Uplistsikhe
Uplistsikhe (Georgian: უფლისციხე [upʰlistsʰixɛ]; literally, "the lord's fortress") is an ancient rock-hewn town in eastern Georgia, some 10 kilometers east of the town of Gori, Shida Kartli.
Built on a high rocky left bank of the Mtkvari River, it contains various structures dating from the Early Iron Age to the Late Middle Ages, and is notable for the unique combination of various styles of rock-cut cultures from Anatolia and Iran, as well as the co-existence of pagan and Christian architecture.[1]
History
Uplistsikhe is identified by archaeologists as one of the oldest urban settlements in Georgia. Strategically located in the heartland of ancient kingdom of Kartli (or Iberia as it was known to the Classical authors), it emerged as a major political and religious center of the country. The town's age and importance led medieval Georgian written tradition to ascribe its foundation to the mythical Uplos, son of Mtskhetos, and grandson of Kartlos.[1]
The earliest traces of human presence in Uplistsikhe date back to the end of the 2nd millennium BC. Its earliest remaining structures are from the beginning of the 1st millennium AD. With the Christianization of Kartli early in the 4th century, Uplistsikhe seems to have declined in its importance and lost its position to the new centers of Christian culture – Mtskheta and, later Tbilisi. Meanwhile, it continued to develop as a town. The first Christina basilica was constructed in the 6th century. However, Uplistsikhe reemerged as a principal Georgian stronghold during the Muslim conquest of Tbilisi in the 8th-10th centuries. Another, three-church basilica was constructed at that time. The Mongol raids in the 14th century marked the ultimate eclipse of the town; it was virtually abandoned, and only occasionally used as a temporary shelter in times of foreign intrusions.[1]
Architecture

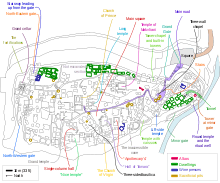
The town was cut into a flat, straight, but slightly inclining mountain. Nearly straight western wall went down to the river. Outside protection of the town was also facilitated by two motes, northern and eastern, with wall built into them. The river itself closed access to the town from the south, but it was possible to get into the town through a 3 m tunnel that functioned as water supply. The tunnel was closed by metal gate in case of invasion. Two of the three roads that approached the town were not protected, but the third, coming from the north, was cut in rock, with up to 10 m high walls[2].
The Uplistsikhe complex can tentatively be divided into three parts: south (lower), middle (central) and north (upper) covering an area of approximately 8 hectares. The middle part is the largest, contains a bulk of the Uplistsikhe rock-cut structures, and is connected to the southern part via a narrow rock-cut pass and a tunnel. Narrow alleys and sometimes staircases radiate from the central "street" to the different structures.[1] Th southern part has a complex of structures. Among them a ceremonial hall is the most notable.
A pillar hall with two adjacent rooms is one of the most important structures in the town. Its ceiling was supported by two pillars. A stone bench, probably, served as a ruler's seat.
The majority of the caves are devoid of any decorations, although some of the larger structures have coffered tunnel-vaulted ceilings, with the stone carved in imitation of logs. Some of the larger structures also have niches in the back or sides, which may have been used for ceremonial purposes. The facade of the large ceremonial hall of the southern part is decorated by the Roman type arch with pediment.
The 6th century basilica was largely cut into the rock, except its southern wall, built from the rocks. At the summit of the complex is a Christian basilica built of stone and brick in the 9th-10th centuries. Archaeological excavations have discovered numerous artifacts of different periods, including gold, silver and bronze jewellery, and samples of ceramics and sculptures. Many of these artifacts are in the safekeeping of the National Museum in Tbilisi.
Several parts of the most vulnerable areas were completely destroyed by an earthquake in 1920. The stability of the monument remains under substantial threat, prompting the Fund of Cultural Heritage of Georgia (a joint project of the World Bank and Government of Georgia) to launch a limited program of conservation in 2000.[3] The Uplistsikhe cave complex has been on the tentative list for inclusion into the UNESCO World Heritage program since 2007.
Notes
- Khimshiashvili (1999), Online version Archived 2004-08-18 at the Wayback Machine.
- Zakaraya, P. (1983) Pamyatniki Vostochnoi Gruzii. Iskusstvo, Moskva, 376 p. (In Russian) [Monuments of the Eastern Georgia]
- Georgia – ICOMOS World Report on Monuments and Sites in Danger 2001. Accessed on November 23, 2007.
References
- Khimshiashvili, Kakha (1999). The Architecture of. Uphlistsikhe, Georgia. Transactions of the Ancient Monuments Society 43, pp. 77–100.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Uplistsikhe. |