William Becknell
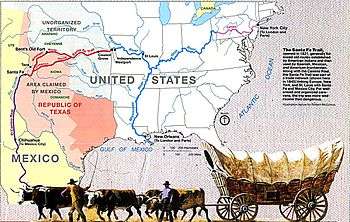
William Becknell (1787 or 1788 – April 30, 1865) was an American soldier, politician, and freight operator who is credited by Americans with opening the Santa Fe Trail in 1821. He found a trail for part of the route that was wide enough for wagon trains and draft teams, making it easier for trader and emigrants along this route. The Santa Fe Trail became an early major transportation route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri with Santa Fe, New Mexico, serving both trading and emigrant parties. It served as a vital commercial highway from the 1820s until 1880, when the railroad was introduced to Santa Fe. Becknell made use of long-established trails made by Native Americans, and Spanish and French colonial explorers and traders for centuries before his trip.
William Becknell | |
|---|---|
| Born | 1787 or 1788 |
| Died | (aged 76–78) |
| Resting place | Private family plot off US 82 west of Clarksville, Texas |
French colonists in St. Louis had a monopoly on trade with Santa Fe, which was granted by the Spanish crown before the Louisiana Purchase. When Mexico achieved independence from Spain in 1821, it opened up trade to its territories; residents of Santa Fe were eager for more trade goods. In 1822, Becknell altered his route to Santa Fe in order to find a trail more suitable for wagon trains so that he could enable transport of more trade goods. Earlier travelers had ridden on horseback, trailing packhorses. By 1825, he assisted a surveyor with the federal government in mapping the trail, so that it could be available for commercial and military use.
Early life
William Alexander Becknell was born in the Rockfish Creek area of Amherst County, Virginia to parents Micajah and Pheby (Landrum) Becknell. Conflicting sources say his year of birth was 1787 or 1788.[1] Young Becknell's father and grandfather were veterans of the American Revolution, as were two uncles who died in the war.[2]
Becknell married Jane Trusler in 1807 in Virginia. In 1810 the young family migrated to the new Missouri Territory, homesteading west of present-day St. Charles. During the War of 1812, Becknell served in the United States Mounted Rangers under Captain Daniel Morgan Boone, a son of the famed explorer. He participated in several engagements, including the Battle of Credit Island and the defense of Fort Clemson, near St. Louis. In the latter engagement, he took control of the defense after senior officers fell. For this he was promoted to the rank of Captain, and was long known as Captain Becknell.[2] Following his discharge from Federal service in June 1815, Becknell moved west to the area known as the Boonslick in central Missouri along the Missouri River.[3]
Jane Becknell died of unknown circumstance, possibly in childbirth, around the time of her husband's military discharge. In January 1817 the widower married again, to Mary Cribb. According to U.S. Census Bureau records, Becknell was the father of at least five children in total: Mary Jane born in 1815, John Calhoun born in 1817, William Alexander Jr. also born in 1817, Lucy born in 1818, and Cornelia born in 1827.[2] Becknell supported his family by working as a ferryman on the Missouri river and by managing the Boone's Lick Salt Works. In early 1820 he purchased 180 acres in Howard County, Missouri and moved the family there.[1]
Trailblazer
In 1821 Becknell faced substantial debt.[1] He had bought out the Boone family interest in the aforementioned salt works around 1818. In 1820 he ran unsuccessfully for the Missouri Legislature, having borrowed money to finance the campaign. The Panic of 1819 took its toll on his business activities by limiting the amount of credit and hard currency available. Owing creditors more than $1,200 dollars ($20,000 in today's money), Becknell was briefly jailed until a friend posted bail. The judge in the case gave Becknell until early 1822 to pay his creditors or face more jail time.[2]
Under pressure, Becknell left Franklin in September 1821 on an extended trading trip, including hunting and trapping for furs, as the fur trade was still lucrative. He bought $300 worth of trade goods for his trip. According to an advertisement Becknell placed in the Missouri Intelligencer newspaper, his intent was "for the purpose of trading for horses and mules and catching wild animals of every description."[3] Becknell and his group were not the only ones searching for a convenient trade route to Santa Fe, but that fall they were the first to reach the city, in mid-November 1821.[1] Becknell's timing was near perfect.
Mexico had recently become independent of Spain. It lifted the ban against trade with outsiders. French colonists from St. Louis had traded with Santa Fe when both were still under Spanish rule before the Louisiana Purchase. The Chouteau brothers of St. Louis had been given a monopoly with the Spanish for trade in Santa Fe, and this trade contributed greatly to the wealth of the city on the Mississippi River.
The people of Santa Fe were eager for the variety of goods which Becknell offered from his string of pack horses. They were willing to pay high prices: some cotton cloth and calico brought the then-unheard of sum of three dollars a yard. After a month of trading, Becknell and his party left Santa Fe on December 13 with their saddlebags overflowing with silver.[4] His investment of $300 in trading goods had returned approximately $6000 in coin.[2]
Reaching Missouri in January 1822, Becknell almost immediately began planning his next trading trip to Santa Fe. For his second journey, he chose to haul trade goods by wagon instead of pack horse. He had to slightly alter his original route in order to accommodate the width of wagons and draft teams. The wagon train left Franklin in May 1822 and suffered considerable hardship, with both animals and people nearly dying of thirst in the parched Cimarron Desert. The 'train' arrived in Santa Fe forty-eight days later. The second trip proved to be even more profitable than the first. Taking an estimated $3,000 in goods to Santa Fe, Becknell's party returned with a profit of around $91,000 dollars. They paid some of that total as dividends to shareholders who had helped fund the trip, and even the smallest investor reaped great returns.[2]
Becknell made a third profitable trip to Santa Fe in 1824. The following year in 1825, he helped map the trail for surveyors hired by the U.S. Congress. For his efforts in opening up an improved route for regular traffic and military movement, William Becknell became known as the Father of the Santa Fe Trail
Later life
In 1827 Becknell was appointed as a Justice of the Peace for Saline County, Missouri. The following year he was elected to the first of two terms in the Missouri House of Representatives. Retaining his rank of Captain, Becknell served in the Missouri state militia during a Native American uprising in 1829 and again during the 1832 Black Hawk War.
In 1835 Becknell sold all his Missouri property and business interests and moved to present-day Red River County, Texas in northeast Texas. During the Texas War of Independence, Becknell organized and led a cavalry unit known as the Red River Blues. Later he would serve briefly as a Texas Ranger. He was also elected as a member of the legislature in the newly established Republic of Texas.
Becknell died on April 30, 1865, at his home. He is buried in a private family cemetery. US 82 passes by the site a few miles west of Clarksville, Texas.[5]
References
- Dictionary of Missouri Biography, Lawrence O. Christensen, University of Missouri Press, 1999.
- "The Life of William Becknell". Allan Wheeler. 2012. Retrieved 12 July 2012.
- "Becknell, William biography". Oklahoma Historical Society website. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- "Captain Wm. Becknell". Kansas Genealogy Society. 2002. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- Browning, James A. Violence Was No Stranger (1993). Barbed Wire Press. ISBN 0-935269-11-8.
External links
- William Becknell from the Handbook of Texas Online
- William Becknell and the Santa Fe Trail
- Santa Fe Trail Research
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
- Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture - Becknell, William
- Santa Fe Trail Association