Statine
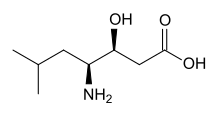
Statine is a gamma amino acid that occurs twice in the sequence of pepstatin, a protease inhibitor that is active against pepsin and other acid proteases.[1] It is thought to be responsible for the inhibitory activity of pepstatin because it mimics the tetrahedral transition state of peptide catalysis.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,4S)-4-amino-3-hydroxy-6-methylheptanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | AHMHA, Sta |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.428 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H17NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 175.228 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Umezawa, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Morishima, H.; Matsuzaki, M.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. (1970). "Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes". The Journal of Antibiotics. 23 (5): 259–262. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. PMID 4912600.
- Marciniszyn Jr, J.; Hartsuck, J. A.; Tang, J. (1976). "Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 251 (22): 7088–7094. PMID 993206.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.