Saschiz fortified church
The Saschiz fortified church (Romanian: Biserica fortificată din Saschiz; German: Kirchenburg von Keisd) is a Lutheran fortified church in Saschiz (Keisd), Mureș County, in the Transylvania region of Romania. It was built by the ethnic German Transylvanian Saxon community at a time when the area belonged to the Kingdom of Hungary. Initially Roman Catholic, it became Lutheran following the Reformation. Together with the surrounding village, the church forms part of the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania UNESCO World Heritage Site.
| Saschiz Fortified Church Biserica fortificată din Saschiz | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Lutheran |
| Location | |
| Location | Saschiz, Romania |
| Geographic coordinates | 46.194074°N 24.960175°E |
| Architecture | |
| Type | Fortified church |
| Style | Gothic |
| Groundbreaking | 1493 |
| Completed | 1496 |
| Official name: Villages with fortified churches in Transylvania | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iv |
| Designated | 1993 (17th session) 1999 (23rd session – Extension) |
| Reference no. | 596 |
| State Party | Romania |
| Region | Europe and North America |
| Official name: Historic monuments in Mureș County | |
| Type | architectural |
| Reference no. | LMI Code: MS-II-a-A-15782 (RAN Code: 119215.02.01) |
Description
Background and church
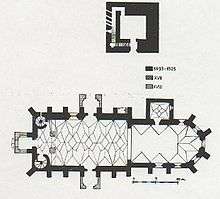
Construction of a large fortified late Gothic church began in 1493 on the site of a Romanesque basilica,[1][2] and the main structure was completed in 1496.[3] The church was dedicated to Saint Stephen of Hungary.[4] A few payments from the authorities at Sibiu for building the church survive; these date from 1494 to 1525. From 1503 to 1507, the village received a Papal indulgence upon the request of a parishioner, and was no longer obliged to quarter troops or send provisions to the army of the Kingdom of Hungary.[1]
The large structure, built of quarried stone, is a hall church strengthened by 22 high buttresses. The nave is very wide and long, while the choir is closed on three sides. A brick defensive level was built above the choir, while there are two such levels above the sacristy's vaulted ceiling. These floors are accessed through two small brick towers on the western part of the church.[1] The defensive portion is slightly wider than the hall beneath. The nave ceiling, also vaulted, was rebuilt in 1878. The interior decor is mainly Baroque, with only the richly decorated choir pulpit being Gothic. Inscription fragments survive on the exterior walls.[2] Among the church's features are the two arched portals at the north and south sides, the upper windows with their delicate Gothic details, the Baroque altar and its floral decorations made of carved wood, and the 1786 organ.[4]
Fortifications and recognition
The complex was surrounded by a powerful defensive wall, the perimeter of which is today marked by a fence.[1] The only surviving portion is the northern tower, which was fitted with a prominent spire in 1677,[2] and is located 10 m away from the church. Its multicolored slate roof can be seen from afar; it has twelve dormers (three to a side) and four little towers at the corners.[4] A nearby hill was once the site of a 14th-century citadel for protecting the peasants, but only ruins survive.[1] It was located 2 km away from the village center so that people from nearby places could also shelter there, and was reportedly a gift from a childless woman who willed it to the residents. Legend has it that the hill is haunted by a noose-wielding protective giant who emits ghostly sounds on one night a year.[2] This distance is one reason why the church was later fortified, so that the inhabitants would have readier access to a refuge.[4]
Earthquakes in 1977, 1986 and 1990 damaged the church and tower, while the site's immediate proximity to European route E60 leaves it vulnerable.[4] In 1999, Saschiz, together with five other places, was added to the already-listed Biertan to form the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania UNESCO World Heritage Site.[5] Additionally, the church is listed as a historic monument by Romania's Ministry of Culture and Religious Affairs, with the wall and tower being listed as a separate entry, as well as the citadel ruins.[6]
- Saschiz fortified church
 Winter view
Winter view View showing fence
View showing fence- Tower
- Church interior
- Altar
- Organ
 Plan
Plan Citadel ruins
Citadel ruins
Notes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lutheran church in Saschiz, Mureș. |
- (in Romanian) Saschiz/Keisd Archived 2014-05-04 at the Wayback Machine at biserici-fortificate.com
- (in Romanian) Saschiz/Keisd Archived 2014-05-04 at the Wayback Machine at biserici-fortificate.org
- Vasile Drăguț, Dicționar enciclopedic de artă medievală românească, p.266. Editura Științifică și Enciclopedică, Bucharest, 1976
- (in Romanian) "Atemporalul satului săsesc la Saschiz și Dârjiu" Archived 2014-05-03 at the Wayback Machine, Jurnalul Național, January 18, 2007
- "World Heritage Committee Inscribes 48 New Sites on Heritage List" at the UNESCO site
- (in Romanian) Lista Monumentelor Istorice 2010: Judeţul Mureş