Three-field system
The three-field system is a regime of crop rotation that was used in medieval and early-modern Europe. Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons.
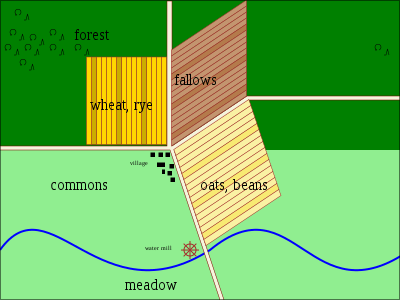
The three-field system let farmers plant more crops and therefore increase production. Under this system, the arable land of an estate or village was divided into three large fields: one was planted in the autumn with winter wheat or rye; the second field was planted with other crops such as peas, lentils, or beans; and the third was left fallow (unplanted). Cereal crops deplete the ground of nitrogen, but legumes can fix nitrogen and so fertilize the soil. The fallow fields were soon overgrown with weeds and used for grazing farm animals. Their excrement fertilized that field's soil to regain its nutrients. Crop assignments were rotated every year, so each field segment would be planted for two out of every three years.
Previously a two-field system had been in place, with half the land being left fallow. With more crops available to sell and agriculture dominating the economy at the time, the three-field system created a significant surplus and increased economic prosperity.[1]
The three-field system needed more plowing of land and its introduction coincided with the adoption of the moldboard plow. These parallel developments complemented each other and increased agricultural productivity. The legume crop needed summer rain to succeed, and so the three-field system was less successful around the Mediterranean. Oats for horse food could also be planted in the spring, which, combined with the adoption of horse collars and horseshoes, led to replacement of oxen by horses for many farming tasks, with an associated increase in agricultural productivity and the nutrition available to the population.[2]
One of the first Germans to question this system, and new ways of expanding beyond this medieval system was Johann Friedrich Mayer, in his 1769 work Lehre vom Gyps als vorzueglich guten Dung zu allen Erd-Gewaechsen auf Aeckern und Wiesen, Hopfen- und Weinbergen.[3]
References
- Noble, Thomas (2002). (33)
|chapter-format=requires|chapter-url=(help). The foundations of Western civilization. Chantilly, VA: Teaching Co. ISBN 978-1565856370. - Wigelsworth, Jeffrey R. (2006). Science and technology in medieval European life. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 10.
- Roeber, A. G. (1998). Palatines, Liberty, and Property: German Lutherans in Colonial German America. p. 58.