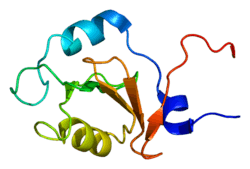
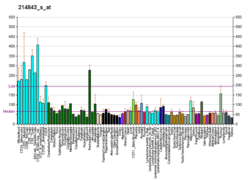
USP33
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 33 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP33 gene.[5][6]
Interactions
USP33 has been shown to interact with DIO2,[7] SELENBP1[8] and Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor.[9]
gollark: They're very cool tech.
gollark: Actually, it's just orbital mind control lasers at low power.
gollark: I dislike the fact that this person apparently doesn't know how screenshots work.
gollark: Oh, this is part of an implementation of a blockchain for some reason? Interesting.
gollark: Oh, Jupyter, right. Still weird.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000077254 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025437 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Puente XS, Sánchez LM, Overall CM, López-Otín C (Jul 2003). "Human and mouse proteases: a comparative genomic approach". Nat Rev Genet. 4 (7): 544–558. doi:10.1038/nrg1111. PMID 12838346.
- "Entrez Gene: USP33 ubiquitin specific peptidase 33".
- Curcio-Morelli C, Zavacki AM, Christofollete M, Gereben B, de Freitas BC, Harney JW, Li Z, Wu G, Bianco AC (Jul 2003). "Deubiquitination of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase by von Hippel-Lindau protein-interacting deubiquitinating enzymes regulates thyroid hormone activation". J. Clin. Invest. 112 (2): 189–196. doi:10.1172/JCI18348. PMC 164294. PMID 12865408.
- Jeong JY, Wang Y, Sytkowski AJ (Feb 2009). "Human selenium binding protein-1 (hSP56) interacts with VDU1 in a selenium-dependent manner". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 379 (2): 583–588. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.12.110. PMID 19118533.
- Li Z, Na X, Wang D, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (Feb 2002). "Ubiquitination of a novel deubiquitinating enzyme requires direct binding to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (7): 4656–4662. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108269200. PMID 11739384.
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–174. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–156. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Kikuno R, Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Hirosawa M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XIV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 6 (3): 197–205. doi:10.1093/dnares/6.3.197. PMID 10470851.
- Li Z, Na X, Wang D, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (2002). "Ubiquitination of a novel deubiquitinating enzyme requires direct binding to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (7): 4656–4662. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108269200. PMID 11739384.
- Li Z, Wang D, Na X, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (2002). "Identification of a deubiquitinating enzyme subfamily as substrates of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294 (3): 700–709. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00534-X. PMID 12056827.
- Curcio-Morelli C, Zavacki AM, Christofollete M, Gereben B, de Freitas BC, Harney JW, Li Z, Wu G, Bianco AC (2003). "Deubiquitination of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase by von Hippel-Lindau protein-interacting deubiquitinating enzymes regulates thyroid hormone activation". J. Clin. Invest. 112 (2): 189–196. doi:10.1172/JCI18348. PMC 164294. PMID 12865408.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–1178. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Allen MD, Bycroft M (2007). "The solution structure of the ZnF UBP domain of USP33/VDU1". Protein Sci. 16 (9): 2072–2075. doi:10.1110/ps.072967807. PMC 2206988. PMID 17766394.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.