Transversion
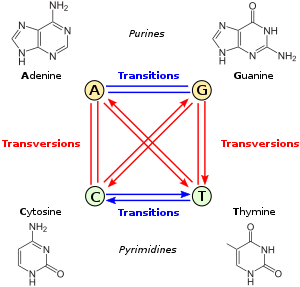
Transversion, in molecular biology, refers to a point mutation in DNA in which a single (two ring) purine (A or G) is changed for a (one ring) pyrimidine (T or C), or vice versa.[1] A transversion can be spontaneous, or it can be caused by ionizing radiation or alkylating agents. It can only be reversed by a spontaneous reversion.
Ratio of transitions to transversions
Although there are two possible transversions but only one possible transition, transition mutations are more likely than transversions because substituting a single ring structure for another single ring structure is more likely than substituting a double ring for a single ring. Also, transitions are less likely to result in amino acid substitutions (due to wobble base pair), and are therefore more likely to persist as "silent substitutions" in populations as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).[2] A transversion usually has a more pronounced effect than a transition because the third nucleotide codon position of the DNA, which to a large extent is responsible for the degeneracy of the code, is more tolerant of transition than a transversion: that is, a transition is more likely to encode for the same amino acid.
Spontaneous germline transversion
8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG) is an oxidized derivative of deoxyguanosine, and is one of the major products of DNA oxidation. During DNA replication in the germ line of mice, the oxidized base 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) causes spontaneous and heritable G to T transversion mutations.[3] These mutations occur in different stages of the germ cell lineage and are distributed throughout the chromosomes.
See also
- Transition
- Aristolochic acid, a natural plant chemical causing A → T and T → A transversions in humans
References
- Futuyma, D.J. (2013). Evolution (3rd ed.). Sinauer. ISBN 978-1605351155.
- Diagram at mun.ca
- Ohno M, Sakumi K, Fukumura R, Furuichi M, Iwasaki Y, Hokama M, Ikemura T, Tsuzuki T, Gondo Y, Nakabeppu Y (2014). "8-oxoguanine causes spontaneous de novo germline mutations in mice". Sci Rep. 4: 4689. doi:10.1038/srep04689. PMC 3986730. PMID 24732879.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Transversion. |
- Carr, Steven M. "Transition versus Transversion mutations". Memorial University of Newfoundland.
- Nikolay's Genetics Lessons (2014). Transition versus Transversion mutations (how to memorize). Youtube.