Shiveluch
Shiveluch (Russian: Шивелуч) is the northernmost active volcano in Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It, and Karymsky are Kamchatka's largest, and most active and most continuous erupting volcanoes.
| Shiveluch | |
|---|---|
 Shiveluch from space, July 2007. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 3,307 m (10,850 ft) [1] |
| Prominence | 3,168 m (10,394 ft) [1] Ranked 73rd |
| Isolation | 80 km (50 mi) |
| Listing | Ultra |
| Coordinates | 56°39′12″N 161°21′42″E [1] |
| Geography | |
 Shiveluch Location in Russian Far East | |
| Location | Kamchatka, Russia |
| Parent range | Eastern Range |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano (active) |
| Last eruption | 1999 to 2020 (ongoing, non-stop)[2] |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | basic rock/snow climb |
History
Shiveluch began forming about 60,000 to 70,000 years ago, and it has had at least 60 large eruptions during the Holocene.[3] During this era, the most intense period of volcanism — including frequent large and moderate eruptions — occurred around 6500–6400 BC, 2250–2000 BC, and AD 50–650. This coincides with the peak of activity in other Kamchatka volcanoes. The current active period started around 900 BC. Since then, the large and moderate eruptions have been following each other at 50 to 400 year-long intervals.[4] Catastrophic eruptions took place in 1854 and 1956, when a large part of the lava dome collapsed and created a devastating debris avalanche.[5]
The most recent eruption of Young Shiveluch started on August 15, 1999, and continues as of 2020.[3] On February 27, 2015 Shiveluch erupted shooting ash into the atmosphere about 30,000 feet crossing the Bering Sea and into Alaska.[6]
Characteristics
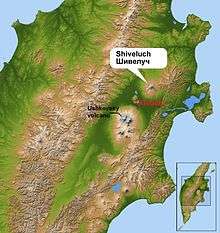
Shiveluch belongs to the Kliuchevskaya volcano group.[5] There are three elements of the volcano: the stratovolcano Old Shiveluch (Старый Шивелуч); an ancient caldera; and the active Young Shiveluch (Молодой Шивелуч), with an elevation of about 2,800 metres (9,186 ft).[7] Shiveluch is one of Kamchatka's largest and most active volcanic structures.[3] It is a stratovolcano composed of alternating layers of solidified ash, hardened lava and volcanic rocks.[8]
The nearest settlement from the volcano is Klyuchi, situated 50 km from the mountain.[9] The settlement is small enough to evacuate rapidly in case of a major eruption.[5]
Gallery
%2C_2012-11-06.png) Activity on 6 November 2012.
Activity on 6 November 2012. The heat signature of a pyroclastic flow on Shiveluch in January 2011.
The heat signature of a pyroclastic flow on Shiveluch in January 2011. This false-colour satellite image shows the remnants of a large pyroclastic flow on the slopes of Shiveluch.
This false-colour satellite image shows the remnants of a large pyroclastic flow on the slopes of Shiveluch. Activity on 7 September 2010.
Activity on 7 September 2010. Activity on 13 February 2010.
Activity on 13 February 2010.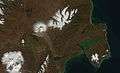 Activity on 3 October 2009.
Activity on 3 October 2009. Activity on 9 May 2004.
Activity on 9 May 2004.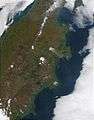 Activity (red dot) on 17 September 2002.
Activity (red dot) on 17 September 2002. Shiveluch releases a small plume of vapour.
Shiveluch releases a small plume of vapour.
References
- "Russia: Kamchatka and the Russian Pacific Islands". Peaklist.org. Retrieved 2014-09-01.
- "Shiveluch volcano". 19 Feb 2018.
- Global Volcanism Program
- "Holocene Eruptive History of Shiveluch Volcano, Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia". Geophysical monograph. 2007. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- "Kamchatka volcano Shiveluch emitted a 7-km column of ash". Vesti.ru. 2009-04-27. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- "Alaska flights canceled over ash from Russian volcano". Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- Holocene Volcanoes in Kamchatka / Shiveluch
- "Shiveluch Volcano". NASA. 2007-03-29. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- "Klyuchi: Russia". Geographic.org. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shiveluch. |
- Shiveluch at map
- Webcam of Shiveluch
- Shiveluch activity at official site of Institute Volcanology and Seismology DVO RAS
- Article about volcano at official site
- Shiveluch at Global Volcanism Program
- Shiveluch at Volcano Live
- Article about volcano Shiveluch
- Google Maps satellite image