Sucumbíos Province
Sucumbíos (Spanish pronunciation: [sukumˈbi.os]) is a province in northeast Ecuador. The capital and largest city is Nueva Loja (normally referred to as Lago Agrio). It is the fifth largest province in the country, with an area of 18,084 km². In 2010, it had a population of 176,472 inhabitants.
Sucumbios | |
|---|---|
Province | |
| Province of Sucumbios | |
 Flag | |
.svg.png) Location of Sucumbíos Province in Ecuador. | |
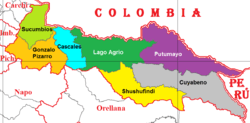 Cantons of Sucumbíos Province | |
| Country | Ecuador |
| Established | February 11, 1989. |
| Capital | Nueva Loja |
| Cantons | List of Cantons |
| Government | |
| • Type | Provincial |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18,084.42 km2 (6,982.43 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 176,472 |
| • Density | 9.8/km2 (25/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 50,198 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (ECT) |
| Vehicle registration | K |
| HDI (2017) | 0.716[2] high · 18th |
| Website | www |
Geography
Sucumbíos is bounded on the north by Colombia, on the south by Napo and Orellana, on the west by Carchi and Imbabura, on the southwest by Pichincha, and on the east by Peru. Sucumbíos is the only province in Ecuador that borders two different countries.
The province is one of the six provinces in the Amazon Region, a natural region of Ecuador.
Orography
The western area of the province belongs to the Eastern Andes Mountains, where most rivers in the province have their sources. The most important elevation in the province is the Reventador, an active volcano. The eastern portion of the province is part of the Amazon Basin, with high temperatures.
Hydrography
The main river in the province is the Aguarico River. It passes close to Nueva Loja, and empties into the Napo, on the Peruvian border. Other important rivers are the Putumayo, which marks the border with Colombia, and the Coca and Napo Rivers, in the south.
History
Sucumbíos was an unexplored area, where only indigenous people lived, until oil was discovered in its soil. In 1979, after nine years of foundation, Nueva Loja became the seat of its own canton, Lago Agrio Canton, in the Napo Province. On February 13, 1989, Sucumbíos became the 21st province in the country when it separated from Napo province.
Economy
The most important natural resource in the province is oil, the Lago Agrio oil field. Thus, Sucumbíos is one of the most important provinces in the country, economically.
Political division
The province is divided into seven cantons. The following table lists each with its population at the 2001 census, its area in square kilometres (km²), and the name of the canton seat or capital.[3]
| Canton | Pop. (2019) | Area (km²) | Seat/Capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascales | 15,390 | 1,248 | El Dorado de Cascales |
| Cuyabeno | 7,200 | 3,875 | Tarapoa |
| Gonzalo Pizarro | 9,910 | 2,223 | Lumbaqui |
| Lago Agrio | 117,050 | 3,139 | Nueva Loja (Lago Agrio) |
| Putumayo | 15,450 | 3,559 | Puerto Carmen |
| Shushufindi | 56,700 | 2,463 | Shushufindi |
| Sucumbíos | 3,790 | 1,502 | La Bonita |
Places of interest
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sucumbíos Province. |
- http://www.inec.gob.ec/preliminares/base_presentacion.html
- Villalba, Juan. "Human Development Index in Ecuador". Scribd (in Spanish). Retrieved 2019-02-05.
- Cantons of Ecuador. Statoids.com. Retrieved 4 November 2009.