Vinyl ester resin
Vinyl ester resin, or often just vinyl ester, is a resin produced by the esterification of an epoxy resin with acrylic or methacrylic acids.[1] The "vinyl" groups refer to these ester substituents, which are prone to polymerize. The diester product is then dissolved in a reactive solvent, such as styrene, to approximately 35–45 percent content by weight. Polymerization is initiated by free radicals, which are generated by UV-irradiation or peroxides.
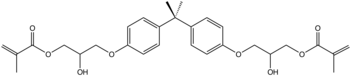
This thermoset material can be used as an alternative to polyester and epoxy materials as the thermoset polymer matrix in composite materials, where its characteristics, strengths, and bulk cost are intermediate between polyester and epoxy. Vinyl ester has lower resin viscosity (approx 200 cps) than polyester (approx 500cps) and epoxy (approx 900cps).
In homebuilt airplanes, the Glasair and Glastar kit planes made extensive use of vinylester fiberglass-reinforced structures. It is a common resin in the marine industry due to its corrosion resistance and ability to withstand water absorption. Vinyl ester resin is extensively used to manufacture FRP tanks and vessels as per BS4994. For laminating process, vinyl ester is usually initiated with methyl ethyl ketone peroxide. It has greater strength and mechanical properties than polyester and less than epoxy resin.
Renewable precursors to vinyl ester resins have been developed.[2]
Vinyl resins are often used in repair materials and laminating because it is waterproof and reliable.
References
- Pham, Ha Q.; Marks, Maurice J. (2012). "Epoxy Resins". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_547.pub2.
- Santosh K. Yadav, Kevin M. Schmalbach, Emre Kinaci, Joseph F. Stanzione III, Giuseppe R. Palmese (2018). "Recent advances in plant-based vinyl ester resins and reactive diluents". European Polymer Journal: 199–215. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.11.002.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ResinNavigator.org's Epoxy-based vinyl esters benefits