Trilogy of Fallot
The Trilogy of Fallot is a rare congenital heart disease consisting of the following defects: pulmonary valve stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy and atrial septal defect. This disease is 1.6-1.8% of all congenital heart defects.
| Trilogy of Fallot | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Mechanism
Trilogy of Fallot is a combination of three congenital heart defects: pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an atrial septal defect.
The first two of these are also found in the more common tetralogy of Fallot. However, the tetralogy has a ventricular septal defect instead of an atrial one, and it also involves


Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
an overriding aorta.
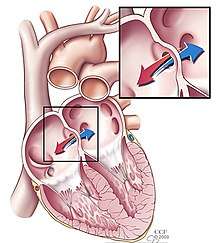
The Three Malformations
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary Stenosis | A malformation near or on the pulmonary valve (the valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery) that causes the opening of the valve to be narrowed, affecting blood flow. This narrowing can occur when one or more of the cusps is too thick or is otherwise defective, preventing the valve from opening fully and properly. [1] |
| Right Ventricular Hypertrophy | The right ventricle is more muscular than normal, causing a characteristic boot-shaped appearance as seen by chest X-ray. This enlargement is generally a secondary condition, resulting from increased pressure. Pulmonary valve defects resulting in tricuspid regurgitation, a common effect of pulmonary stenosis, can cause this increase in muscle mass.[2] |
| Atrial Septal Defect | An atrial septal defect is a hole in the septum that divides the right and left atria (the upper two chambers) of the heart. In the heart of a developing fetus, there are several holes between the atria, however these are expected to close before birth. This congenital condition arises if one of these holes remains. [3] Depending on the severity of the defect, it may need to be repaired surgically, as a significant defect can cause further damage to the heart and lungs.[4] |
Diagnosis
Clinically trilogy of Fallot can have cardiomegaly, less symptomatic when compared to ToF, JVP increased, a wave is more elevated, delayed P2, apex beat will be of LV type. S4+, ejection click+, On doing Cath, RV angiogram, when RV is flicked, to create a RV ectopic, there is post ectopic potentiation of the murmur, unlike ToF
Treatment
Thoracotomy is used to surgically correct this pathology.[5]
History
It is named in honor of its discoverer: Etienne Fallot.[6]
References
- "Pulmonary valve stenosis - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- Bhattacharya, Priyanka T.; Sharma, Sandeep (2020), "Right Ventricular Hypertrophy", StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 29763051, retrieved 2020-04-14
- CDC (2019-11-19). "Congenital Heart Defects - Facts about Atrial Septal Defects | CDC". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- "Atrial septal defect (ASD) - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- Wang YQ, Chen RK, Ye WW, et al. (1999). "Open-heart surgery in 48 patients via a small right anterolateral thoracotomy". Tex Heart Inst J. 26 (2): 124–8. PMC 325616. PMID 10397435.
- synd/2283 at Who Named It?