Triethylindium
Triethylindium is an olorganic chemical compound from the group of organometallic compounds. Its chemical formula is C
6H
15In.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Triethylindium | |
| Other names
Indium triethyl, triethylindigane, indiumtriethyl, TEI, TEIn | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.905 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H15In | |
| Molar mass | 202.004 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 144 °C (291 °F; 417 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  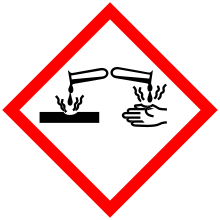 |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H250, H314 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Indium triethyl can be obtained by reacting an ether solution of indium(III) chloride with ethyl magnesium chloride.
InCl
3 + 3C
2H
5MgCl → In(C2H5)3 + 3MgCl
2
Other syntheses are also known.[3]
Properties
Indium triethyl is a colorless, toxic, oxidation and hydrolysis-sensitive liquid. It is a monomer in the gaseous and dissolved state. The compound reacts with halomethanes to diethyl indium halides.[4]
Triethylindium is highly reactive with water:
In(C2H5)3 + H
2O → In(C2H5)2OH + C
2H
6↑
Applications
Indium triethyl is used to prepare indium phosphide layers for semiconductors.[5]
gollark: As such, Windows 10 will schedule threads suboptimally.
gollark: Intel's new Alder Lake architecture has multiple core types and a fancy scheduler microcontroller thing, proper support for which will only be in Windows 11.
gollark: MS is also forcing Win11 via the Alder Lake scheduler changes.
gollark: https://appuals.com/create-offline-local-user-account-windows-11/
gollark: > a philosophical debate about the meaning of life?42> linux? Quite possibly.> how windows bad?Windows 11 no longer has offline accounts.> randomly aquired knowledge?Platypi are apparently rather bright in UV, and have venomous spurs.
See also
References
- "INDIUM TRIETHYL". chemicalbook.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- "Substance Name: Indium, triethyl". chem.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- Cowley, Alan H. (2009). Inorganic Syntheses. John Wiley & Sons. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-470-13297-5.
- Maeda, Takayoshi; Tada, Hisashi; Yasuda, Kiyoshi; Okawara, Rokuro (11 September 1970). "Reactions of triethylindium with halomethanes: preparations and properties of diethylindium halides". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 27 (1): 13–18. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)82987-3.
- Sakaki, H.; Woo, J.C.; Yokoyama, N.; Harayama, Y. (1999). Compound Semiconductors: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors held in Nara, Japan, 12-16 October 1998. CRC Press. p. 529. ISBN 978-0750306119.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.