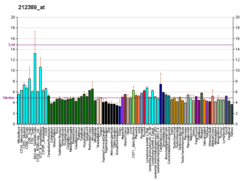
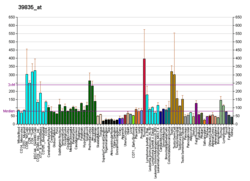
SBF1
Myotubularin-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF1 gene.[5][6][7]
Interactions
SBF1 has been shown to interact with MTMR2[8] and SUV39H1.[9]
gollark: git.osmarks.net™ features:- 46 repositories, which are mostly just mirrors of neat open source projects I like- gitea, a very not lightweight git server written in accursed golang- Git LFS- a highly reliable* postgres database backend
gollark: Anyway, palaiologos/gnobody, you should obviously use git.osmarks.net for all projectuous hosting.
gollark: No, although it is in the repos somehow.
gollark: I have no idea what that is.
gollark: And "micro".
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000100241 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036529 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Cui X, De Vivo I, Slany R, Miyamoto A, Firestein R, Cleary ML (April 1998). "Association of SET domain and myotubularin-related proteins modulates growth control". Nat. Genet. 18 (4): 331–7. doi:10.1038/ng0498-331. PMID 9537414.
- Laporte J, Blondeau F, Buj-Bello A, Tentler D, Kretz C, Dahl N, Mandel JL (December 1998). "Characterization of the myotubularin dual specificity phosphatase gene family from yeast to human". Hum. Mol. Genet. 7 (11): 1703–12. doi:10.1093/hmg/7.11.1703. PMID 9736772.
- "Entrez Gene: SBF1 SET binding factor 1".
- Kim SA, Vacratsis PO, Firestein R, Cleary ML, Dixon JE (April 2003). "Regulation of myotubularin-related (MTMR)2 phosphatidylinositol phosphatase by MTMR5, a catalytically inactive phosphatase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (8): 4492–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0431052100. PMC 153583. PMID 12668758.
- Firestein R, Cui X, Huie P, Cleary ML (July 2000). "Set domain-dependent regulation of transcriptional silencing and growth control by SUV39H1, a mammalian ortholog of Drosophila Su(var)3-9". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (13): 4900–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.13.4900-4909.2000. PMC 85941. PMID 10848615.
Further reading
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, Chissoe S, Hunt AR, Collins JE, Bruskiewich R, Beare DM, Clamp M, Smink LJ, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Babbage A, Bagguley C, Bailey J, Barlow K, Bates KN, Beasley O, Bird CP, Blakey S, Bridgeman AM, Buck D, Burgess J, Burrill WD, O'Brien KP (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–95. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Firestein R, Cui X, Huie P, Cleary ML (2000). "Set domain-dependent regulation of transcriptional silencing and growth control by SUV39H1, a mammalian ortholog of Drosophila Su(var)3-9". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (13): 4900–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.13.4900-4909.2000. PMC 85941. PMID 10848615.
- Firestein R, Cleary ML (2001). "Pseudo-phosphatase Sbf1 contains an N-terminal GEF homology domain that modulates its growth regulatory properties". J. Cell Sci. 114 (Pt 16): 2921–7. PMID 11686296.
- Firestein R, Nagy PL, Daly M, Huie P, Conti M, Cleary ML (2002). "Male infertility, impaired spermatogenesis, and azoospermia in mice deficient for the pseudophosphatase Sbf1". J. Clin. Invest. 109 (9): 1165–72. doi:10.1172/JCI12589. PMC 150957. PMID 11994405.
- Kim SA, Vacratsis PO, Firestein R, Cleary ML, Dixon JE (2003). "Regulation of myotubularin-related (MTMR)2 phosphatidylinositol phosphatase by MTMR5, a catalytically inactive phosphatase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (8): 4492–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0431052100. PMC 153583. PMID 12668758.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q6ZPE2 (Mouse Myotubularin-related protein 5) at the PDBe-KB.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.