Wrench size
Width across flats is the distance between two parallel surfaces on the head of a screw or bolt, or a nut, mostly for torque transmission by positive locking.


The term width across flats (AF) is used for the following forms:
- 2-socket = round material with two surfaces
- 4-socket = profile square section
- 6-socket, 8-square = regular polygons
Spanner
The width across flats indicates the "size" of the spanner. It is imprinted on the spanners in millimeter (mm) values. Older English and current American spanners (wrenches) have inch sizes that are imprinted in intermediate sizes in fractions.
The two systems are in general not compatible, which can result in rounding of nuts and bolts (i.e. using a 13 mm spanner in place of a 1⁄2 in (12.7 mm)). There are some exceptions with a few sizes being close enough in sizes to interchange. This includes 19 mm and 3⁄4 in (19.05 mm), which are interchangeable for most purposes. Sizes that may interchange, depending on the precision needed, includes 2 mm (close to 5⁄64 in (1.98 mm)), 4 mm (close to 5⁄32 in (3.97 mm)) and 8 mm (close to 5⁄16 in (7.94 mm)).
Width across flats
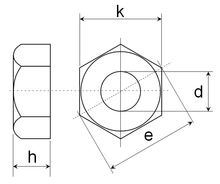
d: Nominal thread diameter
k: Wrench size (width across flats)
h: Thickness
e: Width across corners
The width across flats of the fastener (for example screws, nuts, clamps) is nominally the same as that on the tool. The table below shows dimensions of standard metric spanners:
| Nominal thread diameter (mm) | M1.6 | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M33 | M36 | M39 | M42 | |||||
| Width across flats (mm) | 3.2 | 4 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 34 | 36 | 41 | 46 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| DIN | ISO 272 |
|---|---|
| Area | fasteners |
| Last output | 1979-10 |
| ISO | 272 |
Widths for bicycles
In addition to industry standards, there are special thread standards, such as the bicycle threads according to DIN 79012, a fastening thread on metric-inch size basis of the designation. Modern bicycle spokes carry the bike thread FG 2.3.[1]