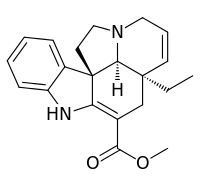
Tabersonine
Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus. Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzyme tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H) to form 16-hydroxytabersonine.[1] The enzyme leading to its formation is currently unknown. Tabersonine is the first intermediate leading to the formation of vindoline one of the two precursors required for vinblastine biosynthesis.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl (5α,12β,19α)-2,3,6,7-tetradehydroaspidospermidine-3-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.378 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 336.435 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- St-Pierre and De Luca (1995) A Cytochrome P-450 Monooxygenase Catalyzes the First Step in the Conversion of Tabersonine to Vindoline in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiology. 109(1). 131-139
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.