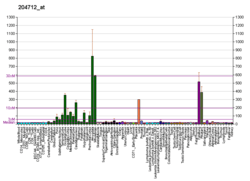
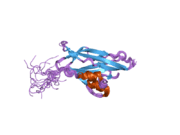
WIF1
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WIF1 gene.[5] WIF1 is a lipid-binding protein that binds to Wnt proteins and prevents them from triggering signalling.[6][7][8]
Function
WNT proteins are extracellular signaling molecules involved in the control of embryonic development. This gene encodes a secreted protein, which binds WNT proteins and inhibits their activities. This protein contains a WNT inhibitory factor (WIF) domain and 5 epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains. It may be involved in mesoderm segmentation. This protein is found to be present in fish, amphibia and mammals.[5]
gollark: More effective than most AVs since it actually hooks into OS functionality.
gollark: PotatOS has built in antivirus.
gollark: Yes, sort of.
gollark: UFW is just a firewall configuration interface.
gollark: Or you can use PotatoAV™.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000156076 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020218 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: WIF1 WNT inhibitory factor 1".
- Malinauskas T, Aricescu AR, Lu W, Siebold C, Jones EY (July 2011). "Modular mechanism of Wnt signaling inhibition by Wnt inhibitory factor 1". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 18 (8): 886–893. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2081. PMC 3430870. PMID 21743455.
- Malinauskas T (2008). "Docking of fatty acids into the WIF domain of the human Wnt inhibitory factor-1". Lipids. 43 (3): 227–30. doi:10.1007/s11745-007-3144-3. PMID 18256869.
- Hsieh JC, Kodjabachian L, Rebbert ML, Rattner A, Smallwood PM, Samos CH, Nusse R, Dawid IB, Nathans J (Apr 1999). "A new secreted protein that binds to Wnt proteins and inhibits their activities". Nature. 398 (6726): 431–6. doi:10.1038/18899. PMID 10201374.
Further reading
- Shepelev MV, Korobko EV, Korobko IV (2006). "[WIF1: perspectives of application in oncology]". Mol. Gen. Mikrobiol. Virusol. (4): 3–7. PMID 17094650.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Reguart N, He B, Xu Z, et al. (2004). "Cloning and characterization of the promoter of human Wnt inhibitory factor-1". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 323 (1): 229–34. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.075. PMID 15351726.
- Esufali S, Bapat B (2004). "Cross-talk between Rac1 GTPase and dysregulated Wnt signaling pathway leads to cellular redistribution of beta-catenin and TCF/LEF-mediated transcriptional activation". Oncogene. 23 (50): 8260–71. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208007. PMID 15377999.
- Ohigashi T, Mizuno R, Nakashima J, et al. (2005). "Inhibition of Wnt signaling downregulates Akt activity and induces chemosensitivity in PTEN-mutated prostate cancer cells". Prostate. 62 (1): 61–8. doi:10.1002/pros.20117. PMID 15389810.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Simon M, Grandage VL, Linch DC, Khwaja A (2005). "Constitutive activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway in acute myeloid leukaemia". Oncogene. 24 (14): 2410–20. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208431. PMID 15735743.
- Taniguchi H, Yamamoto H, Hirata T, et al. (2005). "Frequent epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in human gastrointestinal cancers". Oncogene. 24 (53): 7946–52. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208910. PMID 16007117.
- Lin YC, You L, Xu Z, et al. (2006). "Wnt signaling activation and WIF-1 silencing in nasopharyngeal cancer cell lines". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 341 (2): 635–40. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.220. PMID 16427602.
- Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, et al. (2006). "Epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 plays an important role in bladder cancer through aberrant canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway". Clin. Cancer Res. 12 (2): 383–91. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1344. PMID 16428476.
- Liepinsh E, Bányai L, Patthy L, Otting G (2006). "NMR structure of the WIF domain of the human Wnt-inhibitory factor-1". J. Mol. Biol. 357 (3): 942–50. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.047. PMID 16476441.
- Batra S, Shi Y, Kuchenbecker KM, et al. (2006). "Wnt inhibitory factor-1, a Wnt antagonist, is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in malignant pleural mesothelioma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 342 (4): 1228–32. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.084. PMID 16516163.
- Chim CS, Chan WW, Pang A, Kwong YL (2006). "Preferential methylation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia: an independent poor prognostic factor". Leukemia. 20 (5): 907–9. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404176. PMID 16525492.
- Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, et al. (2006). "Combination analysis of hypermethylated Wnt-antagonist family genes as a novel epigenetic biomarker panel for bladder cancer detection". Clin. Cancer Res. 12 (7 Pt 1): 2109–16. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2468. PMID 16609023.
- Milutinovic S, D'Alessio AC, Detich N, Szyf M (2007). "Valproate induces widespread epigenetic reprogramming which involves demethylation of specific genes". Carcinogenesis. 28 (3): 560–71. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl167. PMID 17012225.
- Queimado L, Lopes CS, Reis AM (2007). "WIF1, an inhibitor of the Wnt pathway, is rearranged in salivary gland tumors". Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 46 (3): 215–25. doi:10.1002/gcc.20402. PMID 17171686.
- Chan SL, Cui Y, van Hasselt A, et al. (2007). "The tumor suppressor Wnt inhibitory factor 1 is frequently methylated in nasopharyngeal and esophageal carcinomas". Lab. Invest. 87 (7): 644–50. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700547. PMID 17384664.
- Veeck J, Wild PJ, Fuchs T, et al. (2009). "Prognostic relevance of Wnt-inhibitory factor-1 (WIF1) and Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) promoter methylation in human breast cancer". BMC Cancer. 9: 1–13. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-217. PMC 2717119. PMID 19570204.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.