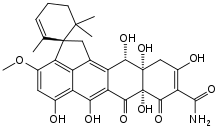
Viridicatumtoxin A
Viridicatumtoxin A (also simply called viridicatumtoxin) is a fungus-derived tetracycline-like antibiotic, whose chemical structure was determined in 1976.[1][2] It is found in Penicillium viridicatum,[1] Penicillium aethiopicum,[2] among other fungi.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,7a'S,11a'S,12'S)-5',6',7a',10',11a',12'-Hexahydroxy-3'-methoxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-7',8'-dioxo-7',7a',8',11',11a',12'-hexahydro-1'H-spiro[cyclohex-2-ene-1,2'-cyclopenta[de]tetracene]-9'-carboxamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H31NO10 | |
| Molar mass | 565.575 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Like viridicatumtoxin B, viridicatumtoxin A inhibits growth of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin resistant S. aureus and quinolone-resistant S. aureus, with an activity 8 to 64 times greater than that of tetracycline.[2]
References
- Raju, M. S.; Wu, G.-S.; Gard, A.; Rosazza, J. P. (1982). "Microbial Transformations of Natural Antitumor Agents. 20. Glucosylation of Viridicatumtoxin". Journal of Natural Products. 45 (3): 321. doi:10.1021/np50021a014.
- Chooi, Yit-Heng; Cacho, Ralph; Tang, Yi (2010). "Identification of the Viridicatumtoxin and Griseofulvin Gene Clusters from Penicillium aethiopicum". Chemistry & Biology. 17 (5): 483. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.03.015. PMC 2884005. PMID 20534346.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.