Willoughby Delta 8
The Willoughby Delta 8, or Delta F was a small twin-engined aerodynamic test bed for a proposed flying wing airliner - the Delta 9. The Delta 8 flew in the United Kingdom for a few months during 1939 before crashing; there were no developments.
| Delta 8 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Willoughby Delta, 1939 | |
| Role | Aerodynamic test aircraft |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | Willoughby Delta Company |
| Designer | Percival Willoughby |
| First flight | 11 March 1939 |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
From about 1937, the London-based Willoughby Delta Company was considering the construction of a flying wing airliner. The novelty of the design became apparent early in 1939: the Delta 9 was to be a tri-motor monoplane with a span of over 100 ft (30 m) with a thick and wide chord centre section, outboard of which the wing was thicker and much greater in chord, in part forming one of a pair of tail booms that carried the double finned empennage. Its trailing edge was at about 20° to the centre line, continuing forwards then turning through 70° to produce the trailing dge of the outer wing section. This was narrower in chord than the centre section. The Delta 9 was seen as a realistic approximation to a true flying wing, with its advantage of a well-distributed load because of the absence of parts like a fuselage which did not contribute to lift. There was also the intention of producing an aircraft that was essentially stall-free.[1]
Such an unusual design called for a lot of preparatory wind tunnel work, carried out in the UK at the National Physical Laboratory, the City & Guilds, Farnborough and Queen Mary College, London. Valuable pressure distribution measurements were made in the United States at the Guggenheim Institute of New York University. The results were encouraging, producing for example curves of lift coefficient versus angle of incidence that increased linearly in the normal way and then flattened without the usual decrease in lift associated with the stall. It appeared that, at high speed and low angles the forward part of the wing provided most of the lift, but as the stall approached the rear part contributed more. These results encouraged the company to build the Willoughby Delta 8 to investigate the general aerodynamics of the layout with a smaller aeroplane.[1] The exact name seems to be uncertain: the contemporary (February 1939) Flight article[1] calls it Delta 8, in line with the airliner named as Delta 9, but the registration documents from that January[2] refer to the Delta F and the latter name has been widely used. The design had first been announced in Flight in 1937 as the Delta F.[3] Certainly the Delta 8 was not a scale model of the proposed airliner, but the arrangement of its lifting surfaces was similar.[1]
A twin-engined aircraft constructed of wood, the Delta 8 looked at first sight rather like a conventional pod and twin boom machine. It had a central nacelle, almost elliptical in profile, suspended beneath the wing and containing the glazed cabin. This had tandem seats, accessed via a starboard side door. The wings were built around two conventional transverse spars, unusual only in becoming deeper between the outer boundary of the centre section and the inboard limit of the narrow chord outer sections. The latter carried ailerons over the whole of its trailing edges. The longitudinal spars of the "side wings", acting as booms, slipped into slots cut into the transverse wing spars. On each side, three longitudinal and very long chord ribs, plus a stiffening diagonal rib that ran to the rear end of the side wing, formed the aerofoil section of these wings. The transverse section of the side wings was also aerofoil shaped, blunt on the inner edge and fine outboard.[1][4]
Two 125 hp (93 kW) Menasco Pirate C.4 four-cylinder air-cooled inline engines driving two-bladed propellers were mounted against the underside of the wing in steel cradles, at the points where the wing thickness increased. There was a wooden fairing behind, through which ran, to the front spar, the cantilever fixed main undercarriage legs, faired and spatted. The tailplane joined the rearmost inner edges of the side wings, carrying the tailwheel at its centre, and a broad elevator hinged clear of the rest of the structure. Small fins mounted over the tailplane carried balanced rudders, their overall profile almost triangular. The fins were externally braced to the tailplane.[1]
Delta 9
The Delta 9 as described in Flight was expected to carry 36 passengers in two side wing cabins for a gross weight of 38,000 lb on three 1,000 hp engines. The cabins were expected to have at least a 6-foot headroom but lacked side windows.
Operational history
The Delta first flew on 11 March 1939, registered as G-AFPX.[2][5] On 14 May 1939, piloted by A.N. Kingwill, it was demonstrated at the Royal Aeronautical Society's garden party fly-in at Great West Aerodrome, also at Heston Aerodrome.[4][6] On 10 July 1939, it crashed near Bicester, killing the pilot Hugh Olley and the Delta's designer, Percival Willoughby. The crash was not attributed to the novel configuration but to an ill-designed elevator trim tab that sent the Delta into a dive.[4] Nonetheless, with the death of the designer and the coming of war, no more was heard of this type of flying wing.
Specifications
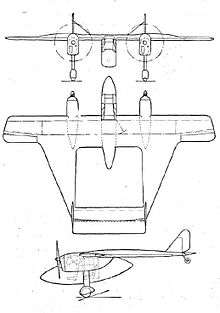
Data from Ord-Hume 2000, p. 500
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 26 ft 1 in (7.95 m)
- Wingspan: 34 ft 6 in (10.52 m)
- Empty weight: 1,585 lb (719 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,350 lb (1,066 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Menasco Pirate C.4 4-cylinder air-cooled inline inverted piston, 125 hp (93 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 183 mph (295 km/h, 159 kn)
- Cruise speed: 165 mph (266 km/h, 143 kn)
- Stall speed: 60 mph (97 km/h, 52 kn)
- Range: 340 mi (550 km, 300 nmi)
Notes
References
- Jackson, A.J. (1974). British Civil Aircraft since 1919 Volume 3. London: Putnam. ISBN 0-370-10014-X.
- Ord-Hume, Arthur W.J.G. (2000). British Light Aeroplanes. Peterborough: GMS Enterprises. ISBN 1-870384-76-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Delaying the stall". Flight. 9 February 1939.
External links
YouTube The Delta 8 flies from Heston