TADA3L
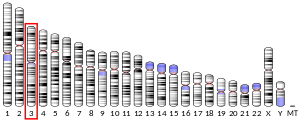
Transcriptional adapter 3-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TADA3 gene.[4][5][6] Cytogenetic location: 3p25.3 [7]
Function
Many DNA-binding transcriptional activator proteins enhance the initiation rate of RNA polymerase II-mediated gene transcription by interacting functionally with the general transcription machinery bound at the basal promoter. Adaptor proteins are usually required for this activation, possibly to acetylate and destabilize nucleosomes, thereby relieving chromatin constraints at the promoter. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional activator adaptor and has been found to be part of the PCAF histone acetylase complex. In addition, it associates with the tumor suppressor protein p53 and is required for full activity of p53 and p53-mediated apoptosis. At least four alternatively spliced variants have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been determined.[6]
Interactions
TADA3L has been shown to interact with:
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000171148 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Ogryzko VV, Kotani T, Zhang X, Schiltz RL, Howard T, Yang XJ, Howard BH, Qin J, Nakatani Y (Jul 1998). "Histone-like TAFs within the PCAF histone acetylase complex". Cell. 94 (1): 35–44. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81219-2. PMID 9674425.
- Wang T, Kobayashi T, Takimoto R, Denes AE, Snyder EL, el-Deiry WS, Brachmann RK (Nov 2001). "hADA3 is required for p53 activity". The EMBO Journal. 20 (22): 6404–13. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.22.6404. PMC 125723. PMID 11707411.
- "Entrez Gene: TADA3L transcriptional adaptor 3 (NGG1 homolog, yeast)-like".
- Sulimova G, Kutsenko A, Rakhmanaliev E, Udina I, Kompaniytsev A, Protopopov A, Moisjak E, Klimov E, Muravenko O, Zelenin A, Braga E, Kashuba V, Zabarovsky E, Kisselev L (2002). "Human chromosome 3: integration of 60 NotI clones into a physical and gene map". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 98: 177–183. doi:10.1159/000069814. PMID 12698000.
- Zeng M, Kumar A, Meng G, Gao Q, Dimri G, Wazer D, Band H, Band V (Nov 2002). "Human papilloma virus 16 E6 oncoprotein inhibits retinoic X receptor-mediated transactivation by targeting human ADA3 coactivator". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (47): 45611–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208447200. PMID 12235159.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Martinez E, Palhan VB, Tjernberg A, Lymar ES, Gamper AM, Kundu TK, Chait BT, Roeder RG (Oct 2001). "Human STAGA complex is a chromatin-acetylating transcription coactivator that interacts with pre-mRNA splicing and DNA damage-binding factors in vivo". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (20): 6782–95. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.20.6782-6795.2001. PMC 99856. PMID 11564863.
Further reading
- Struhl K, Moqtaderi Z (Jul 1998). "The TAFs in the HAT". Cell. 94 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81213-1. PMID 9674419.
- Brand M, Yamamoto K, Staub A, Tora L (Jun 1999). "Identification of TATA-binding protein-free TAFII-containing complex subunits suggests a role in nucleosome acetylation and signal transduction". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (26): 18285–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.26.18285. PMID 10373431.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (Nov 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (Mar 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, Pepperkok R, Wiemann S (Sep 2000). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Reports. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Brand M, Moggs JG, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Lejeune F, Dilworth FJ, Stevenin J, Almouzni G, Tora L (Jun 2001). "UV-damaged DNA-binding protein in the TFTC complex links DNA damage recognition to nucleosome acetylation". The EMBO Journal. 20 (12): 3187–96. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.12.3187. PMC 150203. PMID 11406595.
- Martinez E, Palhan VB, Tjernberg A, Lymar ES, Gamper AM, Kundu TK, Chait BT, Roeder RG (Oct 2001). "Human STAGA complex is a chromatin-acetylating transcription coactivator that interacts with pre-mRNA splicing and DNA damage-binding factors in vivo". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (20): 6782–95. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.20.6782-6795.2001. PMC 99856. PMID 11564863.
- Benecke A, Gaudon C, Garnier JM, vom Baur E, Chambon P, Losson R (Jun 2002). "ADA3-containing complexes associate with estrogen receptor alpha". Nucleic Acids Research. 30 (11): 2508–14. doi:10.1093/nar/30.11.2508. PMC 117179. PMID 12034840.
- Kumar A, Zhao Y, Meng G, Zeng M, Srinivasan S, Delmolino LM, Gao Q, Dimri G, Weber GF, Wazer DE, Band H, Band V (Aug 2002). "Human papillomavirus oncoprotein E6 inactivates the transcriptional coactivator human ADA3". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 22 (16): 5801–12. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.16.5801-5812.2002. PMC 133989. PMID 12138191.
- Zeng M, Kumar A, Meng G, Gao Q, Dimri G, Wazer D, Band H, Band V (Nov 2002). "Human papilloma virus 16 E6 oncoprotein inhibits retinoic X receptor-mediated transactivation by targeting human ADA3 coactivator". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (47): 45611–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208447200. PMID 12235159.
- Goehler H, Lalowski M, Stelzl U, Waelter S, Stroedicke M, Worm U, Droege A, Lindenberg KS, Knoblich M, Haenig C, Herbst M, Suopanki J, Scherzinger E, Abraham C, Bauer B, Hasenbank R, Fritzsche A, Ludewig AH, Büssow K, Buessow K, Coleman SH, Gutekunst CA, Landwehrmeyer BG, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (Sep 2004). "A protein interaction network links GIT1, an enhancer of huntingtin aggregation, to Huntington's disease". Molecular Cell. 15 (6): 853–65. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.016. PMID 15383276.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, Bechtel S, Sauermann M, Korf U, Pepperkok R, Sültmann H, Poustka A (Oct 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Meng G, Zhao Y, Nag A, Zeng M, Dimri G, Gao Q, Wazer DE, Kumar R, Band H, Band V (Dec 2004). "Human ADA3 binds to estrogen receptor (ER) and functions as a coactivator for ER-mediated transactivation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (52): 54230–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404482200. PMID 15496419.