Saleh al-Ali
Saleh al-Ali or Shaykh Saleh Ahmad al-Ali (Arabic: الشيخ صالح أحمد العلي) (1884 in Al-Shaykh Badr – 13 April 1950 in Tartus) was a Syrian Alawi leader who commanded the Syrian Revolt of 1919, one of the first rebellions against the French mandate of Syria before the Great Syrian Revolt.[1]
Saleh al-Ali صالح العلي | |
|---|---|
 Saleh al-Ali during the rebellion of 1919 | |
| Born | Saleh Ahmad al-Ali 1883 |
| Died | 13 April 1950 (aged 65–66) |
| Known for | Commander of the Syrian Revolt of 1919 |
Background
Saleh al-Ali was born in 1883 to a family of Alawi notables from Al-Shaykh Badr, in the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range in northwest. He reportedly clashed with the Ottomans in 1918 before their withdrawal from Syria,[2] killing two Ottoman soldiers who were harassing a wife of his father. This act gained him a local reputation as a rebel. After his father's death, he built a shrine for him and reportedly performed miracles at the site, according to local legend.[3]
Rebellion against the French
Start of the rebellion
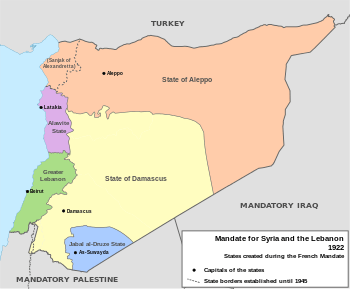
In 1918 the French occupied the Syrian coast and began to move into the interior. On December 15, 1918, Saleh al-Ali called for a meeting of prominent Alawi notables in the town of Sheikh Badr. Al-Ali alerted the attendees that the French had occupied the Syrian coast with the intention of separating the region from the rest of the country, and urged them to revolt and expel the French from Syria. When the French authorities heard of the meeting, they sent a force from Al-Qadmus to the town of Sheikh Badr in order to arrest Saleh al-Ali. Al-Ali and his men ambushed the force at the village of Niha, west of Wadi al-Oyoun. The French forces were defeated and suffered more than 35 casualties.[2]
Organizing the rebellion

After the initial victory, al-Ali started to organize his rebels into a disciplined force, with its own general command and military ranks. The army was supported by the local population, and some women supplied water and food and replaced the men at work in the fields.[2] Al-Ali also allied himself with the rebellion of Ibrahim Hananu in Aleppo, the uprising in Talkalakh by the Dandashi tribe and the revolt in Antioch by Subhi Barakat. He also received funds and arms from Kemal Atatürk of Turkey which was also at war with France at the time.[1]
In July 1919, in retaliation to French attacks against rebel positions, al-Ali attacked and occupied several Ismaili villages that were allied to the French. A truce was concluded between the two, but the French violated it by occupying and burning the village of Kaf al-Jaz. Al-Ali retaliated by attacking and occupying al-Qadmus from which the French conducted their military operations against him.[2]
Final stages
The balance of power began to shift in favor of the French after they conquered Damascus, defeating a makeshift army at the Battle of Maysalun on 24 July 1920. In November, General Henri Gouraud mounted a full-fledged campaign against Saleh al-Ali's forces in the An-Nusayriyah Mountains. They entered al-Ali's village of Ash-Shaykh Badr and arrested many Alawi notables. Al-Ali fled to the north, but a large French force overran his positions and al-Ali went into hiding.[2] A French court-martial convened in Latakia and sentenced him to death in absentia.[1]
Legacy
Saleh Al-Ali became a celebrated figure after the Syria's independence. Al-Ali, in his first public appearance since 1922, was a guest of honor of president Shukri al-Quwatli at the Evacuation Day celebrations on 17 April 1946.[1]
References
- Moubayed, Sami M. (2006). Steel & Silk: Men & Women Who Shaped Syria 1900–2000. Cune Press. pp. 363–364. ISBN 1-885942-41-9.
- Moosa, Matti (1987). Extremist Shiites: The Ghulat Sects. Syracuse University Press. pp. 282–283. ISBN 0-8156-2411-5.
- Douwes, Dick (2011). "Modern History of the Nizari Ismailis of Syria". In Farhad Daftary (ed.). A Modern History of the Ismailis: Continuity and Change in a Muslim Community. I. B. Tauris. p. 33.