Skarkos
Skarkos (Greek: Σκάρκος) is an early Bronze Age settlement on the island of Ios in Greece. Owing to its well preserved state, Skarkos is one of the most important prehistoric sites in the Aegean and especially the Cyclades.[1][2]

Geography
Ios, with one of the most sheltered natural harbours in the Cyclades, is located at the crossroads of Cycladic maritime routes. The settlement of Skarkos is situated on a hill in the middle of the west side of Ios, in proximity to the island’s most fertile plains and to its harbour.
Excavations
Skarkos was systematically excavated during the years 1984-1997. The excavations have been carried out in the north and east sides of the hill. They have brought to light an important early Cycladic settlement (mid-3rd millennium BC) in an exceptionally good state of preservation (two-storey buildings, four-metre-high walls), and an overlying late middle/early late Bronze Age cemetery (mid-2nd millennium BC). The settlement covers an area of 1.1 hectares and is the largest and best preserved site of the Keros-Syros culture, estimated to have been home to between 200 and 300 people.[3]
Architecture
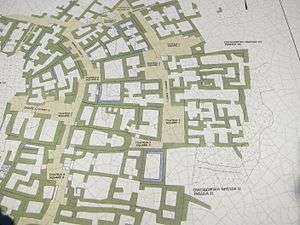
Skarkos is built on terraces that follow the natural relief of the hill. Its rectangular, stone-built residential buildings consist of a ground floor, a first floor and an enclosed courtyard. Their varying sizes reveal a social differentiation in the community. Streets between one and two meters wide and public spaces were uncovered. Walls are preserved to a height of three to four meters.[3] The urban planning system of Skarkos is comparable to that of Poliochne on Lemnos from the beginning of the 3rd millennium BC. Archaeological evidence suggests that the ground floor was used for food preparation whereas the first floor served as living room, storage area for pottery and other goods and occasionally as workshop.
Findings
Excavations have unearthed several small artifacts such as marble figurines, obsidian ware, seals, ceramics, marble and stone vessels, tools, animal bones and seashells.[3] Numerous pithoi from 1 to 1.30 in height were used for the storage of agricultural goods. Smaller amphorae were used to transport liquids. Clay seals on pottery indicate the control of agricultural production and the organization of the distribution of goods. Several of these findings are now on display at the archaeological museum in Chora.
Conservation
The site of Skarkos became publicly accessible after extensive conservation works between 2002 – 2007. The project was awarded the 2008 EU Prize for Cultural Heritage / Europa Nostra Top Prize for Conservation, for the outstanding quality of conservation work and above all the minimal and extremely sensitive character of the interventions, having no detrimental impact on a unique landscape.
References
- Eric H. Cline (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of the Bronze Age Aegean, ISBN 9780199873609, Jan. 2012.
- M. Marthari, Aspects of Potery Circulation in the Cyclades during the Early EB II Period: Fine and Semi-fine Imported Ceramic Wares at Skarkos, Ios, Horizon 71-84, 2008.
- Μαρίζα Μαρθάρη, Σκάρκος Ίου, Hellenic Ministry of Culture.



