Salvia aethiopis
Salvia aethiopis is a species of perennial plant known by the common names Mediterranean sage or African sage. It is best known as a noxious weed, particularly in the western United States. It is native to Eurasia and was probably introduced to North America as a contaminant of alfalfa seed. It is a weed of rangelands and pastures. It is unpalatable to livestock, it disrupts native floral communities, and it becomes a physical nuisance due the similarity of the persistent dried stems to tumbleweed. The weevil Phrydiuchus tau is used as an agent of biological pest control on this plant.
| Salvia aethiopis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Salvia |
| Species: | S. aethiopis |
| Binomial name | |
| Salvia aethiopis | |
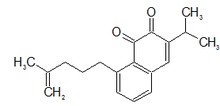
Boya and Valderde examined a sample of Salvia aethiopis. Acetone extracts of the root furnished a new orthoquinone diterpene, aethiopinone (4,5-seco-5,10-friedo-abieta-4(18),5,6,8,13-pentaen-l1,12-dione). This compound was isolated in 0.15% yield from the dry roots.[1]
References
- Boya, Ma Teresa; Valverde, Serafin (1981). "AN ORTHOQUINONE ISOLATED FROM SALVlA AETHIOPIS". Phytochemistry. 20 (6): 1367–1368. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(81)80041-6.