Velocity triangle
In turbomachinery, a velocity triangle or a velocity diagram is a triangle representing the various components of velocities of the working fluid in a turbomachine. Velocity triangles may be drawn for both the inlet and outlet sections of any turbomachine. The vector nature of velocity is utilized in the triangles, and the most basic form of a velocity triangle consists of the tangential velocity, the absolute velocity and the relative velocity of the fluid making up three sides of the triangle.
Velocities involved
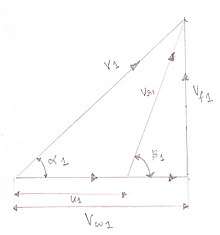
An example of a velocity triangle drawn for the inlet of a turbomachine. The "1" subscript denotes the high pressure side (inlet in case of turbines and outlet in case of pumps/compressors).
A general velocity triangle consists of the following vectors:[1][2]
- V : Absolute velocity of the fluid.
- U : Blade Linear velocity.
- Vr: Relative velocity of the fluid after contact with rotor.
- Vw: Tangential component of V (absolute velocity), called Whirl velocity.
- Vf: Flow velocity (axial component in case of axial machines, radial component in case of radial machines).
The following angles are encountered during the analysis:
- α: Angle made by V with the plane of the machine (usually the nozzle angle or the guide blade angle).
- β: Angle of the rotor blade. Absolute angle
gollark: Nvidia has the highest-end GPUs, sure, but most of the time what actually matters is what the best GPU which fits within your budget is.
gollark: I can't tell if you're being jokey or not.
gollark: This post made by intel HD 620 graphics gang, which I guess is technically a GPU but not a dedicated one.
gollark: Imagine having a GPU.
gollark: Unless the macros are just done in software on the computer itself.
References
- Venkanna, B.K. (2011). Fundamentals of Turbomachinery. Prentice Hall India. ISBN 978-81-203-3775-6.
- Govinde Gowda, M.S. (2011). A Text book of Turbomachines. Davangere: MM Publishers.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.