |
| Chan | 17 | Gap year | 2016/10/14 | [52] |
| Lau | 19 | Year 2 (香港專業教育學院) | 2016/10/16 | [53] |
| Lee | 13 | Secondary 2 | 2016/11/1 | [54] |
| Fung | 21 | Bachelor degree 4 (香港樹仁大學) | 2016/11/12 | [55] |
| Chung | 20 | Bachelor degree 3 (嶺南大學) | 2016/11/21 | [56] |
| So | 20 | Bachelor degree 2 (香港理工大學) | 2016/11/21 | [57] |
| Tsui | 16 | Secondary 3 (北角培僑中學) | 2016/11/23 | [58] |
| Ho | 19 | Associate degree | 2016/12/10 | [59] |
| Tsim | 15 | Secondary 2 | 2016/12/12 | [60] |
| Ng | 16 | Secondar 5 (東涌天主教學校) | 2016/12/16 | [61] |
| Leung | 13 | Secondary 2 | 2016/12/16 | [62] |
| Ko | 19 | Bachelor degree 3 (香港浸會大學) | 2016/12/19 | [63] |
| Chu | 25 | Secondary graduate | 2017/1/12 | [64] |
| Lam | 19 | gap year | 2017/1/22 | [65] |
| Yeung | 21 | Associate degree 2 (香港理工大學) | 2017/1/24 | [66] |
| Law | 19 | Year 2 (香港專業教育學院) | 2017/2/2 | [67] |
| Law | 16 | Secondary 4 | 2017/2/5 | [68] |
| Tsoi | 13 | Secondary 1 | 2017/2/6 | [69] |
| Tam | 15 | Secondary 4 | 2017/2/12 | [70] |
| Boy | 15 | Grade 11 (Secondary 5) (西島中學) | 2017/2/17 | [71] |
| Lung | 13 | Secondary 2 | 2017/2/21 | [72] |
| Boy | 19 | Study oversea | 2017/2/28 | [73] |
| Lau | 13 | Secondary 2 | 2017/3/1 | [74] |
| Tam | 21 | Associate degree student | 2017/3/9 | [75] |
| Lee | 18 | Secondary 5 | 2017/3/15 | [76] |
| Wong | 21 | Bachelor degree 3 (香港理工大學) | 2017/3/17 | [77] |
| Cheung | 20 | Associate degree student | 2017/3/20 | [78] |
| Leung | 17 | Secondary 4 (東華三院甲寅年總理中學) | 2017/3/21 | [79] |
| Girl | 21 | Bachelor degree 3 (Exchange in CUHK) | 2017/4/3 | [80] |
| Chan | 10 | Primary student | 2017/4/5 | [81] |
| Fong | 19 | Gap year | 2017/4/9 | [82] |
| Lee | 23 | Nursing school year 2 (屯門醫院普通科護士學校) | 2017/4/12 | [83] |
| Chan | 20 | 香港大學專業進修學院 | 2017/4/19 | [84] |
| Lau | 15 | Secondary 3 | 2017/4/27 | [85] |
| Yung | 22 | IVE | 2017/6/26 | [86] |
| Sun | 19 | study oversea | 2017/6/28 | [87] |
| Ho | 23 | Bachelor degree 4 (香港理工大學) | 2017/7/5 | [88] |
| Girl | 21 | University香港城市大學 | 2017/7/11 | [89] |
| Lam | 17 | Secondary 5 | 2017/7/27 | [90] |
| To | 17 | Secondary 4 | 2017/7/31 | [91] |
Academic year 2017-2018
| Stundet | Age | Grade (School) |
Date | Reference |
| Wong | 18 | study oversea | 2017/8/6 | [92] |
| Ho | 17 | gap year | 2017/8/10 | [93] |
| Mak | 21 | Bachelor degree 3 (香港中文大學) | 2017/8/13 | [94] |
| Ho | 15 | Secondary 4 | 2017/8/26 | [95] |
| Lam | 19 | Post-secondary (IVE) | 2017/8/31 | [96] |
| Fung | 23 | Study oversea | 2017/9/2 | [97] |
| Man | 16 | Secondary 5 | 2017/9/5 | [98] |
| Ng | 17 | Secondary 6 (元朗公立中學校友會鄧兆棠中學) | 2017/9/25 | [99] |
| Ng | 20 | Associate degree (香港能仁專上學院) | 2017/10/6 | [100] |
| Tsang | 11 | Primary 6 | 2017/10/12 | [101] |
| Mak | 17 | Secondary 6 (油塘天主教普照中學) | 2017/10/12 | [102] |
| Chau | 19 | gap year | 2017/10/20 | [103] |
| Lam | 21 | part time student | 2017年11月6日 | [104] |
| Chin | 17 | Secondary 6 (滙基書院(東九龍)) | 2017/11/20 | [105] |
| Kan | 19 | Associate degree (gap year) | 2017/11/23 | [106] |
| Chan | 16 | Secondary 5 | 2017/11/28 | [107] |
| Lau | 21 | Bachelor degree 1 (香港中文大學) | 2017/12/9 | [108] |
| Wong | 15 | Secondary 4 | 2017/12/10 | [109] |
| Hung | 25 | Bachelor degree 4 (香港浸會大學) | 2017/12/15 | [110] |
| Chow | 23 | Bachelor degree 4 (香港理工大學) | 2017/12/17 | [111] |
| Hung | 14 | Secondary 3 (順德聯誼總會梁銶琚中學) | 2018/1/2 | [112] |
| Wong | 17 | Secondary 6 (保良局何蔭棠中學) | 2018/1/2 | [113][114] |
| Lam | 17 | Gap year | 2018/1/14 | [115] |
| Tsoi | 19 | Bachelor degree 1 (香港中文大學) | 2018/1/16 | [116] |
| Chan | 17 | Secondary 6 | 2018/1/26 | [117] |
| Cheung | 21 | Secondary 6 (中華基督教會公理高中書院) | 2018/2/19 | [118] |
| Lam | 16 | Secondary 5 (中華傳道會李賢堯紀念中學) | 2018/2/28 | [119] |
| Wan | 25 | Bachelor degree 2 (香港理工大學設計學院) | 2018/4/5/ | [120] |
| Mak | 14 | Secondary 5 (神召會康樂中學) | 2018/5/6 | [121] |
| Leung | 22 | Bachelor degree 4 (香港中文大學) | 2018/5/26 | [122] |
| Cheung | 20 | University (香港理工大學) | 2018/5/29 | [123] |
| Poon | 11 | Primary 5 | 2018/6/19 | [124] |
| Lee | 16 | Gap year | 2018/6/20 | [125] |
Academic year 2018-2019
| Student | Age | Grade (School) |
Date | Reference |
| Sum | 21 | gap year | 2018/8/1 | [126] |
| Tsui | 19 | University (香港公開大學) | 2018/8/4 | [127] |
| Yuen | 17 | University (香港大學) | 2018/8/13 | [128] |
| Fan | 21 | University | 2018/8/17 | [129] |
| Choi | 22 | Bachelor degree 4 | 2018/8/22 | [130] |
| Cheung | 34 | Computer course | 2018/8/30 | [131] |
| Wong | 20 | University | 2018/9/19 | [132] |
| Lee | 19 | Bachelor degree 2 (香港中文大學) | 2018/9/21 | [133] |
| Wong | 17 | Secondary 6 | 2018/10/6 | [134] |
| Lung | 18 | 展亮技能發展中心 | 2018/10/7 | [135] |
| LAm | 17 | Secondary 6 (順德聯誼總會梁銶琚中學) | 2018/10/8 | [136] |
| Sum | 13 | Secondary 2 (迦密中學) | 2018/10/10 | [137] |
| Chung | 10 | Primary 5 | 2018/10/13 | [138] |
| Leung | 22 | University (香港理工大學) | 2018/11/2 | [139] |
| Ng | 12 | Secondary 1 | 2018/11/11 | [140] |
| Lui | 22 | Post-graduate degree (香港科技大學) | 2018/11/16 | [141] |
| Chan | 24 | Bachelor degree 5 (香港大學) | 2018/12/10 | [142] |
| Leung | 19 | Bachelor degree 2 (香港大學) | 2018/12/10 | [143] |
| Chan | 16 | Secondary 5 | 2019/1/6 | [144] |
| Lai | 17 | Secondary 6 | 2019/1/14 | [145] |
| Lee | 16 | Secondary 4 | 2019/3/14 | [146] |
| Poon | 16 | Secondary 5 | 2019/3/15 | [147] |
Causes of Suicide
There are multiple and interlocking causes of suicide suggested in the following.
Education in Hong Kong
In Hong Kong, the belief of "academic results determines the future" is prevailing. Schools, parents and students become oriented towards attaining good academic results, and this puts great pressure on students to pursue academic excellence.[148] The Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education (HKDSE) is seen as a "one-off exam". In a poll conducted by the "New Youth World", students rated their level of pressure as 7.44 out of 10 under HKDSE.[149] The life planning support is insufficient in Hong Kong, such that students see progression as their only way out, but neglecting their own abilities and interests. Therefore, they may easily feel stressed when they are not performing well academically.
Copycat suicide
Suicide cluster is defined as an emulation of another suicide that the person attempting suicide knows about, either from local knowledge or due to accounts or depictions of the original suicide on Television and in other media.[150] Imitative suicide is common in the under 25 age group.[151] In Hong Kong, it has been suggested that due to the widespread news report of youth suicide, students are driven to imitate such suicides.[152]
Psychological Concerns
In 2015–2016, 24 out of 38 suicide case involved psychological factors.[3] 13 victims displayed suicidal ideation and 17 victims showed feeling of hopelessness. However, current psychological support from schools, teachers, social workers and parents is not enough.[153]
Existing Support
The help and resources available for students divided into three levels: universal help (for students in general), selective help (for vulnerable students) and indicated help (for students with risk of suicide).
Universal help consists of information, workshops and other tools to help prevent student suicide and improve mental health, as well as raise awareness of the topic. It is also possible for schools to apply for up to HKD$150,000 from the Quality Education Fund to finance activities related to student's well-being.
Selective help is aimed at students with heightened risk of suicide. An example of selective help can be screening tools to find at-risk cases in time. For example, The Centre for Suicide Research provide hands-on advise on their web page to teachers, parents and friends who are worried that someone close to them may be at risk of suicide.
Indicated help is aimed at students with a risk of suicide. Post-secondary institutions are advised to have a 24-hotline and easy access to psychiatric and psychological services. Schools do not always live up to this standard. There are multiple independent hotlines, as well as hotlines run by the Social Welfare Department. Examples of suicide hotlines are the Suicide prevention Services, The Samaritan Befrienders Hong Kong, and Youth Outreach.[3][154]
Response from the Education Bureau
Attitude of the Bureau
In a legislative council meeting on 16 March 2016, former legislative council member Wong Yuk-man raised that one of the possible causes of students suicide could be the Hong Kong's education system which places too much emphasis on competition. He suggested that parents and teachers barely have time to help students cope with emotional distress as most effort are spent on academic results of students. He questioned the Education Bureau regarding whether it will identify the causes in the current education system that can lead to enormous study pressure for students.
In response to the question, former Secretary for Education Eddie Ng answered that suicide is a complex behaviour with no single cause, and that in fact students’ academic pressure has been reduced under the implementation of New Academic Structure (NAS) in 2009. For example, students under the NAS only have to sit for one public examination, and are able to choose elective subjects in accordance with their interests and abilities to develop their potential.[155]
He further raised that suicides could be prevented by better life planning.[156]
On 13 November 2016, the Education Bureau raised a similar viewpoint, restating that evidence based research indicated that the cause of suicide is complicated. Reasons behind each case are rarely the same and it cannot be proved that the education system or a particular academic environment could directly lead to suicide.[157]
Policies and Committees
Healthy School Policy
In February 2010, the Education Bureau circled a memorandum encouraging the implementation of the Healthy School Policy in primary and secondary schools. Each school was encouraged to formulate their own implementation plan.[158] This policy was implemented starting in the school year of 2010–2011. Furthermore, the policy's aim is divided into four different elements: developing a management and organisation system for health matters, encourage a healthy school environment, promote a healthy lifestyle for students and improve recognition of students in need and creating a system for handling these students.[159] The policy is foremost an anti substance abuse effort but also touches upon issues related to students’ mental health and student suicide.
Prevention of Student Suicide Committee
On 30 March 2016, the Educational Bureau set up the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee in response to the spate of students' suicides in the 2015–16 school year. The committee is tasked with studying student suicide in Hong Kong and to offer preemptive solutions to the problem ofyouth suicide.[160] The committee consists 21 members ranging from teachers, parents, psychiatrists and the president of the student union at the University of Hong Kong.[161] Professor Paul Yip Siu Fai (Chinese: 葉兆輝) is the director of the Centre for Suicide Research and Prevention in addition to being a chairperson in the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee.[162]
In November 2016, the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee released their final report which presents the current understanding of the student suicide problem and possible solutions. The measures suggested in the report are, including but not limited to, enhancement of the support for families, student support in schools, and promoting the acceptance of alternative career paths. In relation to the Report, the Education Bureau has formulated several practicable and follow-up actions to build a multi-layered safety net for students according to four areas, which includes Promotion of Students’ Mental Well-being and Health, Strengthening Support for Schools and Teachers, Reviewing Relevant Domains in the Education System, and Enhancement of Family Life and Parent Education.[163]
In addition, the Education Bureau proceeded with different policies and projects in response to the 2015–2016 student suicides and the following public discontent.[164] Including but not limited to, providing education material to schools to be able to identify students with difficulties and to provide education for students on coping strategies and positive attitudes. In this case, the educational material for schools, parents and students consisted of pamphlets on the topic of "Enhancing Life Resilience". A memo was sent out on 24 June 2016 to inform the heads of different schools of this material.[165]
Committee on Home-School Co-operation
The Committee on Home-School Co-operation (abbr.: CHSC), was set up after a recommendation from Education Commission, to encourage cooperation between parents and teachers. Chiefly by encouraging the set-up of Parent-Teacher Association and by organising activities made to improve home-school cooperation. A memorandum was sent out on 10 June 2016 from the Secretary for Education to inform supervisors and heads of schools. To achieve these goals the Committee on Home-School Co-operation has set up three different types of grants that schools can apply for. The first of grant, with a maximum sum of around HKD$5000 is for schools seeking to set up a Parent-Teacher Association. The second type of grant, with a maximum sum of HKD$5000, is for schools seeking to organise an activity with the purpose of encouraging home-school cooperation. Activities can, for example, be aimed at parenting training, assisting parents to support their children, or student health. The third type of grant is for joint Home-School Co-operation Projects.[166][167]
Other initiatives
No-Suicide Contracts

No suicide contracts for students have been a long debated in topic in Hong Kong. Nevertheless, they are used by mental health care professionals as a way to prevent suicides. The contract is an agreement that the student will not commit suicide or harm himself in any other way. Furthermore, the contract lists hotlines, contacts, and an emergency number that the student should call in case of suicidal thoughts. However, the No-Suicide contract is not a legal document. In March 2016 a copy of the Educational Bureaus No-Suicide Contract for students was circulated on the internet.[168][169]
Detecting youths at risk online
The Prevention of Student Suicide Committee has, in 2017, been in talks with Facebook and Google about the possibility of using these platforms as a tool for detecting student at risk of committing suicide. Facebook and Google already have their own suicide detection and prevention systems.[170]
Criticism
- Hong Kong Professional Teachers' Union
- The HKPTU criticised that the final report lack recurrent input of resources, manpower, and concrete suggestions.
- The Civil Alliance for Student Suicide (Chinese: 防止學生自殺民間聯席)
- The Alliance criticised that the Committee of Prevention of Student Suicide was shirking its responsibility and blaming the victims by stating that there is no substantial link between suicide incidents and the education system in the Final Report.
- Ip Kin-yuen (Legislative Councillor for Education constituency)
- Ip is disappointed by the Final report: by pointing out there is no direct relationship between the education system and youth suicide, the Education Bureau is in effect evading its responsibility and it missed the chance to review the education system. He further criticised that the current education system puts students under unnecessary pressure, and that the Report failed to address the root problem and he therefore request more resources from the government.[171]
- Shiu Ka-chun (Social Worker, Legislative Councillor for Social Welfare Constituency, Associate director of the Center for Youth Research and Practice (Chinese: 青年研究實踐中心) at Hong Kong Baptist University)
- Shiu suggested that there are lots of causes behind youth suicide, including the education system, economy, societal culture and structure, amongst others.[172] He criticised the government for ignoring the suggestion of organising a summit to address the problem and to make concrete anti-suicide policies.[173]
- Althea Suen Hiu-nam (Chinese: 孫曉嵐) (Former president of the Hong Kong University Students' Union, a social work student, member of the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee)
- Suen is the only youth member in the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee. She suggested how Hong Kong's exam-oriented education placed undue pressure on both teacher and students, and reduce time for teachers to take care of students’ mental well-being in the meetings. Her views were however absent in the Final report, stating that there is no substantial direct link between student suicides and the education system. She questioned whether the government is genuine in including young voices and participation on advisory bodies, and accused the pro-establishment forces of the committee for disregarding her views.
Suggestions
In the final report, the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee divided their recommendations into universal, selective and indicated support. Furthermore, the 19 suggestions are divided into areas of improvement, as follows: student support, families, traditional and social media, multiple articulation pathways, and systematic. The 19 suggestions are:[3]
| 1. Promote mental well-being and health | 11. Enhance referral mechanism to mental health services |
| 2. Facilitate students’ school adjustment | 12. Provide gatekeeper training for parents |
| 3. Enhance family life and parent education | 13. Arrange counselling and support services for needy parents |
| 4. Foster promotional use of social media | 14. Implement gate keeping on social media |
| 5. Advocate responsible media reporting | 15. Strengthen cyber-based outreaching services |
| 6. Enhance publicity of multiple pathways | 16. Continue developing online screening tools and conducting ongoing research |
| 7. Facilitate career exploration | 17. Establish school-based multi-disciplinary platforms |
| 8. Review relevant domains in the educational system,
duly support and address the development and diverse needs of the students and young people |
18. Enhance accessibility of mental health services |
| 9. Conduct gatekeeper training for early identification and intervention | 19. Publicise outreach services for needy families. |
| 10. Develop screening tools and guidelines for school to identify at-risk students |
In November 2016, the Hong Kong Professional Teachers' Union made the following suggestions: (1) Alleviation of teachers’ pressure e.g. increasing the quota of regular teachers and increase the teacher-student ratio per class; (2) Enhancing support from social workers (e.g. ensuring there is at least one social worker and one counsellor in each school); (3) Enhancing School-based Educational Psychology Service (Chinese: 校本教育心理服務); (4) Reform of education system, e.g. abolish Territory-wide System Assessment.[174]
In 2017, the Civil Alliance for Student Suicide Prevention publicised a survey that indicated public support for capping the number of hours spent studying each day to 7 hours. Lai Pak-yin, the spokesperson from the Civil Alliance for Student Suicide Prevention argues that excessive studying can have a harmful effect on family relationships. Therefore, he suggested that the Educational Bureau should issue guidelines to help decrease the number of hours spent studying each day.[175]
Controversy
Prevention of Student Suicides Page
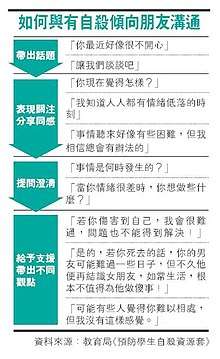
In April 2017, the Education Bureau set up the "Prevention of Student Suicides" page. They uploaded different resources and tips about how to identify and manage students with suicidal tendencies.[176] In a Chinese-language document titled "The Package on Prevention of Student Suicide (2010)" on the Bureau's website, one of the examples suggested as a way to communicate with friends who have suicidal tendencies has attracted huge public backlash – "If you die, your boyfriend may be sad for a few days, but he will soon find a new girlfriend and live normally. It is not worth doing such a silly thing for him!".[177]
Various educators and social workers commented that the controversial example can be very dangerous for people with suicidal thoughts. According to Shiu Ka-chun, the example provided was irritating and may encourage the person at risk to think pessimistically.[178]
Suicide of Choi Yuk-lin's son
On 7 September 2017, the Under-secretary for Education Christina Choi Yuk-lin's (Chinese: zh:蔡若蓮; born 1966) 25-year-old son, Poon Hong-yan, jumped to his death from the family's flat on the 41st floor at Sorrento. It was revealed that he suffered from depression due to serious injuries from a triathlon accident. Various officials, such as the Chief Executive Carrie Lam and Secretary for Education Kevin Yeung,[179] expressed their condolences to Choi and her family.
As Choi Yuk-lin is a member of the Prevention of Student Suicide Committee, some critics linked the incident with student suicide problem, and attacked Choi's failure to consider adolescents' concerns and perspectives before her son's death. Suen Hiu-nam, head of HKU's student union, further criticized officials for only sending their condolences to Choi's son, and ignoring other students who had committed suicide.[180]
On the same day, signs bearing the slogan "Congratulations Choi Yuk-lin's son on going west" appeared on the Education University of Hong Kong Democracy Wall, on top of banners supporting freedom of expression and Hong Kong independence. The University later issued a statement condemning the signs and apologising for any hurt they may have caused.[181]
References
- "2016年香港整體自殺率下跌 惟青少年自殺率升 (16:50) – 20170908 – 港聞". 即時新聞 instant news (in Chinese). Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- "【中一生墮樓】9月開學至今多宗學生自殺或企圖自殺案件". Apple Daily (in Chinese). Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- Committee on Prevention of Student Suicides (2016).Final Report November 2016
- "15歲女生思覺失調跳樓亡 家人傷心認屍" (in Chinese). 東方日報. 16 October 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- "19歲文憑試考生 離奇墮獅子山". Apple Daily 蘋果日報 (in Chinese). Retrieved 16 March 2015.
- "男友指因畢業論文不順利尋死教院自殺女生 捐眼角膜遺愛". Apple Daily 蘋果日報 (in Chinese). Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- "憂前景恐競爭力弱 21歲準副學士愁爆跳樓亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "夜蒲遭薄責 17歲女跳樓亡 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "明報工業中心 青年墮斃". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "中大男生開學日疑不堪壓力跳樓亡 - 快訊-文匯網". news.wenweipo.com. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "觀塘寶珮苑剛升中11歲男童墮樓死亡 - 香港經濟日報 - TOPick - 新聞 - 社會". topick.hket.com. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "港圖灣跳樓13歲男童 因學業問題不快樂 - 香港經濟日報 - TOPick - 新聞 - 社會". topick.hket.com. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "情緒病15歲少年跳樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "華員邨17歲仔跳樓亡 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "兩大學生13小時內墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "理大生墮樓:沙角邨21歲男生倒斃平台". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "中大女生 墮樓分屍 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "返工被「照肺」 21歲VTC畢業女生上吊身亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "中大生西環墮樓爆頭亡 慈母哭斷腸". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "15歲女WhatsApp道別 旺角墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "18歲中六男生身纏電線 家中通電自殺亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "15歲仔自縊:校方指事主近日無異樣". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "19歲樹仁女生 欠卡數墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 蔡靜心 (17 January 2016). "中六女生失蹤第5日 浮屍現大浪灣海面". 香港01. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "為學業與父爭吵 星籍少年墮樓亡 - 20160119 - 港聞 - 港聞二". 明報新聞網 - 每日明報 daily news (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "學業抑鬱 中大女生校園墮斃 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "校內犯錯唔開心 中一女生墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "【中學生墮樓】農曆年假後首開課 將軍澳男生墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- Pao, Ming. "疑不堪考試壓力 中大醫科女生墮樓亡 沈祖堯籲珍惜生命 需要時尋輔導" (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "曾透露不愛讀書 15歲仔竹園邨墮樓亡|壹週Plus". 壹週Plus. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "學業困擾 12歲男生墮斃 - 太陽報". 太陽報 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 呂凝敏 (9 March 2016). "港大生呻壓力大後墮樓亡 5日內第四宗學生自殺". 香港01. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "20歲青年墮樓亡 沈祖堯籲主動關懷". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "【學生墮樓】一周第5宗 乙明邨女生墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 12 March 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "20歲理大女護士生墮樓亡 9日第7跳 - 快訊-文匯網". news.wenweipo.com (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "理大生家中上吊 父揭發解下已氣絕". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "17歲生日 女生墮樓亡 - 20160329 - 港聞 - 港聞二". 明報新聞網 - 每日明報 daily news (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "自修生WhatsApp道別 考DSE前墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- 鄧栢良, 蔡靜心 (13 April 2016). "【青少年自殺】全家傷病折磨 成績優異中四生寓所縊亡". 香港01. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "22歲演藝女生 前男友面前墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 余睿菁, 鄧栢良 (19 April 2016). "中三生WhatsApp向母預告自殺 跳城門河自盡". 香港01. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "19歲留英學生唔想返學 重慶大廈賓館燒炭亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- 王譯揚, 蔡靜心 (10 June 2016). "疑受學業問題困擾 18歲男生逸東邨跳樓亡". 香港01. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "膠袋笠頭吸氦氣 DSE考生墮樓撞凹頭". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "向老友發死亡訊息 14歲仔墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "失戀 失意 19歲城大生墮斃 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- "中五男生返校跳樓亡". 蘋果日報. 6 August 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "中大畢業男生留死亡短訊回校跳樓亡 - 香港經濟日報 - TOPick - 新聞 - 社會". topick.hket.com. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- "學業有壓力 菲籍青年灣仔墮樓亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "升讀大學無望 20歲女墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 29 September 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "16歲VTC男生校內墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "家事唔開心 17歲少年上吊亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "健明邨墮斃少女為IVE學生 與母及妹相依". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "擅取零用錢遭薄責 13歲男童墮樓亡". on.cc 東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "原本是「陽光少女」 21歲樹仁大學女生墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- 呂凝敏, 梁銘康 (21 November 2016). "20歲哲學系女生嶺大宿舍上吊 送院搶救後不治". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "理大二年級退學生 石硤尾邨墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 21 November 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "中三生疑功課壓力大墮樓亡 祖父激動送院". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "19歲大專男生墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 11 December 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 香港01記者 (21 December 2016). "【盲亨尋女】警拘詹詠嵐男友 疑殉情獲救後隱瞞內情". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- 徐雲庭 (17 December 2016). "中五生拆窗花跳樓亡". 蘋果日報 (in Chinese). Retrieved 21 October 2018.
- "16歲男13歲女 一日兩宗學生墮斃 - 20161217 - 港聞 - 港聞二". 明報新聞網 - 每日明報 daily news (in Chinese). Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- 潘安奇, 魯嘉裕 (20 December 2016). "20歲浸大女生廣福球場公廁USB線上吊亡 浸會大學:痛心及惋惜". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "升U困擾 25歲仔愛蝶灣墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- "19歲青年翠竹花園墮樓亡 家人不明原因". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "21歲理大生搵女同學訴苦不果 梨木樹邨墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- 黃煒堯, 余睿菁 (2 February 2017). "【伏屍酒店】19歲IVE生倒斃麗豪酒店 疑割脈食藥雙料自殺". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "16歲中四男生利安邨墮樓亡 原因待查". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "【學生墮樓】農曆年假後開學 13歲女生墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 6 February 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "學業困擾 15歲男生墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 21 February 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "英基外籍男生時代廣場墮斃". 東方日報. 19 February 2017.
- "家人責沉迷遊戲機 14歲中二男生墮樓亡". 蘋果日報. 13 February 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 陳永武, 劉定安 (28 February 2017). "19歲外籍青年 半山豪宅屋苑梯間上吊亡". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "疑因打機與母親爭執 13歲男童墮樓亡 | 立場報道 | 立場新聞". 立場新聞 Stand News. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- "患癌大專生MegaBox墮樓亡 留遺書叫家人照顧自己". 蘋果日報. 9 March 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "18歲仔情困墮斃 母跪哭:點解掉低我 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "21歲女墮斃 女親友癱坐路邊痛哭 - 東方日報". orientaldaily.on.cc (in Chinese). Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- 劉定安 (20 March 2017). "20歲女學生上水寓所墮樓亡". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 20 March 2017.
- "中四男生接老師來電後墮樓亡 生前曾央求:放過我,我下次改!". 蘋果日報. 3 December 2018. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- 劉定安, 魯嘉裕, 陳永武 (3 April 2017). "【學生自殺】以色列女交流生 中大國際生舍堂上吊殞命". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- "【母女墮樓】離婚釀倫常慘劇 遺書揭失婚母尋死9歲女稱願相隨" (in Chinese). 香港01. 6 April 2017.
- 劉定安 (10 April 2017). "19歲小女友跳樓 30歲男子報案返魂乏術". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "23歲女子友愛邨墮樓亡 (12:24) - 20170412 - 港聞". 即時新聞 instant news (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "手機損壞失功課資料 HKU SPACE男生墮樓亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "疑遭家人薄責 15歲仔皮帶上吊亡" (in Chinese). 蘋果日報. 27 April 2017.
- "疑學業問題不開心 22歲IVE男生九龍塘墮斃". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "憂赴美升學 19歲仔跳樓亡". 蘋果日報. 29 June 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "理大畢業生墮樓亡 長髮少女哭成淚人". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 賴南秋, 劉定安 (12 July 2017). "九龍塘城大宿舍 韓裔女生墮樓殞命". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 11 April 2018.
- "17歲仔疑情困留遺書 寓所天台墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "【動畫】17歲仔上吊亡 警指涉圖姦夜跑女". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 陳永武 (7 August 2017). "本月父親死忌 18歲海外留學生家中USB線上吊亡". 香港01. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "沙田17歲女燒炭亡 爸爸掩面落淚". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "21歲中大女生嘆人生好煩 膠袋笠頭吸氦氣亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 15 August 2017.
- 陳永武 (27 August 2017). "情困15歲女學生銅鑼灣天台墮樓撞毀簷篷 搶救不治". 香港01. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "藍田德田邨19歲專業教育院學生墮樓亡". 經濟日報. 31 August 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "23歲加國回流大學生高處墮下 魂斷海逸豪園". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "開學兩日 16歲小發明家跳樓亡". 蘋果日報 (in Chinese). Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- "天水圍中六男生校園內墮樓昏迷 搶救後不治". 香港01. 25 September 2017.
- "中秋食飯替母晾衫無異樣 20歲大學生墮樓亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "學童自殺 林鄭點答?". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 4 January 2018.
- "17歲仔墮樓前 寫遺書交老師". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 4 January 2018.
- "19歲仔葵盛東邨墮樓亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- "壓力爆煲 半工讀青年墮樓亡" (in Chinese). Retrieved 4 January 2018.
- "紅磡女浮屍 為失蹤應屆文憑試女生錢宇凝". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 4 January 2018.
- "19歲全裸青年 西貢墮樓亡". Apple Daily 蘋果日報. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- "16歲女燒炭亡 父返家揭發". 東方日報. 29 November 2017.
- "母面前跳軌中大生輾斃". 明報. 10 December 2017.
- "疑不滿被反對做兼職 15歲女學生墮樓亡". 星島日報.
- "浸大生跳樓亡FB留言:唔好信一地兩檢". 蘋果日報. 16 December 2017.
- "23歲少女吊頸 胞姐發現已太遲". 蘋果日報. 17 December 2017.
- "女生墮樓:績優開朗人緣好 師生感震驚難過". 東網. 2 January 2018.
- "17歲墮樓 慈雲山慈康邨 文憑試男考生墮樓亡 遺血迹拖鞋". 香港01. 2 January 2018.
- "慈雲山名校日日補課長假照上堂 學生:生不如死". 蘋果日報. 11 February 2018.
- 楊婉婷 (14 January 2018). "青衣17歲少女行車天橋躍下 倒臥山坡不治". 香港01. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- 郭倩雯, 呂凝敏, 黃偉民 (16 January 2018). "中大中醫系男學生疑學業壓力墮樓亡 地上遺手機及拖鞋". 香港01. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- "文武雙全不敵學業壓力 應屆DSE女考生墮樓亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- 林振華, 楊婉婷, 魯嘉裕 (20 February 2018). "【少女伏屍】死者疑有精神病無覆診 天眼揭往雜貨店購百條索帶". 香港01. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- 陳永武, 劉定安 (March 2018). "少女葵涌墮樓殞命 消息稱死者身穿校服". 香港01. Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- "日 25歲理大男生墮樓亡 父母一度以為電騙". 蘋果日報. 5 April 2018.
- "14歲男生大埔墮樓亡 慈母認屍哭斷腸". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- "生活問題困擾 中大22歲非本地男生宿舍自縊亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- "20歲女大學生租酒店房 膠袋笠頭吸氦氣亡". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- 搏鬥3日終不治 |newspaper=頭條日報|accessdate=2018-06-19|language=zh-hk
- "彩盈邨16歲仔危坐窗簷 對峙近3個鐘疑失足墮斃". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- "自閉青年馬鞍山墮樓 分屍慘死". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- "葵涌邨19歲少女燒炭亡 男親友雙手合十跪地送別". 香港01. 4 August 2018.
- "疑學業壓力 準港大女生墮樓亡". 東方日報. 14 August 2018.
- "90後少女留遺書毛巾自縊 送院命殞". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- 彭愷欣 (22 August 2018). "秀茂坪22歲男子墮樓亡 母悲慟大哭". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- "34歲留學生大角嘴墮樓壓毀小巴 母聞子死訊暈倒". 星島日報. 31 August 2018.
- 陳永武, 鄧海興 (19 September 2018). "北角20歲青年墮樓亡 家人蹲地痛哭". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- "男生中大墮樓亡 學生會引述消息指為內地生". 明報. 21 September 2018.
- "17歲女仰藥輕生 阿哥發現及時救番". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- 余睿菁 (7 October 2018). "屯門南浪海灣18歲青年墮樓 現場證實死亡". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- 鄧海興 (9 October 2018). "疑學業壓力爆煲 屯門17歲男生燒炭亡". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- 陳永武, 劉定安, 賴南秋 (10 October 2018). "黃大仙紀律部隊宿舍 13歲女童墮樓殞命 父痛哭:點解會咁㗎 !". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- "灣景花園10歲男童用橡筋繩上吊亡". 蘋果日報 (in Chinese). 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- "被家人揭發兩年冇返學 理大女生吊頸亡". 東網. 2 November 2018.
- "12歲女墮樓壓搬屋貨車頂亡 遷居戶主求安心棄傢俬唔要". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- 陳諾希 (16 November 2018). "【學業壓力】科大畢業典禮 研究生高處墮下送院亡". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 16 November 2018.
- 鄧栢良 (14 December 2018). "【情侶墮海】24歲港大男生留醫4日不治 家人決定捐器官遺愛人間". 香港01 (in Chinese). Retrieved 17 December 2018.
- "港大情侶墮海男生死亡 女生搶救8日後亦告不治". on.cc東網 (in Chinese). Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- "大圍「名城」16歲男童疑學業問題 在家中墮下死亡". 經濟日報 (in Chinese). 6 January 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- "大埔中六男生疑不開心墮樓亡 2個月前檢查發現有情緒病". ToPick (in Chinese). 14 January 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- "16歲青年穿校服置富花園上吊亡" (in Chinese). 明報. 14 March 2019. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- "朗屏邨16歲中五生墮樓亡 家人傷心拜祭" (in Chinese). 蘋果日報. 15 March 2019. Retrieved 15 March 2019.
- Chan Hau-nung (27 Feb 2017) 從學生自殺說起:「學業決定論」與「社會整合論」
- HK01 (29 March 2017) DSE考核心科目下周開考 調查:考生壓力爆標多源自社會
- Halgin, Richard P.; Susan Whitbourne (January 2006). Abnormal Psychology with MindMap II CD-ROM and PowerWeb. McGraw-Hill. p. 62. ISBN 0-07-322872-9.
- Romeo Vitelill (August 2012). When Suicides Come in Clusters. Psychology Today..
- Hong Kong Commercial Daily (13 March 2013). 專家:自殺有模仿效應. Archived 1 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- HK01 (14 Dec 2016).誰來珍惜學童生命? 評《防止學生自殺委員會最終報告》
- "Helpline and Community Resources". Government of Hong Kong. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- "LC Urgent Q2: Alleviating the study pressure on students". Government of Hong Kong. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- "Education Sec. Eddie Ng says student suicide trend linked to poor life planning; report due at end of Oct | Hong Kong Free Press HKFP". Hong Kong Free Press HKFP. 15 October 2016. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- "政策正面睇" (in Chinese). Government of Hong Kong. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- berenicelau (28 August 2014). "The School Safety Team | Healthy School Policy (HSP)" (PDF). Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Education Bureau. (Aug 2015). Content
- Legislative Council Panel on Education. (Nov 2016). Final Report of the Committee on Prevention of Student Suicides
- SCMP (16 April 2016). To prevent student suicides, all of Hong Kong has to fight the battle – each and every day
- HKSAR Press Releases. (7 Nov 2016). Committee on Prevention of Student Suicides submits final report to SED.
- Legislative Council Panel on Education (7 January 2017). Follow-up Progress of the Final Report of the Committee on Prevention of Student Suicides.
- Ejinsight. (23 Oct 2017). Groups hold barefoot rally to highlight student suicide problem
- Secretary for Education. (24 June 2016). Education Bureau Circular Memorandum No. 91/2016 Information Kit and Leaflets on "Enhancing Life Resilience".
- Committee on Home-School Co-operation. Introduction
- Secretary for Education. (10 June 2016). Home-School Co-operation Grants.
- "Psychologists support Education Bureau's 'no suicide' student contracts | Hong Kong Free Press HKFP". Hong Kong Free Press HKFP. 15 March 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
- "University student takes her own life in third student suicide in four days | Hong Kong Free Press HKFP". Hong Kong Free Press HKFP. 21 December 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
- "Google, Facebook in talks to help Hong Kong avert youth suicide". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 20 November 2017.
- HK01 (7 Nov 2016).委員會提19項建議 吳克儉:學生自殺與教育系統無直接關係
- Ejinsight. (2nd, Feb 2017). 尊重死亡才能尊重生命:關於防止學童自殺報告.
- Ming Pao. (13 Oct 2017). 邵家臻﹕民間早促召開關注自殺峰會 林鄭﹕不太記得
- HKPTU. (8 Nov 2016). 教協會評《防止學生自殺委員會最終報告》不投入資源 不改善人手 不檢討制度 空談防止學童自殺
- "Cap hours Hong Kong pupils study to prevent teen suicide". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- "Prevention of Student Suicides". Government of Hong Kong. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- 教育局 (October 2010). "預防學生自殺資源套" (PDF): 29. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Government faces flak over approach to student suicides". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- "Tragic fall leaves son of education under secretary dead | Hong Kong | China Daily". www.chinadailyhk.com. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- "因是副局個仔先問候?港大學生會前會長轟偽善". Apple Daily (in Chinese). Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- "Education Bureau slams signs 'congratulating' education deputy's son following death | Hong Kong Free Press HKFP". Hong Kong Free Press HKFP. 8 September 2017. Retrieved 27 November 2017.