Root complex
In a PCI Express (PCIe) system, a root complex device connects the processor and memory subsystem to the PCI Express switch fabric composed of one or more switch devices.
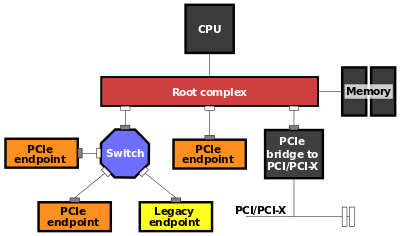
An example of the PCI Express topology, displaying the position of a root complex.[1]
Similar to a host bridge in a PCI system, the root complex generates transaction requests on behalf of the processor, which is interconnected through a local bus. Root complex functionality may be implemented as a discrete device, or may be integrated with the processor. A root complex may contain more than one PCI Express port and multiple switch devices can be connected to ports on the root complex or cascaded.[2]
References
- Richard Solomon (2015-06-17). "PCI Express Basics and Background" (PDF). PCI-SIG. p. 26. Retrieved 2016-04-12.
- "Choosing the Right Programmable Logic Solution for PCI Express Applications". Archived from the original on 21 February 2011. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.