Tralles (crater)
Tralles is an irregular lunar impact crater that is attached to the northwestern rim of the much larger crater Cleomedes, in the northeastern part of the Moon. Within one crater diameter to the northwest is Debes. The crater is named after the German mathematician and physicist Johann Georg Tralles.[1]
 Lunar Orbiter 4 image | |
| Coordinates | 28.4°N 52.8°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 43 km |
| Depth | 3.4 km |
| Colongitude | 308° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Johann G. Tralles |
This is an oddly shaped crater formation with an irregular perimeter. The rugged interior has the appearance of three overlapping craters, with one at the south end, a second to the northeast and a third to the northwest. There are also several tiny craterlets located within the jumbled inner surface.
Satellite craters
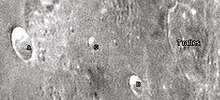
Tralles crater and its satellite craters taken from Earth in 2012 at the University of Hertfordshire's Bayfordbury Observatory with the telescopes Meade LX200 14" and Lumenera Skynyx 2-1
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Tralles.
| Tralles | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 27.5° N | 47.0° E | 18 km |
| B | 27.3° N | 50.6° E | 11 km |
| C | 27.8° N | 49.4° E | 7 km |
gollark: ++exec --debug```pythonhi```
gollark: ++exec --debug```pythonhi```
gollark: ++exec --debug```pythonhi```
gollark: ++exec```pythonhi```
gollark: ++exec```pythonhi```
References
- "Tralles (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tralles (crater). |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.