Zabbix
Zabbix is an open-source monitoring software tool for diverse IT components, including networks, servers, virtual machines (VMs) and cloud services. Zabbix provides monitoring metrics, among others network utilization, CPU load and disk space consumption. Zabbix monitoring configuration can be done using XML based templates which contain elements to monitor.[2] The software monitors operations on Linux, Hewlett Packard Unix (HP-UX), Mac OS X, Solaris and other operating systems (OSes); however, Windows monitoring is only possible through agents. Zabbix can use MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle or IBM DB2 to store data.[3] Its backend is written in C and the web frontend is written in PHP. Zabbix offers several monitoring options:
- Simple checks can verify the availability and responsiveness of standard services such as SMTP or HTTP without installing any software on the monitored host.
- A Zabbix agent can also be installed on UNIX and Windows hosts to monitor statistics such as CPU load, network utilization, disk space, etc.
- As an alternative to installing an agent on hosts, Zabbix includes support for monitoring via SNMP, TCP and ICMP checks, as well as over IPMI, JMX, SSH, Telnet and using custom parameters. Zabbix supports a variety of near-real-time notification mechanisms, including XMPP.
 | |
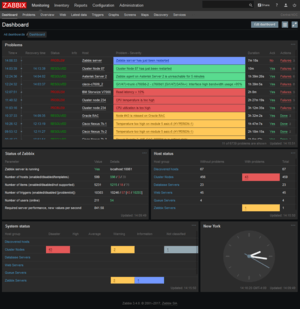 Zabbix 3.4.0 dashboard, dark theme | |
| Developer(s) | Zabbix LLC |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 2001 |
| Stable release | 5.0.2[1]
/ July 13, 2020 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C (server, proxy, agent), PHP (frontend), Java (Java gateway) |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Network management system |
| License | GPLv2 |
| Website | www |
Released under the terms of GNU General Public License version 2, Zabbix is free software.
History
Zabbix started as an internal software project in 1998. After three years, in 2001, it was released to the public under GPL,[4] three years later until the first stable version, 1.0, was released in 2004.
| Timeline of major releases | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Release | End of Full Support (3 years) | End of Limited Support (5 years) |
| Zabbix 1.0 | |||
| 1998 | Zabbix started as an internal project in a bank by Alexei Vladishev[4] | - | - |
| 7 Apr 2001 | Zabbix 1.0alpha1 is released as GPL[5] | - | - |
| 23 Mar 2004 | Zabbix 1.0 released[6] | - | |
| Zabbix 1.x | |||
| 6 Feb 2006 | Zabbix 1.1 released[6] | - | - |
| 29 May 2007 | Zabbix 1.4 released[6] | - | - |
| 11 Sep 2008 | Zabbix 1.6 released[6] | - | - |
| 7 Dec 2009 | Zabbix 1.8 released[6] | - | - |
| Zabbix 2.x | |||
| 21 May 2012 | Zabbix 2.0 Long Term Support (LTS) released[6] | August 2015 [7] | August 2017 [7] |
| 12 November 2013 | Zabbix 2.2 LTS released[6] | August 2017 [7] | August 2019 [7] |
| 11 Sep 2014 | Zabbix 2.4 released[6] | - | - |
| Zabbix 3.x | |||
| 16 Feb 2016 | Zabbix 3.0 LTS released[6] | February 28, 2019 [7] | February 28, 2021 [7] |
| 14 Sep 2016 | Zabbix 3.2 released[6] | - | - |
| 22 Aug 2017 | Zabbix 3.4 released[6] | - | - |
| Zabbix 4.x | |||
| 1 Oct 2018 | Zabbix 4.0 LTS released[8] | October 31, 2021 [7] | October 31, 2023 [7] |
| 2 Apr 2019 | Zabbix 4.2 released[9] | - | - |
| 7 Oct 2019 | Zabbix 4.4 released[10] | May 31, 2020 [7] | June 30, 2020 [7] |
| Zabbix 5.x | |||
| 12 May 2020 | Zabbix 5.0 LTS released[11] | May 31, 2023 [7] | May 31, 2025 [7] |
Features
- High performance, high capacity (able to monitor hundreds of thousands of devices).
- Auto-discovery of servers and network devices and interfaces.[12]
- Low-level discovery,[13] automatically starts monitoring new items, file systems or network interfaces among others.
- Distributed monitoring with centralized web administration.
- Native high performance agents (client software for Linux, Solaris, HP-UX, AIX, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, OS X, Tru64/OSF1, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7)
- SLA, and ITIL KPI metrics on reporting.
- High-level (business) view of monitored resources through user-defined visual console screens and dashboards.
- Remote command execution through Zabbix proxies since August 2017,[14] up to Zabbix 3.4[15]
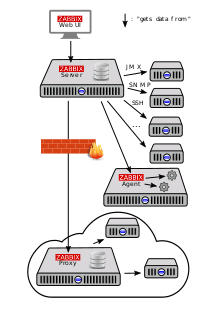
Architecture
- Agent or Agent-less monitoring capabilities.[16]
- Web-based interface.[17]
- Support for both polling and trapping mechanisms.
Monitoring
- JMX monitoring.
- Web monitoring.
Security and authentication
- Audit log.
- Secure user authentication.
- Flexible user permissions.
Notification capabilities
- Flexible e-mail notification on predefined events.
- Near-real-time notification mechanisms, for example using including XMPP protocol
Development
Zabbix is primarily developed by a Zabbix LLC company.
Source code
Zabbix consists of several separate modules:
- Zabbix Server, not supported in Windows,[18] performs the polling and trapping of data, calculates triggers and sends notifications to users, needs a database to store configurations and data.
- Zabbix Agents, installed on the system that is to be monitored to reach out values like CPU/memory usage that can only be accessed from within the OS
- Zabbix Frontend, web front-end used for setup, configuration and data browsing.
- Zabbix Proxy,[19] not supported in Windows, allows to access to systems that can't be reached directly and reduce load on Zabbix Server.[18]
While the server, proxy and agents are written in C, the front-end is implemented in PHP and JavaScript. A Java gateway is also available since Zabbix 2.0.
Releases
Since the first stable version was released as 1.0, Zabbix versioning has used minor version numbers to denote major releases. Each minor release actually implements many new features, while change level releases mostly introduce bugfixes.
Zabbix version numbering scheme has changed over time. While the first two stable branches were 1.0 and 1.1, after 1.1 it was decided to use odd numbers for development versions and even numbers for stable versions. As a result, 1.3 followed 1.1 as a development update to be released as 1.4.
References
- "Release Notes for Zabbix 5.0.2". Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/4.0/manual/config/templates
- List of supported databases in the manual
- Presentation, containing early history
- Freshmeat announcement page
- Zabbix release list
- https://www.zabbix.com/life_cycle_and_release_policy
- "Release Notes for Zabbix 4.0.0".
- "Release Notes for Zabbix 4.2.0".
- "Release Notes for Zabbix 4.4.0".
- "Release Notes for Zabbix 5.0.0".
- https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/current/manual/discovery/low_level_discovery/network_interfaces
- https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/current/manual/discovery/low_level_discovery
- https://www.zabbix.com/rn/rn3.4.0
- https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/3.4/manual/introduction/whatsnew340#remote_command_support_through_proxies
- https://www.zabbix.com/agentless_monitoring
- Di Francesco, Guillaume (28 November 2016). "Installation d'un serveur Zabbix 3.0.3" [Installing a Zabbix server 3.0.3] (html). Supinfo (in French). Retrieved 24 January 2020.
En ce sens, Zabbix est une solution de supervision libre permettant de surveiller des systèmes et des services précis par la génération de graphiques.
- https://www.zabbix.com/requirements
- https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/current/manual/concepts/proxy
- Vidmar, Anže (March 12, 2007). ZABBIX: State-of-the-art network monitoring Linux.com
- Ramm, Mark (March 15, 2005). The Watcher Knows, Linux Magazine
- Schroder, Carla (May 24, 2005). Monitor Your Net with Free, High-Performance ZABBIX, Enterprise Networking Planet
- ZABBIX - monitoring your applications, network and servers debianhelp.co.uk (Installation Instructions for Debian or Ubuntu Machines)
Further reading
- (2011) Zabbix 1.8 Network Monitoring - Packt Publishing ISBN 978-1-84719-768-9
- (2013) Mastering Zabbix - Packt Publishing ISBN 978-1-78328-349-1
- (2015) Zabbix Cookbook - Packt Publishing
- (2015) Zabbix Network Monitoring Essentials - Packt Publishing
- (2016) Zabbix Network Monitoring - Second Edition - Packt Publishing ISBN 9781782161288
External links
- Official website
- Zabbix Share, a Repository of Templates, Addons and Modules for Zabbix
- zabbix on GitHub