Trimethylgallium
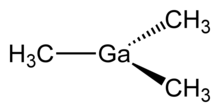
Trimethylgallium, often abbreviated to TMG or TMGa, is the organogallium compound with the formula Ga(CH3)3. It is a colorless, pyrophoric liquid.[1] Unlike aluminium trichloride, but akin to trimethylindium, TMG is monomeric.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trimethylgallane, trimethanidogallium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.452 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ga(CH3)3 | |
| Molar mass | 114.827 g/mol |
| Appearance | clear colourless liquid |
| Melting point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) |
| Boiling point | 55.7 °C (132.3 °F; 328.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | pyrophoric |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
TMG is prepared by the reaction of gallium trichloride with methyl lithium.[1] Trimethylgallium may also be prepared by the reaction of dimethylzinc with gallium trichloride. The less volatile diethyl ether adduct can be prepared by using methylmagnesium iodide in ether in place of dimethylzinc; the ether ligands may be displaced with liquid ammonia as well.[3]
Applications
TMG is the preferred metalorganic source of gallium for metalorganic vapour phase epitaxy (MOVPE) of gallium-containing compound semiconductors, such as GaAs, GaN, GaP, GaSb, InGaAs, InGaN, AlGaInP, InGaP and AlInGaNP.[4] These material are used in the production of LED lighting and semiconductors as a metalorganic chemical vapor deposition precursor.
References
- Bradley, D. C.; Chudzynska, H. C.; Harding, I. S. (1997). "Trimethylindium and Trimethylgallium". Inorganic Syntheses. 31: 67–74. doi:10.1002/9780470132623.ch8.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Kraus, C. A.; Toonder, F. E. (1933). "Trimethyl Gallium, Trimethyl Gallium Etherate and Trimethyl Gallium Ammine". PNAS. 19 (3): 292–8. Bibcode:1933PNAS...19..292K. doi:10.1073/pnas.19.3.292. PMC 1085965. PMID 16577510.
- Shenai-Khatkhate, D. V.; Goyette, R. J.; Dicarlo, R. L. Jr; Dripps, G. (2004). "Environment, health and safety issues for sources used in MOVPE growth of compound semiconductors". Journal of Crystal Growth. 272 (1–4): 816–21. Bibcode:2004JCrGr.272..816S. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2004.09.007.