Tarsonemidae
Tarsonemidae is a family of mites, also called thread-footed mites or white mites.
| Tarsonemidae | |
|---|---|
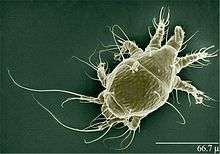 | |
| Acarapis woodi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: | Tarsonemoidea |
| Family: | Tarsonemidae Kramer, 1877 |
| Diversity | |
| 45 genera, > 500 species | |
Only a limited number of tarsonemid genera (Steneotarsonemus, Polyphagotarsonemus, Phytonemus, Floridotarsonemus and Tarsonemus) are known to feed on higher plants while most species in this family feed on the thin-walled mycelia of fungi or possibly algal bodies.[1] Even among the plant-feeding tarsonemid mites, most are confined to areas of new growth where cell walls are thin and therefore easily pierced. However two species (the "broad mite" Polyphagotarsonemus latus and the "cyclamen mite" Steneotarsonemus pallidus) are able to feed on older leaves because of their ability to inject toxins during feeding (presumably of salivary gland origin) causing an increase of thin walled cells surrounding feeding sites.[1] This proliferation of new growth often results in leaves that appear stunted, puckered and twisted.[1]
Taxonomy
Subdivision[2]
- Subfamily Pseudotarsonemoidinae
- Tribe Tarsonemellini
- Tribe Pseudotarsonemoidini
- Subfamily Acarapinae
- Tribe Coreitarsonemini
- Subfamily Tarsoneminae
- Tribe Hemitarsonemini
- Tribe Steneotarsonemini
- Tribe Tarsonemini
- Tribe Pseudacarapin
Selected genera
- Acarapis
- Floridotarsonemus
- Phytonemus
- Polyphagotarsonemus
- Steneotarsonemus
- Tarsonemus
Control
While little pest management research has been done on the majority of tarsonemid species, comprehensive studies have been made into the biological and chemical control of the cyclamen mite and the broad mite. Chemical trials demonstrated that endosulfan and dicofol consistently reduced densities of P. latus and S. pallidus,[3] and planting stock can be effectively decontaminated through fumigation with methyl bromide or 1,2-dibromoethane.[1] Three entomogenous fungi, Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae, and Paecilomyces fumosoroseus, can effectively manage broad mite infestations, with B. bassiana providing the greatest reduction.[4] Predatory phytoseiid mites, in the genus Neoseiulus, can also successfully control P. latus and S. pallidus under greenhouse and field conditions.[5][6]
References
- L. R. Jeppson, Hartford H. Keifer & Edward William Baker (1975). "The Tarsonemidae Kramer". Mites injurious to economic plants. University of California Press. pp. 285–306. ISBN 978-0-520-02381-9.
- JIANZHEN LIN & ZHI-QIANG ZHANG. Tarsonemidae of the World. 2002
- G. Sterk, G. E. Bal, W. Goossens & D. Bylemans (1997). "Semi-field and field experience in the control of the strawberry mite, Tarsonemus pallidus (Banks) (Acarina: Tarsonemidae)". Parasitica. 53 (1): 25–33.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- I. Nugroho & Y. Ibrahim (2004). "Laboratory bioassay of some entomopathogenic fungi against broad mite". Journal of Agricultural Biology. 6 (2): 223 225.
- B. A. Croft, P. D. Pratt, G. Koskela & D. Kaufman (1998). "Predation, reproduction, and impact of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on cyclamen mite (Acari: Tarsonemidae) on strawberry". Journal of Economic Entomology. 91 (6): 1307 1314.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- P. G. Weintraub & E. Palevsky (2003). "Distribution and diel movement of the predatory mite, Neoseiulus cucumeris, on greenhouse sweet pepper – preliminary study". IOBC/WPRS Bulletin. 26: 89–94.
External links
- Joel Hallan's Biology Catalog: Tarsonemidae
- cyclamen mite, Phytonemus pallidus on the University of Florida / Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Featured Creatures website
- Dr. Eddie Ueckermann. TAXONOMY OF TARSONEMIDAE. ARC
