Vitex pinnata
Vitex pinnata is a tree of the family Lamiaceae, native to south and south east Asia. It is a slow growing tree, growing up to 20 metres with 1–3 m. circumference trunk that has a grey-brown-yellow bark; its leaves are scented.
| Vitex pinnata | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Vitex |
| Species: | V. pinnata |
| Binomial name | |
| Vitex pinnata | |
General description
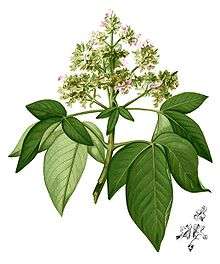
Bark fissured, flaky, pale yellowish grey to brown; inner bark pale yellow becoming green on exposure; sapwood soft yellow to brown. Leaves 3- or 5-foliolate. Leaflets almost sessile, outer two usually much smaller than the others, ovate or elliptic, 3–25 cm long, 1.5–10 cm wide; base rounded to slightly wedge-shaped; apex acuminate; margin entire; secondary veins 10—20 pairs; Inflorescences terminal panicles; Flowers whitish blue. Fruits 5–8 mm in diameter; ripening black [1]
Distribution
Indo-Malaysia covered Borneo; Sabah, Sarawak and all provinces of Kalimantan.[2] Indonesia, North to India, Sri Lanka and Cambodia. In the Philippines this species is only known from the islands of Palawan, Culion and Tawi- Tawi [3]
Taxonomy
Vitex pinnata has many depreciated synonyms, including Vitex pubescens and Vitex arborea.[4]
Ecology
Growing well usually in secondary forests, on riverbanks and along roads including in marginal land such as Imperata cylindrica area.[5][6] The species seemingly tolerates regular fires. In tropic condition such as in East Kalimantan, flowering and fruiting are almost all the time from January to December. The fruits are eaten by birds and seeds cannot germinate under the shade and need light to germinate.[7]
Uses

Vitex pinnata has a very strong and durable wood, it is durable even in contact with water or soil. It is a grayish brown in color. Density is about 930 kg per cubic metre (58 lbs per cubic foot). Wood is used for posts, door and window frames, sleepers and some furniture.
The wood is used for construction and the manufacture of knife handles. Leaves and bark are used to treat abdominal pain, fever and malaria.
Conservation status
Least concern.[8]
Propagation

Vitex pinnata can be propagated by seeds, cuttings and wildlings. One kilogram seeds of Vitex pinnata are around 1100-1200 seeds.[9]
Sources
- Timber and it uses by forest department Sri Lanka in 1962.
References
- Keßler, P.J.A., 2000. A Manual to 300 selected species. Secondary forest trees of Kalimantan, Indonesia. Tropenbos Kalimantan series 3, 198
- Keßler, P.J.A., 2000. A Manual to 300 selected species. Secondary forest trees of Kalimantan, Indonesia. Tropenbos Kalimantan series 3, 198
- De Kok, R., 2008. The genus Vitex (Labiatae) in the flora Malesiana region, excluding New Guinea. KEW Bulletin. Vol 63, 17-40.
- de Kok, Rogier. 2008. The genus Vitex (Labiatae) in the Flora Malesiana region, excluding New Guinea. Kew Bulletin, 63: 17-40, doi:10.1007/s12225-007-9013-7
- Keßler, P.J.A., 2000. A Manual to 300 selected species. Secondary forest trees of Kalimantan, Indonesia. Tropenbos Kalimantan series 3, 198
- Yassir, I., Van der Kamp, J., Buurman, P., 2010. Secondary succession after fire in Imperata grasslands of East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 137: 172-18.
- Yassir, I., Van der Kamp, J., Buurman, P., 2010. Secondary succession after fire in Imperata grasslands of East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 137: 172-18.
- De Kok, R., 2008. The genus Vitex (Labiatae) in the flora Malesiana region, excluding New Guinea. KEW Bulletin. Vol 63, 17-40.
- Yassir, I. and Mulyana, O., 2009. Selection of tree species potential to support restoration activities in ex-coal mining site through an ecological approach. Proseding Workshop IPTEK Penyelamatan Hutan melalui Rehabilatasi Lahan Bekas Tambang Batubara. Balai Besar Penelitian Dipterokarpa. Samarinda. East Kalimantan.
