S-8 (rocket)
The S-8 is a rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force for use by military aircraft. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force and various export customers.
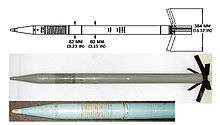
Developed in the 1970s, the S-8 is an 80 mm (3.1 in) rocket used by fighter bombers and helicopters. The system entered service in 1984 and is produced in a variety of subtypes with different warheads, including HEAT anti-armor, high-explosive fragmentation, smoke, and incendiary, as well as the specialized S-8BM runway-destroying munition and the S-8DM fuel-air explosive variants. Each rocket is between 1.5 meters (4 ft 11 in) and 1.7 meters (5 ft 7 in) long and weighs between 11.3 kg (25 lb) and 15.2 kg (33.5 lb), depending on warhead and fuse. Range is 2 to 4 kilometers (1.3 to 2.6 mi).
The S-8 is generally carried in the B series of rocket pods, carrying either seven or 20 rockets.
In 2018, the Russian Aerospace Forces took delivery and completed state tests of several batches of the S-8OFP Broneboishchik, successor to the S-8. While both rockets are unguided, the S-8OFP has greater range, a heavier warhead, and a digital fuse. The rocket is intended for armament of Su-25 type aircraft and Mi-8 helicopters, depending on the settings of the fuse, is able to penetrate obstacles facing the set targets, it can also explode in front of the obstacle and behind the obstacle. [1][2][3]
An armored self-propelled 80-tube MLRS vehicle using S-8 rockets has been developed by Belorussian industry. Relatively short range of the rocket (3 - 5km cross-ground) compared to Grad rockets is compensated for by lower cost and greater beaten area from a high number of rockets.[4]
Rocket specifications
| Designation | Type | Length overall | Launch weight | Warhead weight | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-8 | HEAT | 1.56 m | 11.5 kg | 3.6 kg (0.9 kg of Hecphol-5/A-IX-10 explosive) | 1.3 to 4 km | Basic variant. 350 mm versus RHA. Velocity 692 m/s. N-26A fuze. BIK-2D motor powder. During launch of this model may have black smoke. |
| S-8KO | HEAT | 1.57 m | 11.3 kg | 3.6 kg (1.1 kg of Hecphol-5/A-IX-10 explosive) | 1.3 to 4 km | 400 mm versus RHA. Velocity 610 m/s. Improved fuze V-5KP1. low smoke motor with powder BN-K. |
| S-8KOM [5] | HEAT | 1.57 m | 11.3 kg | 3.6 kg (1.1 kg of Hecphol-5/A-IX-10 explosive) | 1.3 to 4 km | 400 mm versus RHA. Velocity 700 m/s. Used improved BNK-P low smoke motor powder with twice burn time. |
| S-8B | Penetrating | 1.5 m | 15.2 kg | 7.41 kg (0.6 kg of explosive) | 1.2 to 2.2 km | 800 mm versus reinforced concrete. |
| S-8BM[6] | Penetrating | 1.54 m | 15.2 kg | 7.41 kg (0.6 kg of explosive) | 1.2 to 2.2 km | 800 mm versus reinforced concrete. Velocity 450 m/s. |
| S-8D | FAE | 1.66 m | 11.6 kg | 3.8 kg (2.15 kg of explosive) | 1.3 to 3 km | |
| S-8DM | FAE | 1.7 m | 11.6 kg | 3.8 kg (2.15 kg of explosive) | 1.3 to 3 km | 5.5–6 kg TNT equivalent. Velocity 590 m/s |
| S-8DF[7] | FAE | 1.68 m | 13.4 kg | 5.5 kg (3.3 kg of explosive) | 1.3 to 4 km | 6 kg TNT equivalent. Velocity 500 m/s |
| S-8 O | Illuminating | 1.63 m | 12.1 kg | 4.3 kg | 4 to 4.5 km | 2 megacandela flare warhead |
| S-8 OM[8] | Illuminating | 1.63 m | 12.1 kg | 4.3 kg | 4 to 4.5 km | 2 megacandela flare warhead burns for 30 seconds. Velocity 545 m/s. |
| S-8T [9] | Tandem-HEAT | 1.68 m | 15 kg | 6.6 kg (1.6 kg of explosive) | 1.3 to 4 km | Tandem HEAT 360–400 mm versus RHA after ERA, 440 mm versus RHA. Velocity 470 m/s |
| S-8P | Chaff | 1.63 m | 12.3 kg | 4.5 kg of chaff | 2 to 3 km | |
| S-8PM[10] | Chaff | 1.63 m | 12.3 kg | 4.5 kg of chaff | 2 to 3 km | 545 m/s velocity. |
| S-8S | Flechette | 1.612 m | 13 kg | 4.3 kg | 1.2 to 3.5 km | 2,000 flechettes in 5 bundles |
| S-8TsM[11] | Target marking | 1.605 m | 11.1 kg | 3.6 kg | 1.3 to 2 km (heli) 1.3 to 3 km (plane) | target/route marking smoke visible 6 km away |
| S-8OFP1 | HE-Frag-Penetrating | 1.428 m | 16.7 kg | 9.2 kg (2.8 kg of explosive) | up to 6 km | improved motor with twice energy; pre-fragmented body; dual-mode fuzes allow to detonate after penetration of concrete or light armor; nicknamed "Broneboyshchik" |
S-8OFP was already deployed in mid-late 2018 and have been seen at operational launch with Mi-35M helicopter.[12][13][14]
See also
- S-5 rocket
- S-13 rocket
- Ugroza, a proposed upgrade of "dumb" rockets to salvo-fired laser-guided precision missiles
References
- https://ria.ru/20190217/1550984348.html
- New Air-ground Rocket For Russian Attack Aircraft. Aviation International News. 10 July 2018.
- https://www.armyrecognition.com/weapons_defence_industry_military_technology_uk/russia_continues_creating_missiles.html
- Unexpectedly, Syria might buy the Belarusian MLRS instead the Russian Grad. BulgarianMilitary.com. April 29, 2020
- "S-8KOM". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8BM". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8DF". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8OM". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8T". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8PM". Rosoboronexport.
- "S-8TsM". Rosoboronexport.
- https://tvzvezda.ru/news/opk/content/201806251657-kptc.htm
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipfLEMfTLE8
- http://www.tsn24.ru/strelby-tulskoj-raketoj-bronebojshhik-popali-na-video.html
- Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War Two, Yefim Gordon, ISBN 1-85780-188-1
- Mil Mi-24 Hind Attack Helicopter, Yefim Gordon and Dimitri Komissarov, ISBN 1-84037-238-9
- Jane's Air Launched Weapons Issue 36, Duncan Lennox, ISBN 0-7106-0866-7
- Warfare.ru S-8 rockets
- VTTV-99 S-8 rocket specs
- Army-2018: Zaslon Center presents new 80mm MLRS based on 4x4 UAZ pickup