Envelope (music)
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. It may relate to elements such as amplitude (volume), filters (frequencies) or pitch. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero.
Envelope generators, which allow users to control the different stages of a sound, are common features of synthesizers, samplers, and other electronic musical instruments. The most common form of envelope generator is controlled with four parameters: attack, decay, sustain and release (ADSR).
Development
The Hammond Novachord in 1938 used an early implementation of an ADSR envelope. A seven-position rotary knob set preset ADS parameter for all 72 notes; a pedal controls the release.[1]
The envelope generator was created by the American engineer Robert Moog in the 1960s. While experimenting with the first Moog synthesizers, composer Herbert Deutsch suggested Moog find a way to articulate the instrument so notes did not simply trigger on and off. Moog wired a doorbell button to the synthesizer and used a capacitor to store and slowly release voltage produced from hitting a key. He refined the design to remove the need to push a separate button with every keypress, with two switches on every key: one to produce the control voltage determining pitch and the other to trigger the envelope generator. The envelope generator became a standard feature of synthesizers.[2]
Following discussions with engineer and composer Vladimir Ussachevsky (then head of the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center) in 1965, Moog developed a new envelope module whose functions were described in f T1 (attack time), T2 (initial decay time), ESUS (sustain level), and T3 (final decay time). These were later simplified to the modern ADSR form (Attack time, Decay time, Sustain level, Release time) by ARP.[2]
ADSR
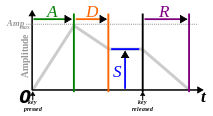
The most common kind of envelope generator has four stages: attack, decay, sustain, and release (ADSR).[3]
- Attack is the time taken for initial run-up of level from nil to peak, beginning when the key is pressed.
- Decay is the time taken for the subsequent run down from the attack level to the designated sustain level.
- Sustain is the level during the main sequence of the sound's duration, until the key is released.
- Release is the time taken for the level to decay from the sustain level to zero after the key is released.[4]
While, attack, decay, and release refer to time, sustain refers to level.[3]
Other envelopes
Some electronic musical instruments can invert the ADSR envelope, reversing the behavior of the normal ADSR envelope. During the attack phase, the modulated sound parameter fades from the maximum amplitude to zero then, during the decay phase, rises to the value specified by the sustain parameter. After the key has been released the sound parameter rises from sustain amplitude back to maximum amplitude.
.jpg)
Some envelopes, such as that of the Korg MS-20, have an extra parameter, hold. This holds notes at the sustain level for a fixed length of time before decaying. The General Instruments AY-3-8912 sound chip includes only a hold time parameter; the sustain level is not programmable.
Another common variation in the same vein is the AHDSR (attack, hold, decay, sustain, release) envelope, in which the "hold" parameter controls how long the envelope stays at full volume before entering the decay phase. Multiple attack, decay and release settings may be found on more sophisticated models.
Certain synthesizers also allow for a delay parameter before the attack. Modern synthesizers, such as the Prophet '08, have DADSR (delay, attack, decay, sustain, release) envelopes. The delay setting determines the length of silence between hitting a note and the attack. Some software synthesizers, such as Image-Line's 3xOSC (included with their DAW FL Studio) have DAHDSR (delay, attack, hold, decay, sustain, release) envelopes.
A common feature on many synthesizers is an AD envelope (attack and decay only). This can be used to control e.g. the pitch of one oscillator,[5] which in turn may be synchronized with another oscillator by oscillator sync.
See also
References
- Cirocco, Phil (2006). "The Novachord Restoration Project". Cirocco Modular Synthesizers.
- Pinch, Trevor; Trocco, Frank (2004). Analog Days: The Invention and Impact of the Moog Synthesizer. Harvard University Press. pp. 43. ISBN 978-0-674-01617-0.
- Vail, Mark (2014). The Synthesizer: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Programming, Playing, and Recording the Ultimate Electronic Music Instrument. OUP USA. ISBN 9780195394894.
- "How to use basic ADSR filter envelope parameters". MusicRadar. June 21, 2013. Retrieved 2018-12-16.
- Synthesizer technique. H. Leonard Books. 1987. p. 64.