U0126
U0126 is a highly selective inhibitor of both MEK1 and MEK2, a type of MAPK/ERK kinase.[1][2] U0126 was found to functionally antagonize AP-1 transcriptional activity via noncompetitive inhibition of the dual specificity kinase MEK with IC50 of 72 nM for MEK1 and 58 nM for MEK2. U0126 inhibited anchorage-independent growth of Ki-ras-transformed rat fibroblasts by simultaneously blocking both extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-p70(S6K) pathways.[3] The effects of U0126 on the growth of eight human breast cancer cell lines shown that U0126 selectively repressed anchorage-independent growth of MDA-MB231 and HBC4 cells, two lines with constitutively activated ERK.[4] Loss of contact with substratum triggers apoptosis in many normal cell types, a phenomenon termed anoikis. U0126 sensitized MDA-MB231 and HBC4 to anoikis, i.e., upon treatment with U0126, cells deprived of anchorage entered apoptosis.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
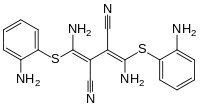
| Formula | C18H16N6S2 |
| Molar mass | 380.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
U0126 is also a weak inhibitor of PKC, Raf, ERK, JNK, MEKK, MKK-3, MKK-4/SEK, MKK-6, Cdk2 and Cdk4.
Its potential for wiping long-term memories in rats has been studied at the Center for Neural Science at New York University.[5]
See also
References
- Favata, M., et al., Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 18623, (1998)
- DeSilva, D., et al., Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase blocks T cell proliferation but does not induce or prevent anergy. J. Immunol. 160, 4175, (1998)
- Duncia, J.V., et al., MEK inhibitors: The chemistry and biological activity of U0126, its analogs, and cyclization products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 8, 2839-2844, (1998)
- Fukazawa, H., et al., Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors restore anoikis sensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines with a constitutively activated extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther., 303-309, (2002)
- Smith, Kerri (2007-03-11). "Wipe out a single memory". Nature Magazine. Retrieved 2017-12-31.