Sertoli cell nodule
A Sertoli cell nodule is a benign proliferation of Sertoli cells that arises in association with cryptorchidism (undescended testis). They are not composed of a clonal cell population, i.e. neoplastic; thus, technically, they should not be called an adenoma.[1]
| Sertoli cell nodule | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pick's adenoma, testicular tubular adenoma, tubular adenoma of the testis |
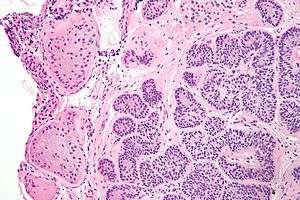 | |
| Micrograph of a Sertoli cell nodule. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Urology |
Pathology
Sertoli cell nodules are unencapsulated nodules that consist of:[1][2][3]
- cells arranged in well-formed tubules (that vaguely resemble immature Sertoli cells), with
- bland hyperchromatic oval/round nuclei that are stratified, and
- may contain eosinophilic (hyaline) blob in lumen (centre).
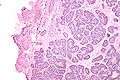 Micrograph of a Sertoli cell nodule. H&E stain.
Micrograph of a Sertoli cell nodule. H&E stain.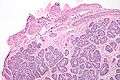 Micrograph of a Sertoli cell nodule. H&E stain.
Micrograph of a Sertoli cell nodule. H&E stain.
gollark: Otherwise you could probably run into weird edge cases and be stuck with it saying "typing" forever.
gollark: I think if they had a network issue it would *stop* saying "typing" after about 5 seconds.
gollark: Directly probably not, but there are 'betalight" things which convert the beta radiation (electrons) from tritium in a tube into light.
gollark: You can get GPS precision of a few metres or better nowadays. It's very neat.
gollark: Relativity has some effects on GPS because of the very precise timing involved.
References
- Tadrous, Paul J. (2007). Diagnostic criteria handbook in histopathology: a surgical pathology vade mecum. John Wiley & Sons Canada. p. 227 =. ISBN 978-0-470-51903-5.
- "Ashwagandha". 2018-09-24. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- Ricco R, Bufo P (October 1980). "[Histologic study of 3 cases of so-called tubular adenoma of the testis]". Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. (in Italian). 56 (20): 2110–5. PMID 6109541.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sertoli cell nodule. |
- Testis, Sex Cord Stromal Tumor - eMedicine.
- Govender, D.; Sing, Y.; Chetty, R. (2004). "Sertoli cell nodules in the undescended testis: A histochemical, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of hyaline deposits". Journal of Clinical Pathology. 57 (8): 802–806. doi:10.1136/jcp.2004.015982. PMC 1770379. PMID 15280399.
- Barghorn, A.; Alioth, H-R; Hailemariam, S.; Bannwart, F.; Ulbright, T. M. (2006). "Giant Sertoli cell nodule of the testis: Distinction from other Sertoli cell lesions". Journal of Clinical Pathology. 59 (11): 1223–1225. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.035253. PMC 1860496. PMID 17071812.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.