Thiouric acid
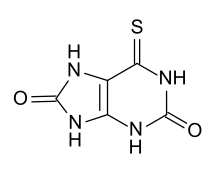
Thiouric acid, more accurately called 6-thiouric acid, is a main inactive metabolite of the immunosuppressive drugs azathioprine, mercaptopurine and tioguanine.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6-Thioxo-7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,8(3H,6H)-dione | |
| Other names
6-Thiouric acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4N4O2S | |
| Molar mass | 184.17 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Mutschler, Ernst; Schäfer-Korting, Monika (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. pp. 107, 936. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- Ansari, A; Aslam, Z; De Sica, A; Smith, M; Gilshenan, K; Fairbanks, L; Marinaki, A; Sanderson, J; Duley, J (2008). "Influence of xanthine oxidase on thiopurine metabolism in Crohn's disease". Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 28 (6): 749–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03768.x. PMID 18557988.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.