Romano-British culture
Romano-British culture is the culture that arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. It survived the fifth-century Roman departure from Britain, eventually finding itself a stronghold in Wales where it was to form the basis of an emerging Welsh culture.[1]
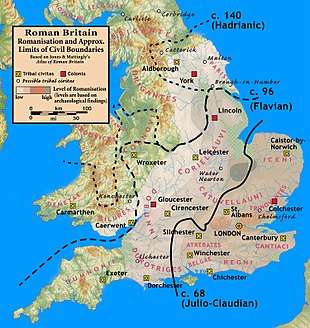
Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture[2] that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing.[3]
Arrival of the Romans
.jpg)
Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.[4] Thousands of Roman businessmen and officials and their families settled in Britannia. Roman troops from across the Empire, as far as Spain, Syria, Egypt, and the Germanic provinces of Batavia and Frisia (modern Netherlands, Belgium, and the Rhineland area of Germany), were garrisoned in Roman towns, and many married local Britons. The Roman army and their families and dependents amounted to 125,000 people, out of Britannia's total population of 3.6 million at the end of the fourth century.[5] There were also many migrants of other professions, such as sculptors from Roman Syria and doctors from the Eastern Mediterranean region.[6] This diversified Britannia's cultures and religions, while the populace remained mainly Celtic, with a Roman way of life.
The bulk of the population was rural; from a total population of 3.6 million at the end of the fourth century, the urban population was about 240,000 people,[5] with the capital city of Londinium having about 60,000 people.[7][8] Londinium was an ethnically diverse city with inhabitants from across the Roman Empire, including natives of Britannia, and immigrants from continental Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.[9] There was also cultural diversity in other Roman-British towns, which were sustained by considerable migration, both within Britannia and from other Roman territories, including North Africa,[10] Syria, the Eastern Mediterranean, and continental Europe.[6]
Later, Britain was independent of the rest of the Roman Empire for a number of years, first as part of the Gallic Empire, then 20 years later under the usurpers Carausius and Allectus.
Christianity came to Britain in the 3rd century. One early figure was Saint Alban, who (according to tradition) was martyred near the Roman town of Verulamium, on the site of the modern St Albans, during the reign of Emperor Decius.
Roman citizenship
One aspect of Roman influence seen in British life was the grant of Roman citizenship.[11] At first this was granted very selectively: to the council members of certain classes of towns, whom Roman practice made citizens; to veterans, either legionaries or soldiers in auxiliary units; and to a number of natives whose patrons obtained citizenship for them. Some of the local Brittonic kings, such as Togidubnus, received citizenship in this manner. The number of citizens steadily increased, as people inherited citizenship and more grants were made. Eventually in 212, everybody except slaves and freed slaves were granted citizenship by the Constitutio Antoniniana.
The other inhabitants of Britain, who did not enjoy citizenship, the Peregrini, continued to live under the laws of their ancestors. The principal handicaps were that they could not own land with a Latin title, serve as a legionary in the army (although they could serve in an auxiliary unit, and become a Roman citizen upon discharge), or, in general, inherit from a Roman citizen. But for the majority of British inhabitants, who were peasants tied to the soil, citizenship would not dramatically alter their daily lives.
Roman departure from Britain
Eventually emperor Honorius ordered Roman troops back home to help fight the invading hordes. Constantine III initially rebelled against Honorius and took further troops to Gaul, but was later recognised as a joint emperor.
After the Roman departure from Britain, the Romano-British were commanded by Honorius to "look to their own defences". A written plea to General Flavius Aëtius, known as the Groans of the Britons, may have brought some brief naval assistance from the fading Roman Empire of the West, but otherwise they were on their own.
Post-Roman period
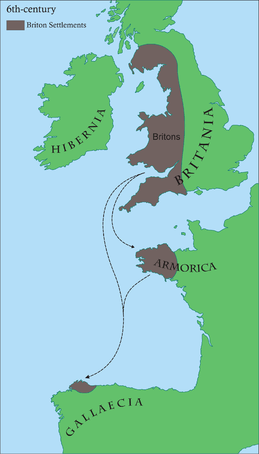
In the early stages the lowlands and cities may have had some organisation or "council" and the Bishop of London appears to have played a key role, but they were divided politically as former soldiers, mercenaries, nobles, officials and farmers declared themselves kings, fighting amongst each other and leaving Britain open to invasion. Two factions may have emerged: a pro-Roman faction and an independence faction. The one leader at this time known by name is Vortigern, who may have held the title of "High King". The depredations of the Picts from the north and Scotti (Scots) from Ireland forced the Britons to seek help from pagan Germanic tribes of Angles, Saxons and Jutes, who then decided to settle in Britain. Some of the Romano-British people migrated to Brittany, the Kingdom of the Suebi and possibly Ireland.
The Anglo-Saxons obtained control of eastern England in the 5th century. In the mid-6th century they started expanding into the Midlands, then in the 7th century they expanded again into the south-west and the north of England. The unconquered parts of southern Britain, notably Wales, retained their Romano-British culture, in particular retaining Christianity.
Some Anglo-Saxon histories (in context) refer to the Romano-British people by the blanket term "Welsh". The term Welsh is derived from an Old English word meaning 'foreigner', referring to the old inhabitants of southern Britain.[12] Historically, Wales and the south-western peninsula were known respectively as North Wales and West Wales.[13] The Celtic north of England and southern Scotland was referred to in Welsh as Hen Ogledd ("old north").
The struggles of this period have given rise to the legends of Uther Pendragon and King Arthur. There are many theories, but it is sometimes said that Ambrosius Aurelianus, the leader of the Romano-British forces, was the model for the former, and that Arthur's court of Camelot is an idealised Welsh and Cornish memory of pre-Saxon Romano-British civilisation.
See also
- British Latin
- Daco-Roman
- Gallo-Roman culture
- Illyro-Roman
- Roman sites in the United Kingdom
- Romano-British temple
- Thraco-Roman
References
- Gerrard James, University Newcastle (2016). "Romano-British Pottery in the Fifth Century". Internet Archaeology (41). doi:10.11141/ia.41.9.
- Snyder Christopher A., University Marymount, Virginia (1997). "A gazetteer of Sub-Roman Britain (AD 400-600): The British sites". Internet Archaeology (3). doi:10.11141/ia.3.2.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sub-Roman Britain. The-orb.net (2 June 2003).
- Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. The Penguin Atlas of World History, Penguin Books, London 1978, ISBN 0-14-051054-0
- Joan P. Alcock, A Brief History of Roman Britain, page 260, Hachette UK
- David Shotter (2012), Roman Britain, page 37, Routledge
- Will Durant (7 June 2011). Caesar and Christ: The Story of Civilization. Simon and Schuster. pp. 468–. ISBN 978-1-4516-4760-0.
- Anne Lancashire (2002). London Civic Theatre: City Drama and Pageantry from Roman Times to 1558. Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-5216-3278-2.
- DNA study finds London was ethnically diverse from start, BBC, 23 November 2015
- Ray Laurence (2012), Roman Archaeology for Historians, page 121, Routledge
- Roman Citizenship. Romanempire.net.
- Balderdash and flummery. World Wide Words (23 November 1996).
- h2g2 – Maps of Cornwall (Kernow) showing a Celtic or Distinct Identity. Bbc.co.uk.
Bibliography
- Jones, Michael (1996) The End of Roman Britain. Ithaca: Cornell University Press
- Myres, John (1960) Pelagius and the End of Roman Rule in Britain. In: Journal of Roman Studies, 50, 21–36.
- Pryor, Francis (2004) Britain AD: a Quest for Arthur, England and the Anglo-Saxons. London: Harper Collins ISBN 0-00-718186-8
- Radford, C. A. Ralegh (1939) Tintagel Castle. London: H.M.S.O. (Reprinted by English Heritage 1985)
- Thomas, Charles (1993) Tintagel: Arthur and Archaeology. London: English Heritage