Stearoyl-CoA
Stearoyl-CoA is a coenzyme involved in the metabolism of fatty acids.[1] Stearoyl-CoA is an 18-carbon long fatty acyl-CoA chain that participates in an unsaturation reaction. The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme stearoyl-CoA desaturase, which is located in the endoplasmic reticulum.[2] It forms a cis-double bond between the ninth and tenth carbons within the chain to form the product oleoyl-CoA.[3]
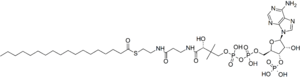 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
S-Stearoylcoenzyme A, Stearyl-CoA, Octadecanoyl-coenzyme A, Octadecanoyl-CoA, stearyl coenzyme A | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.045 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H70N7O17P3S | |
| Molar mass | 1034.00 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Ntambi, J. M. (2002). "Loss of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 function protects mice against adiposity". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (17): 11482–11486. doi:10.1073/pnas.132384699. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 123282. PMID 12177411.
- Ntambi, James (2013). Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase Genes in Lipid Metabolism. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-7969-7.
- Igal, R. Ariel (December 2016). "Stearoyl CoA desaturase-1: New insights into a central regulator ofcancer metabolism". Elsevier. 1861: 1865–1880.
Bibliography
- Miyazaki, M. (2000). "The Biosynthesis of Hepatic Cholesterol Esters and Triglycerides Is Impaired in Mice with a Disruption of the Gene for Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (39): 30132–30138. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005488200. PMID 10899171.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.